Circle Theorems: Definition, Types, Questions and Worksheets
Circle Theorems
- Circle theorems are a set of rules that help us understand the properties and behavior of circles.
- Circles are an essential part of geometry and mathematics.
- They can be found everywhere in our daily lives, from the wheels of our cars to the buttons on our clothes.
In this article, we will discuss:
- What are Circle Theorems?
- Understanding the Seven Main Theorems?
Here is one more link to practice a few extra questions: Corbettmaths Circle Theorems Questions
What are Circle Theorems?
- Circle theorems are fundamental principles in geometry that explain relationships between angles within a circle.
- They enable us to calculate angle measurements without using a protractor, making them valuable tools in geometry.
- By applying circle theorems in conjunction with our understanding of other angle properties, we can determine missing angles in various geometric scenarios.
- These theorems find practical applications in fields such as design and engineering, where precise angle measurements and calculations are essential.
Types of Circle Theorems
There are seven main circle theorems:
- Alternate Segment Circle Theorem
- Angle at the Centre Circle Theorem
- Angles in the Same Segment Circle Theorem
- Angle in a Semi-Circle Theorem
- Chord Circle Theorem
- Tangent Circle Theorem
- Cyclic Quadrilateral Circle Theorem
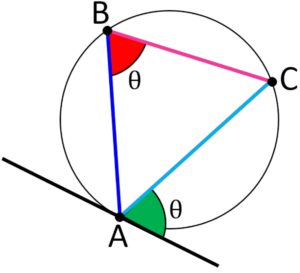
Alternate Segment Circle Theorem
- The alternate segment circle theorem is a fundamental theorem in circle geometry.
- This theorem relates the angles formed by a tangent and a chord at the point of contact with the circle.
- According to the theorem, the angle between the tangent and the chord at the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment of the circle.
- In other words, the angle formed between the tangent and the chord at the point of contact is equal to the angle formed in the opposite segment of the circle.
- This theorem is essential in solving problems related to circles and can be used to find unknown angles or lengths of chords.
- The alternate segment circle theorem is illustrated in the diagram, where the green angle is equal to the red angle.
- To use this theorem, we need to identify the tangent and chord at the point of contact with the circle, and then apply the theorem to find the unknown angle or length.
Solved Example
Question: Find the unknown angles in the figure, given that the chord BC makes angles of 65° with the tangent line PQ.
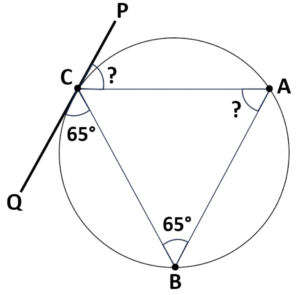
Solution:
Step #1: Understand the Question
- We are presented with a figure in which chord BC forms angles of 65 degrees with the tangent line PQ. The goal is to find the values of the unknown angles in the figure.
Step #2: Apply the Alternate Segment Theorem
- Given that ∠QCB = 65°, we can use the Alternate Segment Theorem, we find that ∠CAB = 65°.
Step #3: Apply the Alternate Segment Theorem Again
- Using the same theorem, we also determine that ∠PCA = 65°.
Step #4: Providing the Answer:
- ∠CAB = 65°
- ∠PCA = 65°.
This means the unknown angles in the figure are both 65 degrees.
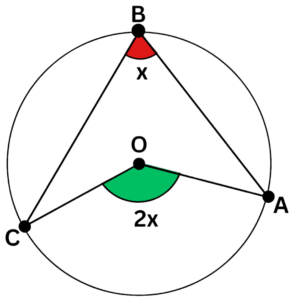
Angle at the Centre Circle Theorem
- The Angle at the Centre Circle Theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry related to the angles formed in circles.
- This theorem states that the angle formed at the centre of a circle is twice the size of the angle formed at any point on the circumference.
- In other words, the angle subtended by an arc at the centre of the circle is twice the angle subtended by the same arc at any point on the circumference.
- This theorem is particularly useful in determining angles and arc lengths in circles.
- The Angle at the Centre Circle Theorem is illustrated in the diagram below, where angle AOC is twice angle ABC.
