Operations of Fractions – GCSE Maths
Introduction
Operations are the basic processes used to manipulate numbers and expressions. The four fundamental operations are:
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (−)
- Multiplication (×)
- Division (÷)
Operations with Fractions-
- In mathematics, an Operation is a process or action that produces a new value from one or more inputs, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
-
Order of Operations:
To solve expressions correctly, follow the order:
Parentheses → Exponents → Multiplication/Division → Addition/Subtraction
Addition of Fractions
1. Same Denominator
- If the denominators (bottom numbers) are the same, just add the numerators (top numbers):
Example-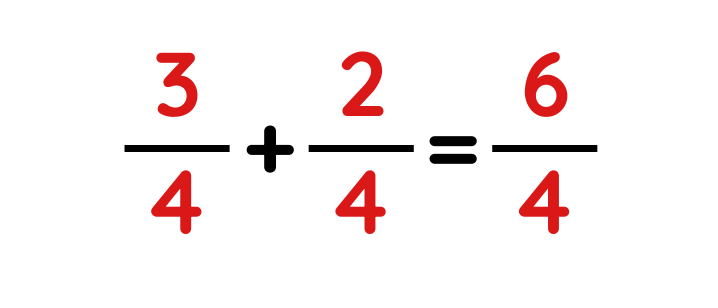
- If the denominators are different, follow these steps:
Step #1: Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD), the smallest number that both denominators can divide into.
Step #2: Convert fractions to have the same denominator
Step #3: Add the numerators
Step #4: Simplify the result (if needed)
Example-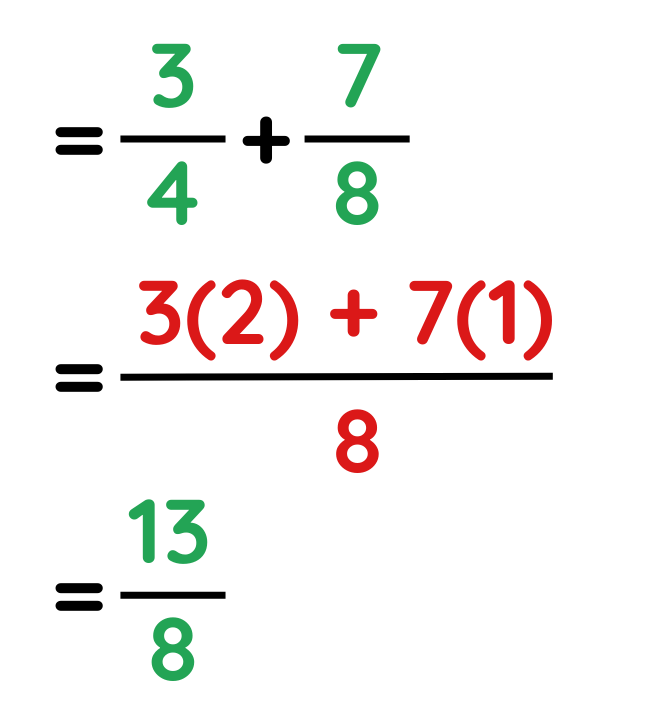
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Convert 3/4 + 7/2 into a single fraction
Solution:
Step #1: Make the bottom numbers the same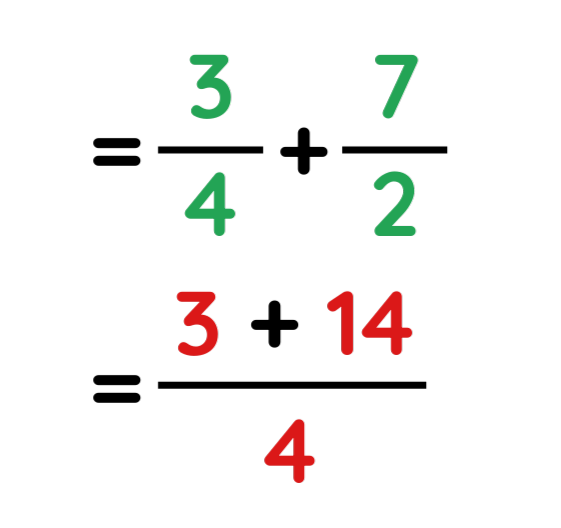
Step #2: Add the top numbers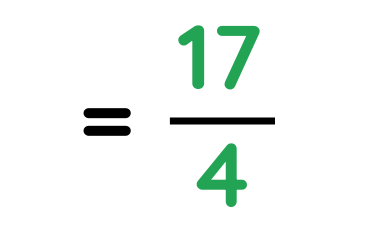
Step #3: Convert back to a Mixed Fraction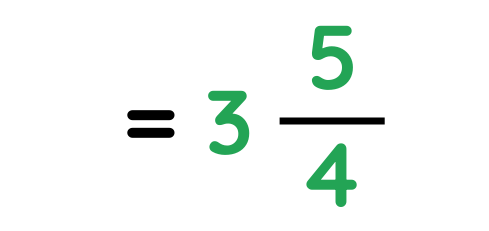
Subtraction of Fractions
1. Same Denominator
- If the denominators (bottom numbers) are the same, just subtract the numerators (top numbers):
Example-
2. Different Denominators
- If the denominators are different, follow these steps:
Step #1: Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD), the smallest number that both denominators can divide into.
