Conditional Probability – GCSE Maths
Introduction
- Conditional Probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
- Studying of Conditional Probability is important because it helps us understand how the probability of an event changes when we know that another event has occurred.
- This concept is essential in real-world situations where outcomes are not independent.
What is Conditional Probability?
- We know, if one event depends upon the outcome of another event, the two events are Dependent events.
- A Conditional Probability is the probability of a dependent event in which probability of the second outcome depends on what has already happened in the first outcome.
Example:
- If there is a bag with red and blue balls. Picking one ball out and don’t put it back, then take another one, the chance of getting a red or blue ball on the second draw depends on what happened first.
How to Calculate Conditional Probability using Tree Diagrams?
- A Tree Diagram can be used to solve Conditional Probability using dependent events
Steps to solve conditional Probability using Tree Diagram:
- Step #1: Draw the Branch and label the probabilities.
- Step #2: Add Dependent Branches
- Step #3: Apply the Condition
- Step #4: Find the Probability
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Ivan has a Bag with 3 red and 2 green marbles. He picks 2 marbles without replacement. What’s the probability the second marble is red given the first was green?
Solution:
Step #1: Draw the Branch and label the probabilities.
Possible outcomes for first pick:
- Total Marbles = 5
- Red (3 out of 5 marbles) = 3/5
- Green (2 out of 5 marbles) = 2/5
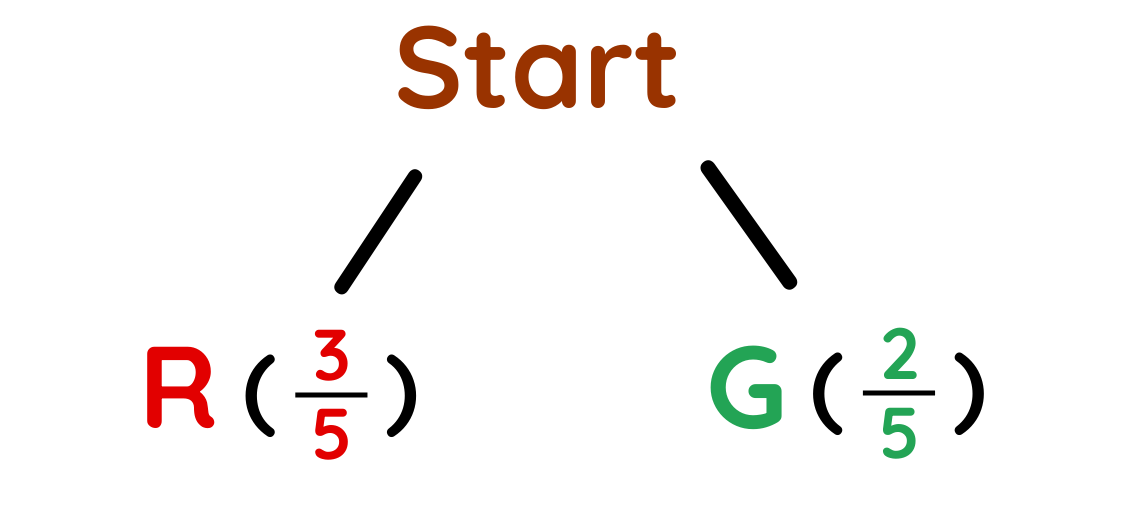
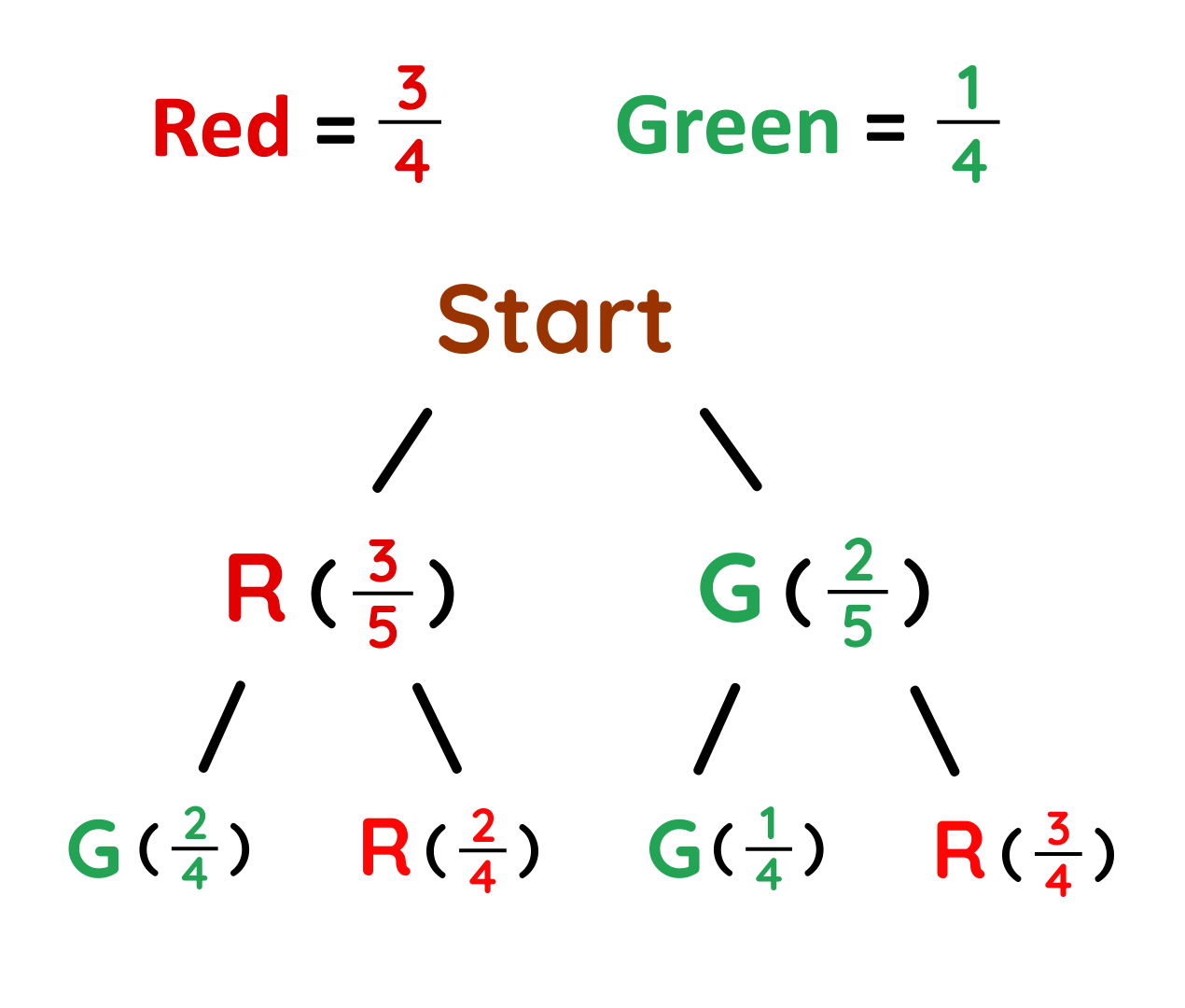
Step #2: Add Dependent Branches
If first was Red:
- Remaining marbles: 2 red, 2 green
- Next pick will be:

If first was Green:
- Remaining marbles: 3 red, 1 green
- Next pick will be:
Step #3: Apply the Condition
First marble was green, so only follow the green path.