Solved Example
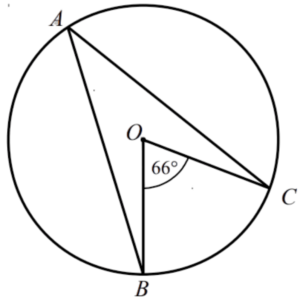
Question: A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle. Angle BOC = 66°, Find the size of angle BAC?
Solution:
Step #1: Understand the Question
- In this Question, we have points A, B, C, and D on the circumference of a circle. We’re given that angle BOC measures 66 degrees, and we need to find the size of angle BAC.
Step #2: Recognize the Inscribed Angle Property
- In a circle, an inscribed angle (an angle formed by two chords from the same starting point on the circle’s circumference) is half the measure of the central angle (the angle formed at the center of the circle). This is known as the Inscribed Angle Theorem.
Step #3: Calculate Angle BAC
- Since angle BOC is a central angle, we can use the Inscribed Angle Theorem to find the measure of angle BAC.
- Angle BAC = (1/2) * Angle BOC
- Angle BAC = (1/2) * 66°
- Angle BAC = 33°
Step #4: Providing the Answer:
- The size of angle BAC is 33 degrees.
Angles in the Same Segment Circle Theorem
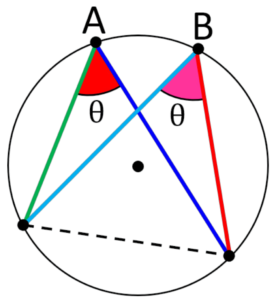
- This theorem applies to any circle, regardless of its size or position.
- The angles in the same segment circle theorem state that if two chords of a circle intersect inside the circle, the angles formed are equal.
- The angles referred to in this theorem are the angles formed between the chord and the tangent line at the point of intersection.
- In simpler terms, if a chord intersects another chord inside a circle, the angles formed in the same segment of the circle are equal.
- For example, in the diagram, angle A is equal to angle B, since they are both in the same segment of the circle.
- This theorem can be useful in solving various circle problems, such as finding missing angles or determining the length of a chord.
- It is important to note that the theorem only applies to angles in the same segment of the circle, and not to angles in different segments.
Solved Example
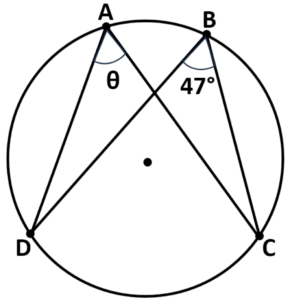
Question: Below is a circle with center O. AC and BD are chords. Calculate the size of angle CAD.
 Solution:
Solution:
Step #1: Identify the Key Parts of the Circle
- In this problem, we need to determine the measure of angle CAD in a circle with center O. We are given the following information:
- The angle CBD = 47°
- AC and BD are chords
- The angle CAD = θ
Step #2: Use other angle facts to determine an angle at the circumference in the same segment.
- In this case, we already have the angle CBD as 47°, so there’s no need to use additional angle facts to find it.
Step #3: Use the angle in the same segment theorem to state the other missing angle.
- The angle CAD is in the same segment as the angle CBD, and according to the Angle in the Same Segment Theorem, these two angles are equal.
- Therefore, we can conclude:
CAD = CBD = 47°
Step #4: Providing the Answer:
- The size of angle CAD is 47 degrees, and we determined this using the Angle in the Same Segment Theorem.
Angle in a Semi-circle Theorem
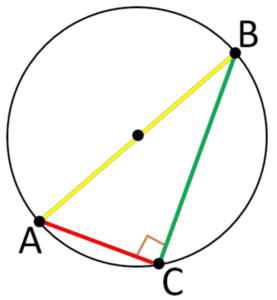
- The angle in a semi-circle theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry that relates to circles.
- According to the theorem, any chord of a circle that subtends the diameter of the circle creates a right angle.
- In other words, if a chord is drawn from one end of the diameter to the other, the angle formed by the chord at the opposite end of the diameter is always a right angle.
- The theorem is illustrated in the diagram where chord AB is drawn to subtend the diameter of the circle at point C.