Step #2: Convert fractions to have the same denominator
Step #3: Subtract the numerators
Step #4: Simplify the result (if needed)
- Example-
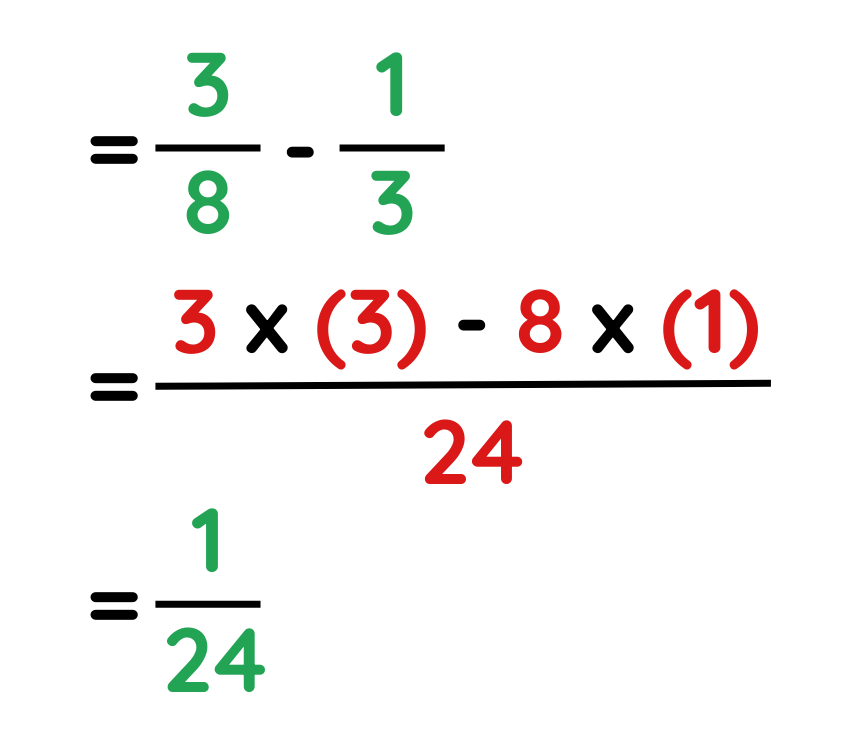
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Convert 9/4 – 5/2 as a fraction.
Solution:
Step #1: Make the bottom numbers the same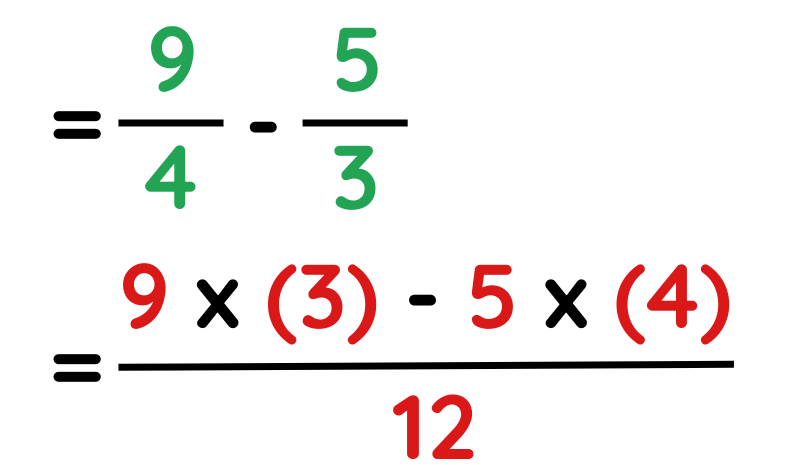
Step #2: Subtract the top numbers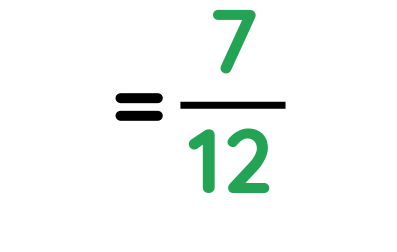
Multiplication of Fractions
1. Basic Rule- For a problem ,such as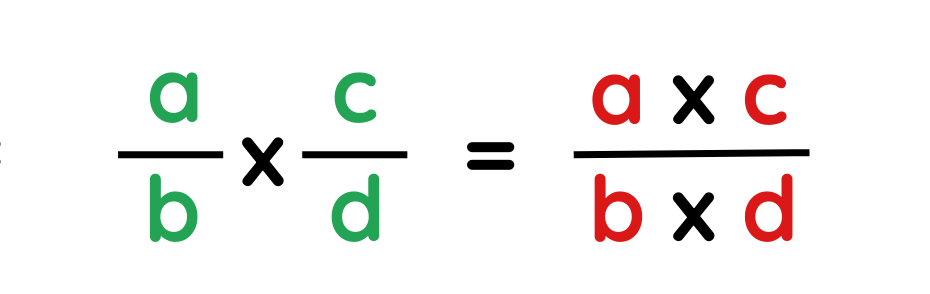
- Numerator of the product = a × c
- Denominator of the product = b × d
2. Steps with Simplification-
Step #1: Multiply the numerators: a × c.