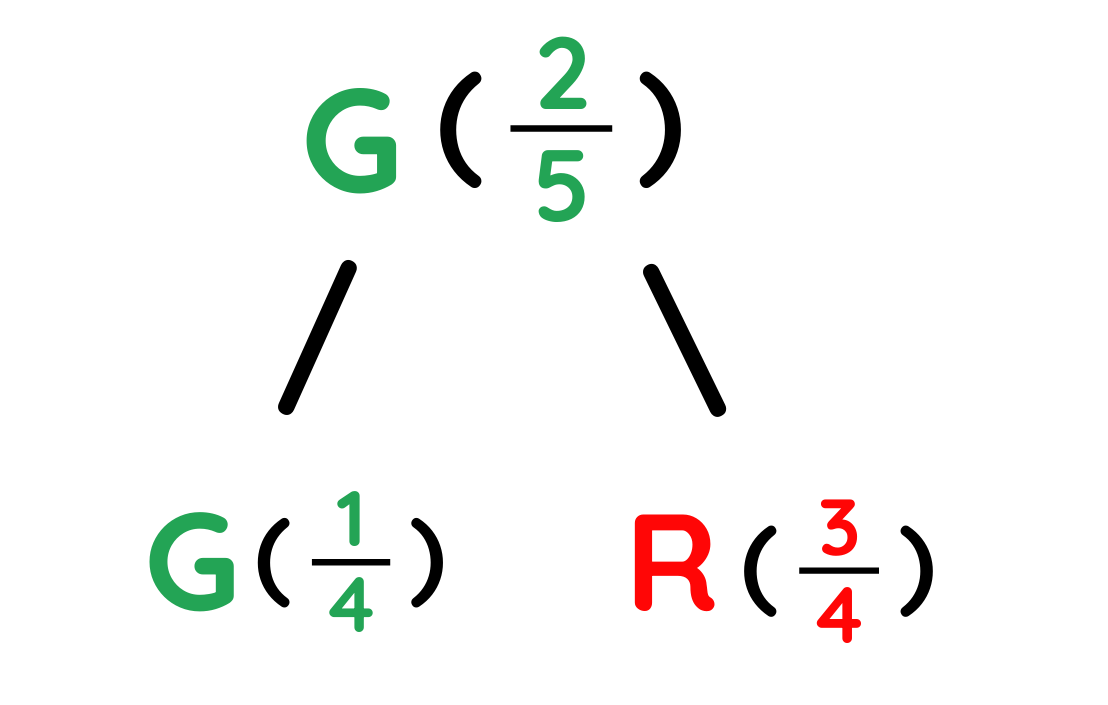
Step #4: Find the Probability
On the Green path, the chance the second marble is red is 3/4
Final Answer: The probability the second marble is red is 3/4
Use Two-way Table to Calculate Conditional Probability
- A Two-way table is a table shows how often different combinations of two events happen together.
Steps to solve conditional Probability using Two-way table:
- Step #1: Create the Two-Way Table
- Step #2: Apply the Condition
- Step #3: Find the Probability
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: If a random cheesy pizza slice is picked from
- 6 pepperonis (with cheese)
- 3 olive pizzas (with cheese)
What’s the probability it’s pepperoni with cheese?

Solution:
Step #1: Create the Two-Way Table
Total Pizza Slices = 9
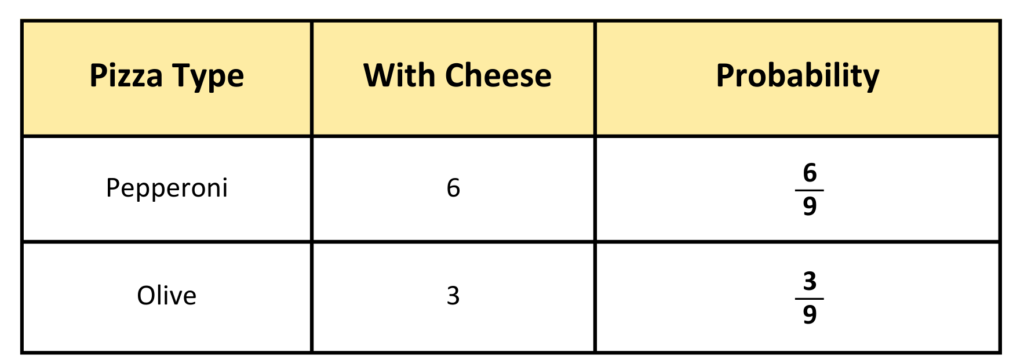
Step #2: Apply the Condition
- The Condition is pepperoni with cheese slice.