- The angle formed by chord AB at point C is a right angle (i.e., 90 degrees), which is consistent with the angle in a semi-circle theorem.
Solved Example
Question: In the arrowhead-shaped figure ABCD, where C is the center of the circle, and points A, B, and D lie on the circumference, what is the measure of angle BAD?
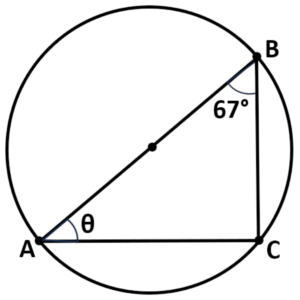
Solution:
Step #1: Identify the Key Parts of the Circle
- To calculate the size of angle BAD, we examine the following components:
- Angle ABC = 67°
- AB is a diameter
- Chords AC and BC
- Angle CAB = θ (the angle we seek)
- To calculate the size of angle BAD, we examine the following components:
Step #2: Utilize Existing Angle Information
- We are given that angle ABC measures 67°, so we don’t need additional angle measures for this calculation.
Step #3: Apply the Angles in a Semicircle Theorem
- The Angles in a Semicircle Theorem states that an angle formed in a semicircle is always 90°. As angle ACB is within a semicircle, we can conclude:
ACB = 90°
Step #4: Calculate the Missing Angle within the Triangle
- Using the concept that the sum of angles in a triangle totals 180°, we can determine the measure of angle BAC:
BAC = 180° – (90° + 67°)
BAC = 180° – 157°
BAC = 23°
The size of angle BAD is 23 degrees. We obtained this value by applying the Angles in a Semicircle Theorem and the principles of triangle angle sums.
Chord Circle Theorem
- The chord circle theorem applies to a circle with intersecting chords.
- It states that if two chords intersect inside the circle, the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord is equivalent to the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord.
- In other words, AB × AC = AD × AE.
- The theorem can be used to find unknown lengths of chords and segments within a circle.
- It is a useful tool in solving geometry problems involving circles and intersecting chords.
Solved Example
Question: In the given circle with center C, points A, B, C, and D are on the circumference. The chord AB is perpendicular to the line CD at point E. The length of line AE is 5 cm, and angle ADE measures 71°. Calculate the length of line BC, rounded to one decimal place.
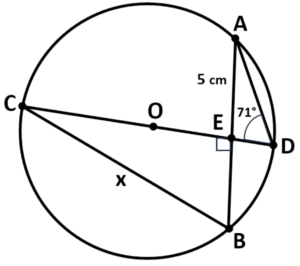
Solution:
Step #1: Identify Key Elements of the Circle
- To determine the length of line BC, we need to consider the following components:
- CD is a diameter
- AB is a chord, perpendicular to CD
- Angle ADE = 71°
- Angle BEC = 90°
- Line AE = 5 cm
- Line BC = x (the value we want to find)
- To determine the length of line BC, we need to consider the following components:
Step #2: Utilize Angle Information
- Given that angles in the same segment are equal, angle ADE is equal to angle ABC, so angle ABC = 71°. Additionally, because the perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord, line BE is equal to line AE, which means BE = 5 cm.
Step #3: Apply Trigonometry
- To calculate the length of chord BC, we need to use trigonometry, considering that we know one side length and two angles, one of which is 90°. We can use the cosine function (cos) to find the length of BC.
- Cosine formula:
cos(θ) = Adjacent side / Hypotenuse
- We want to calculate the hypotenuse (BC), so we rearrange the formula as follows:
BC = AE / cos(θ)
- Plugging in the values:
BC = 5 cm / cos(71°)
Step #4: Calculate the Length of BC
- Now, we can calculate the length of line BC using the formula:
BC ≈ 5 cm / cos(71°)
- Performing the calculation:
BC ≈ 15.4 cm (rounded to one decimal place)
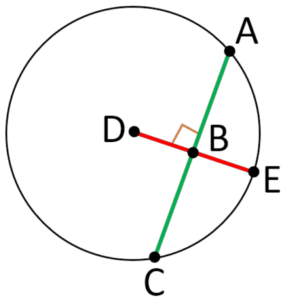
Tangent Circle Theorem
- The tangent circle theorem relates to the relationship between the tangent line and the radius of a circle at the point of contact.