Step #2: Multiply the denominators: b × d.
Step #3: Simplify the resulting fraction by dividing numerator and denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD).
- Example: Multiply

 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Convert 8/3 × 6/5 as a fraction
Solution:
Step #1: Multiply top numbers together.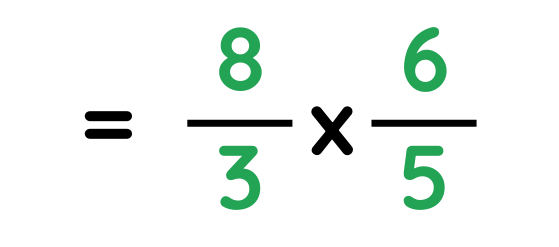
Step #2: Multiply bottom numbers together.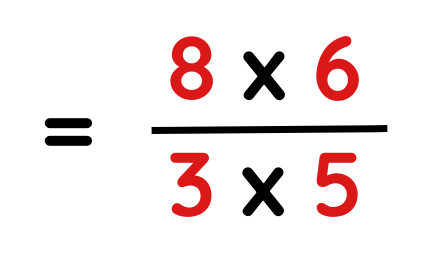
Step #3: Simplify the result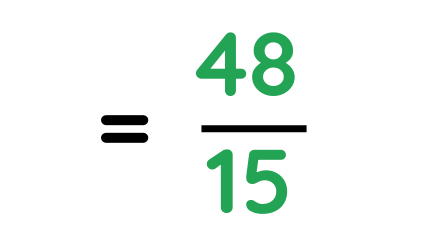
Division of Fractions
1. Basic Rule- For a problem ,such as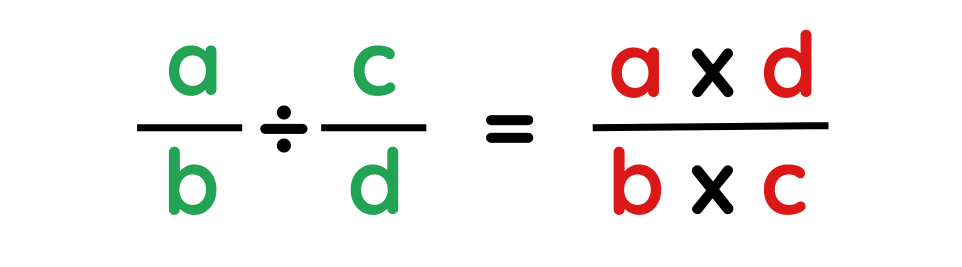
- Numerator of the product = a × d
- Denominator of the product = b × c
2. Steps with Simplification-
Step #1: Write the problem: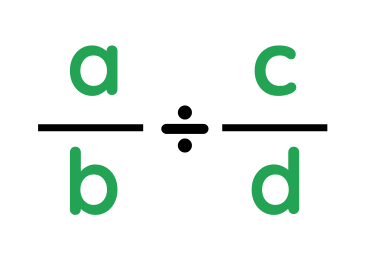
Step #2: Reciprocal, Change to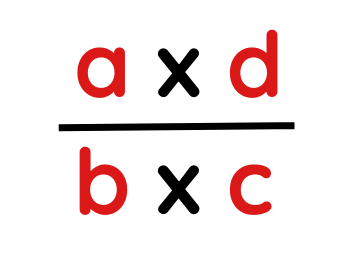
Step #3: Multiply numerators and denominators. Simplify the result by dividing numerator and denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD).