Step #3: Find the Probability
Using the Table:

The probability of the cheesy slice is pepperoni is 6/9
Final Answer: The probability of the cheesy slice is pepperoni is 6/9
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: A bag contains:

You randomly pick one ball, don’t put it back, then pick a second ball. What’s the probability the second ball is red, given that the first ball was blue?
Solution:
Step #1: Create the Two-Way Table
If the first ball was blue then,
- Total number of balls left: 10 – 1 = 9

Step #2: Apply the Condition
- The condition is that if the first ball picked is blue, then the second ball is red.
Step #3: Find the Probability
Using the Table:

The probability of the second ball is red if the first was blue 4/9
Final Answer: The probability of the second ball is red if the first was blue 4/9
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: A standard deck has 52 cards. You draw 2 cards without replacement. What’s the probability the second card is red, given the first card was black?
Solution:
Step #1: Draw the Branch and label the probabilities.
- P(Black): 26/52 = 1/2
- P(Red): 26/52 = 1/2
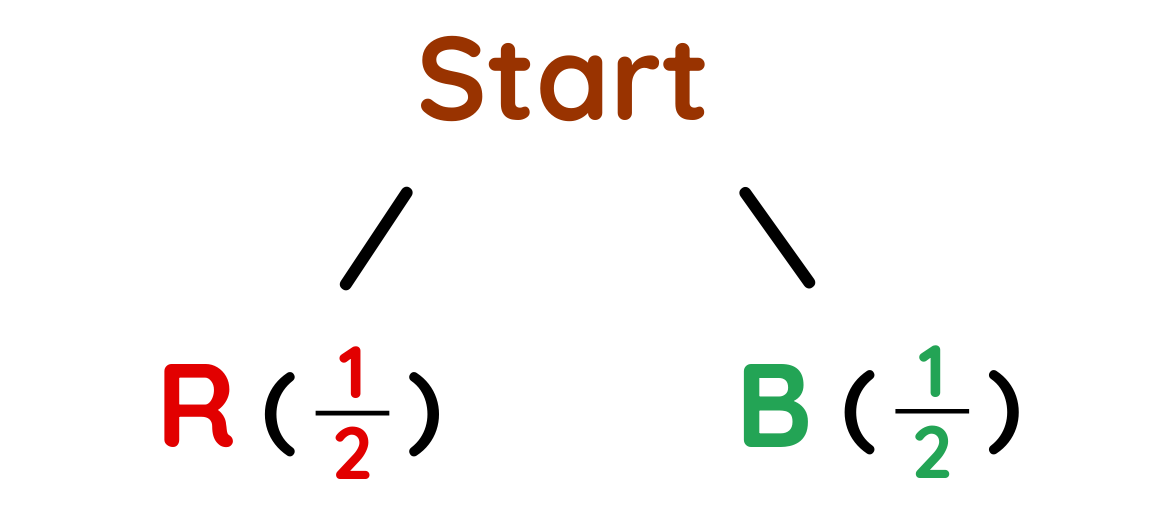
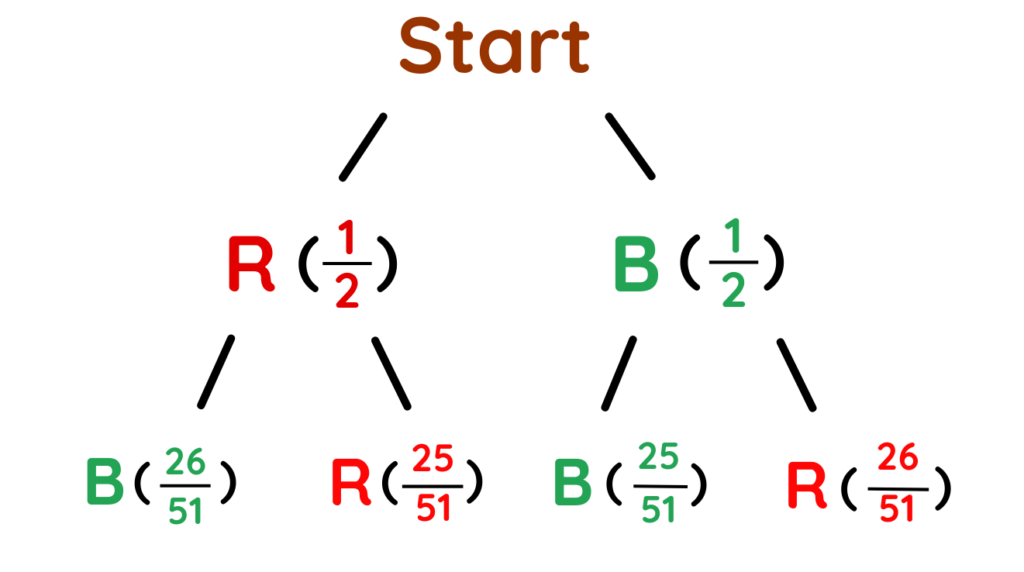
Step #2: Add Dependent Branches
If first was Black:
- Remaining Cards: 26 red, 25 black
- Next pick will be:

If first was Red:
- Remaining Cards: 25 red, 26 black
- Next pick will be:

Step #3: Apply the Condition
First Card was black, so only follow the black path.
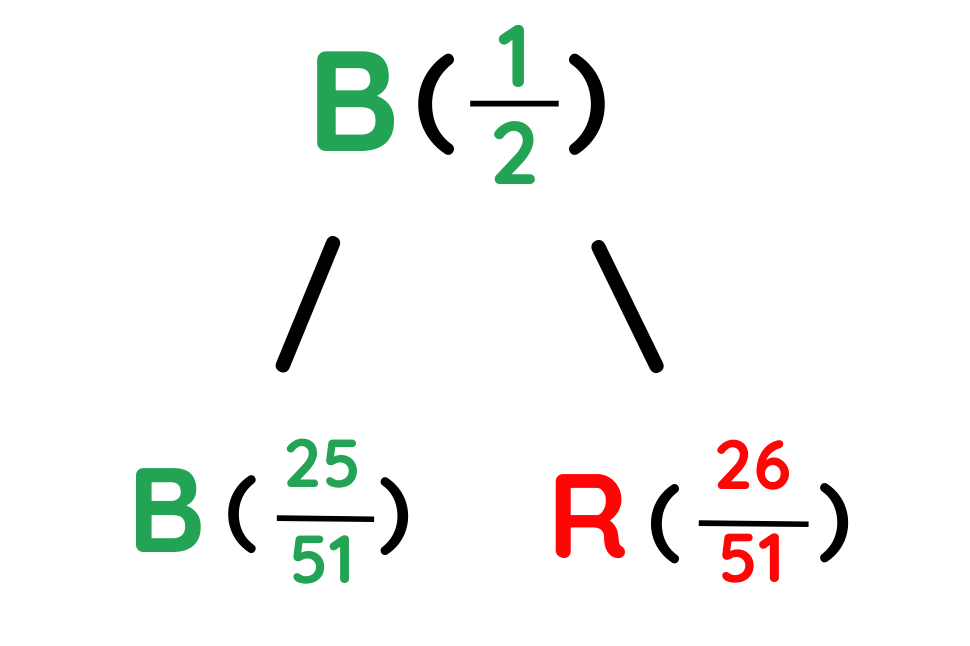
Step #4: Find the Probability
On the Black path, the chance the second card is red is 26/51
Final Answer: The probability the second card is red is 26/51