- The theorem states that the tangent line and the radius of the circle are perpendicular to each other.
- This means that the angle between the tangent line and the radius is a right angle or 90 degrees.
- The point of contact between the tangent line and the circle is known as the point of tangency.
- The theorem can be used to find the length of the radius or the distance between the tangent line and the centre of the circle.
Solved Example
Question: Points A, B, and C are on the circumference of a circle with center O. DE is a tangent at point A. Calculate the size of angle BAD.
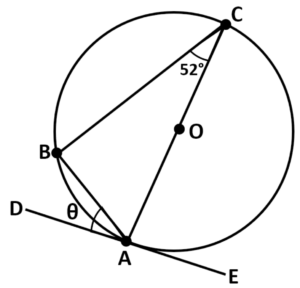
Solution:
Step #1: Identify Key Elements of the Circle
- To calculate the size of angle BAD, we need to consider the following components:
- Angle BCA = 52°
- AC is a diameter
- DE is a tangent
- Angle BAD = θ (the value we want to find)
- To calculate the size of angle BAD, we need to consider the following components:
Step #2: Utilize Angle Information
- Given that AC is a diameter, and the angle in a semicircle is 90°, we can determine that angle ABC = 90°.
- Using the fact that angles in a triangle total 180°, we can find the angle CAB:
CAB = 180° – (90° + 52°)
CAB = 38°
Step #3: Apply the Tangent Theorem
- As the angle between the tangent and the radius is always 90°, we can use this information to calculate angle BAD.
Angle BAD = 90° – 38°
Step #4: Calculate the Angle BAD
- Now, we can calculate the size of angle BAD using the formula:
BAD = 90° – 38°
- Performing the calculation:
BAD = 52°
The size of angle BAD is 52°, and we determined this value using angle properties and the tangent theorem.
Cyclic Quadrilateral Circle Theorem
- The cyclic quadrilateral circle theorem applies to a quadrilateral inscribed within a circle.
- The theorem states that the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary.
- Supplementary angles add up to 180 degrees.
- The theorem means that the sum of the measures of the two opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to 180 degrees.
- For example, in the diagram below, quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed within circle O:
According to the cyclic quadrilateral circle theorem, we have:
angle A + angle C = 180°
angle B + angle D = 180°
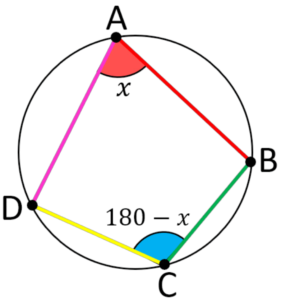
Solved Example
Question: ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Calculate the size of angle BCD?.
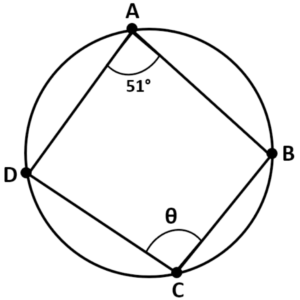
Solution:
Step #1: Identify Key Elements of the Circle
- To calculate the size of angle BCD in the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, we need to consider the following components:
- Angle BAD = 51°
- Angle BCD = θ (the value we want to find)
- To calculate the size of angle BCD in the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, we need to consider the following components:
Step #2: Utilize Angle Information
- Given that angle BAD is 51°, we have one of the two opposing angles in the cyclic quadrilateral.
Step #3: Apply the Cyclic Quadrilateral Theorem
- In a cyclic quadrilateral, the sum of opposite angles is always 180°. Therefore, we can use this theorem to calculate the size of angle BCD:
BCD = 180° – BAD
= 180° – 51°
= 129°
The size of angle BCD in the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is 129 degrees, as determined by the Cyclic Quadrilateral Theorem.
Practice Questions
Question 1: B is a point on the circumference of a circle, center O. AB is a tangent to the circle. Angle BOA = 72° Work out the size of angle BAO.
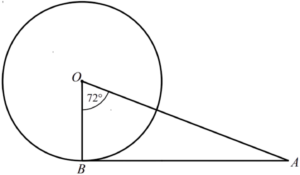
Solution:
Step #1: Understand the Problem
- In this problem, we have a circle with a centre O, a point B on its circumference, and a tangent AB. The task is to determine the measure of angle BAO.
Step #2: Recognize the Tangent Property
- It's important to note that when a tangent intersects a circle, the angle formed between the tangent and the radius at the point of contact is always a right angle or 90 degrees.
Step #3: Calculate Angle BAO
- To find angle BAO, we can apply the fact that the sum of angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Given that angle BOA measures 72 degrees and angle BOA is a right angle (90 degrees), we can calculate angle BAO as follows:
- Angle BAO = 180° - (angle BOA + angle BOA)
- Angle BAO = 180° - (90° + 72°)
- Angle BAO = 180° - 162°
- Angle BAO = 18°
Step #4: Provide the Answer
- The size of angle BAO is 18 degrees.
Question 2: B and C are points on a circle, center O. AB and AC are tangents to the circle. Angle BAC = 40°. Work out the size of angle BOC. You must show all your working.
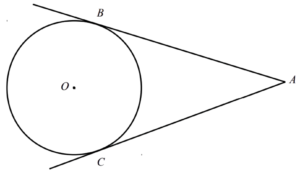
Solution:
Step #1: Understand the Question
- We are presented with a circle having center O, and points B and C on its circumference. Both AB and AC are tangents to the circle. The given information is that angle BAC measures 40 degrees, and we are tasked with finding the size of angle BOC.
Step #2: Recognize the Tangent Property
- Knowing that AB and AC are tangents to the circle, we can apply the principle that the angles formed between a radius and a tangent at the point of contact are always 90 degrees.
Step #3: Calculate Angle BOC
- To find the size of angle BOC, we note that it is formed by two radii, BO and CO. Since the sum of angles around the center of a circle is 360 degrees, we can use this to calculate angle BOC.
Angle BOC = 360° - (Angle BOA + Angle COA)
Step #4: Calculate Angle BOC
- Given that angle BAC is 40 degrees, we substitute this value into the equation.
Angle BOC = 360° - (90° + 90° + 40°)
Angle BOC = 360° - 220°
= 140°
The size of angle BOC is 140 degrees.
Conclusion
- The circle theorems are a fundamental part of geometry.
- They can be used to solve a variety of problems involving circles.
- Understanding these theorems and how to apply them can greatly enhance your problem-solving skills in geometry.
- It is important to use diagrams and clear explanations when presenting your solutions.
Worksheet on Circle Theorems
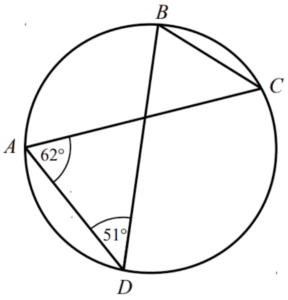
Question 1: A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle. Angle CAD = 62°. Angle ADB = 51°. Find the size of angle ACB?
Question 2: A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle. Angle BAD = 94°. Angle ADC = 83°. Find the size of angle ABC?

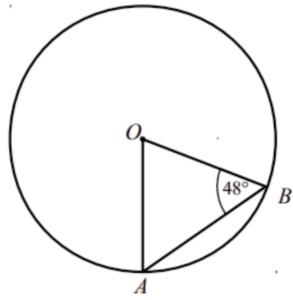
Question 3: A and B are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O. Angle ABO = 48°. Find the size of angle AOB?
Question 4: A and C are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O. AB and BC are tangents to the circle. Angle ABC = 46°. Find the size of angle OAC. Give reasons for each stage of your working. 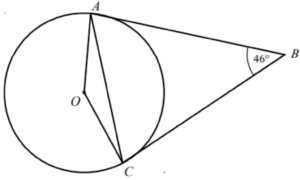
Question 5: A, B and C are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O. BD and CD are tangents to the circle. Angle ODC = 26°. Find the size of angle BAC. Give reasons for each stage of your working.