- Example: Divide

 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Convert 3/4 ÷ 7/2 as a fraction
Solution:
Step#1: Keep the first fraction same and change the divide sign to multiplication sign and reciprocate the second fraction.
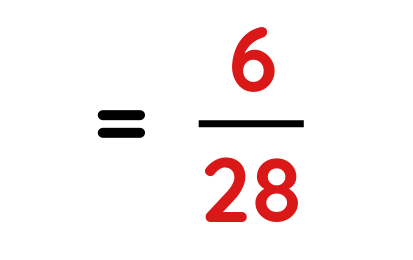
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Emma baked 2/3 of a tray of cookies in the morning and 1/4 of a tray in the afternoon. How much of a full tray did she bake in total?
Solution:
Step #1: Write down the given information
In Morning, Emma baked:-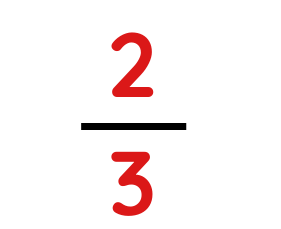
At afternoon, fraction of tray gets completed:-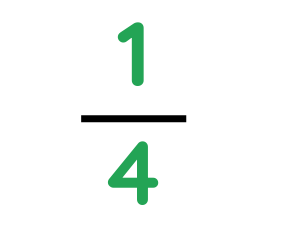
Step #2: Simplify to make a common denominator
We know that:
Step #3: Calculate the final result by applying favorable operations
The total amount of baking that has been completed:
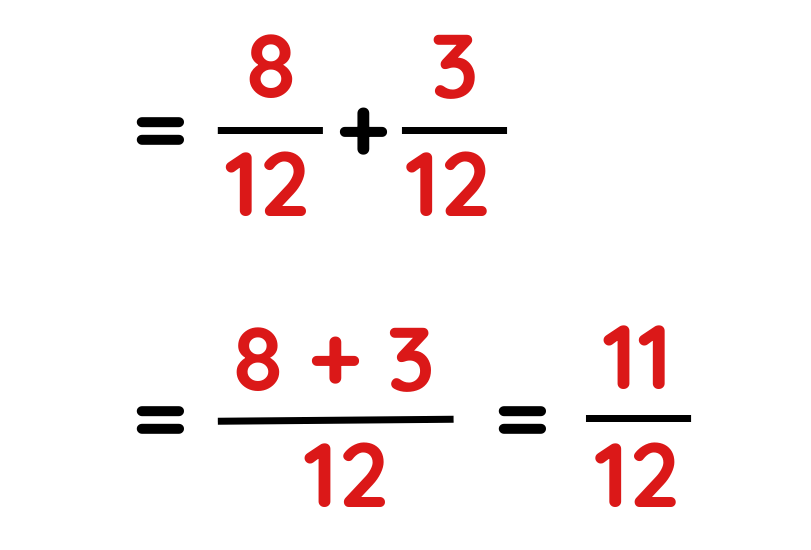
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: A ribbon is 2 3/4 meter long. You need pieces of length 1/6 meter. How many full pieces can you cut?
Solution:
Step #1: Write down the given information
Length of ribbon:-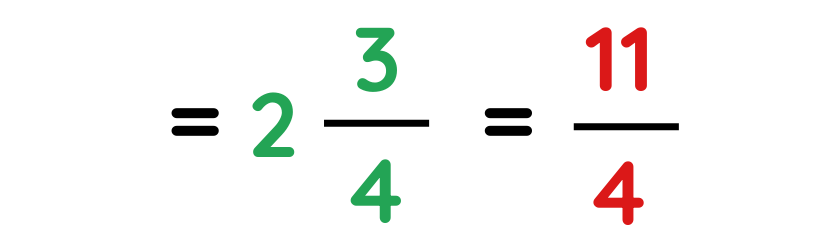
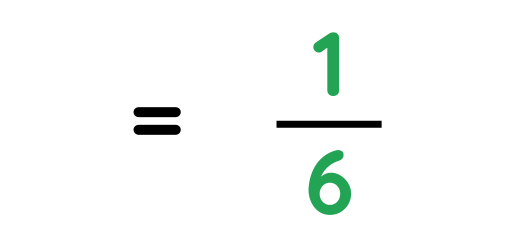
We know that:



