Nuclear Energy: Fission and Fusion
Introduction
- Nuclear energy is generally the energy released from the nucleus (core) of an atom when it undergoes a nuclear reaction—either it can be fission or fusion.
Types of Nuclear Reactions:
1. Nuclear Fission:
- A heavy atom (like uranium-235 or plutonium-239) splits into two smaller atoms, releasing energy.
- Used in nuclear power plants.
2. Nuclear Fusion:
- Two light nuclei (like hydrogen) combine to form a heavier nucleus.
- Happens in sun and stars.
- Still under research for commercial use.
How is Nuclear Energy formed?
- Nuclear energy is formed from the nucleus (center) of an atom. There are two main ways this energy is created:
Nuclear Fission – Splitting Atoms
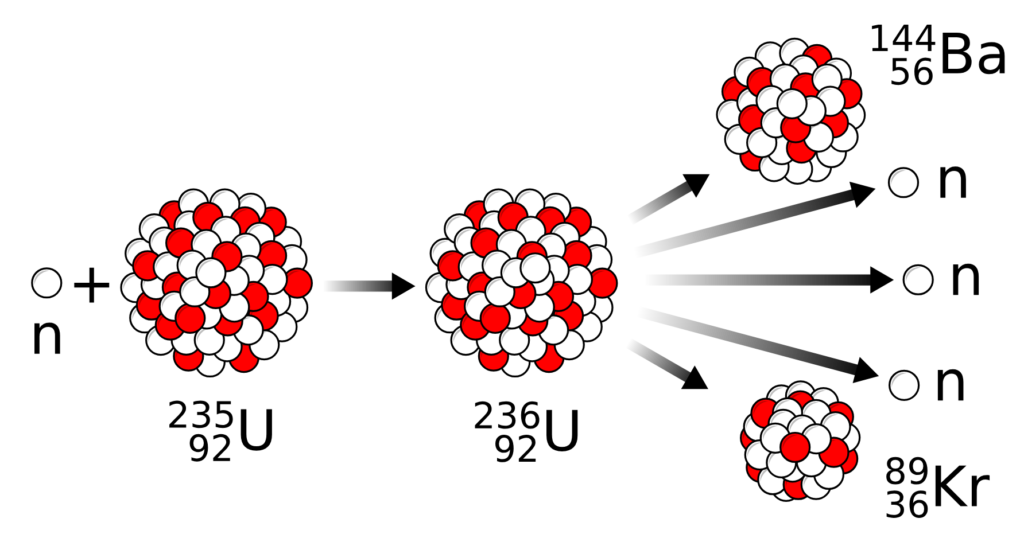
- A heavy atom (like uranium-235) is bombarded by a neutron.
- The atom splits into two smaller atoms.
- This split releases a huge amount of energy, along with more neutrons.
- These neutrons can hit other atoms, creating a chain reaction.
- Example:
Uranium-235 + neutron→Krypton + Barium + Energy + 3
Nuclear Fusion – Combining Atoms
- Two light atoms (like hydrogen isotopes) combine to form a heavier atom (like helium).
- This process releases energy because some mass is converted into energy (Einstein’s formula: E = mc²).
- ✅ Happens naturally in the sun and stars.
- ❌ Very hard to do on Earth – still under research.
Conclusion
Nuclear energy is formed when there is a change in the structure of atomic nuclei, either by fission or fusion.
- Fission is used in today’s nuclear power plants.
- Fusion is the energy of the future — cleaner, safer, and more powerful, but still in development.
Nuclear Fission
Definition:
- Nuclear fission is a process in which a heavy atomic nucleus, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, is split into two lighter nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy, along with free neutrons and gamma radiation.
How it works:
- Let say a neutron hits a uranium-235 atom.
- The uranium atom becomes unstable and splits.
- This produces:
- Two smaller nuclei (e.g., krypton and barium),
- 3 more neutrons, and
- A large amount of heat energy.
🔄 Chain Reaction:
- The neutrons released can hit more
U235+ n → Ba144 + Kr89 + 3n + Energy
Where the energy is used:
- Nuclear power plants (for generating electricity).
- Nuclear submarines and ships.
- Atomic bombs (uncontrolled chain reaction).
Practical Applications of Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear fission has several real-world applications, especially because it produces a large amount of energy from a small amount of fuel. Here’s a detailed list:
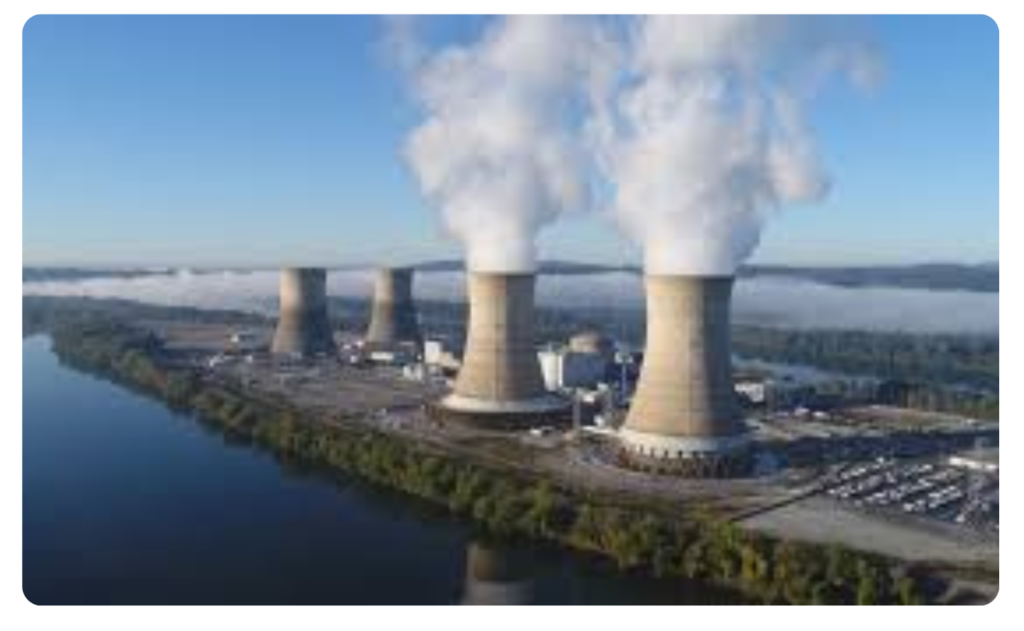
Electricity Generation (Nuclear Power Plants)
- The most common application.
- Nuclear reactors use fission of Uranium-235 to produce heat.
- This heat is used to turn water into steam.
- Steam rotates turbines, which drive generators to produce electricity.
📍 Example:
- Bruce Nuclear Generating Station in Canada

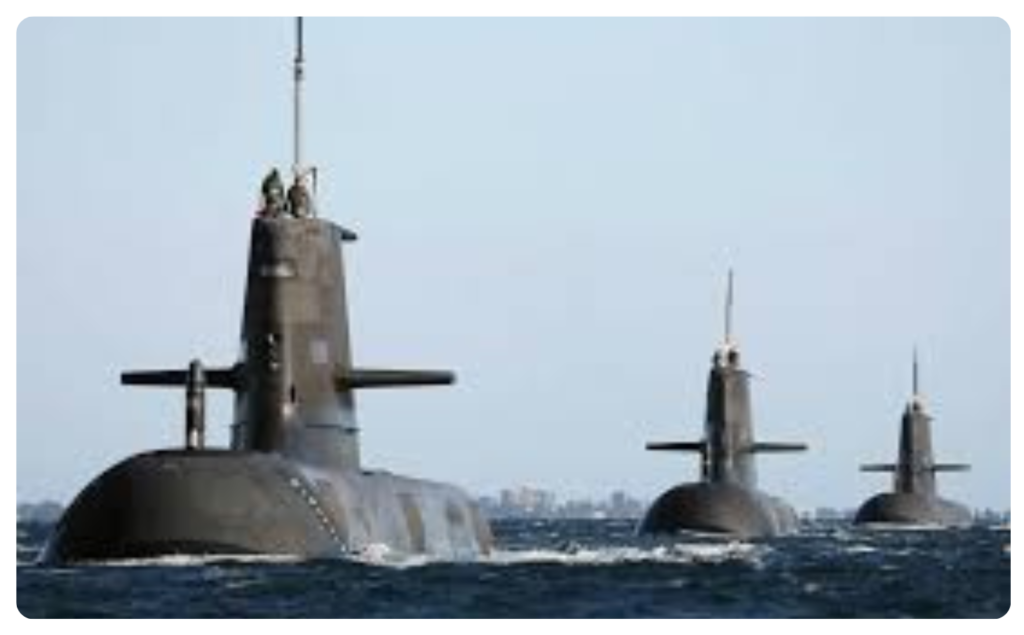
Nuclear-Powered Submarines and Ships
- Fission reactors are used in naval vessels for propulsion.
- They can stay underwater or travel long distances without refueling for years.
📍 Example:
- USS Enterprise (USA) – first nuclear-powered aircraft carrier

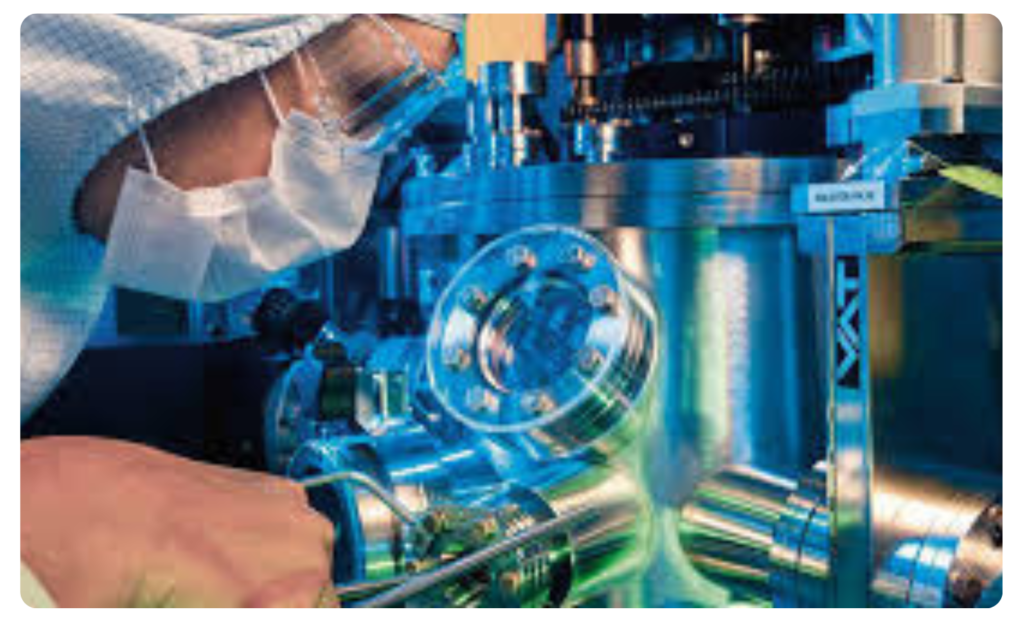
Scientific Research
- Research reactors use controlled fission to study neutron behavior, material properties, and nuclear physics.
- Helps in material testing and developing better fuels.

Nuclear Fusion
Definition:
- Nuclear fusion is a reaction where two light atomic nuclei (like hydrogen isotopes) fuse together to form a heavier nucleus, releasing massive amounts of energy.
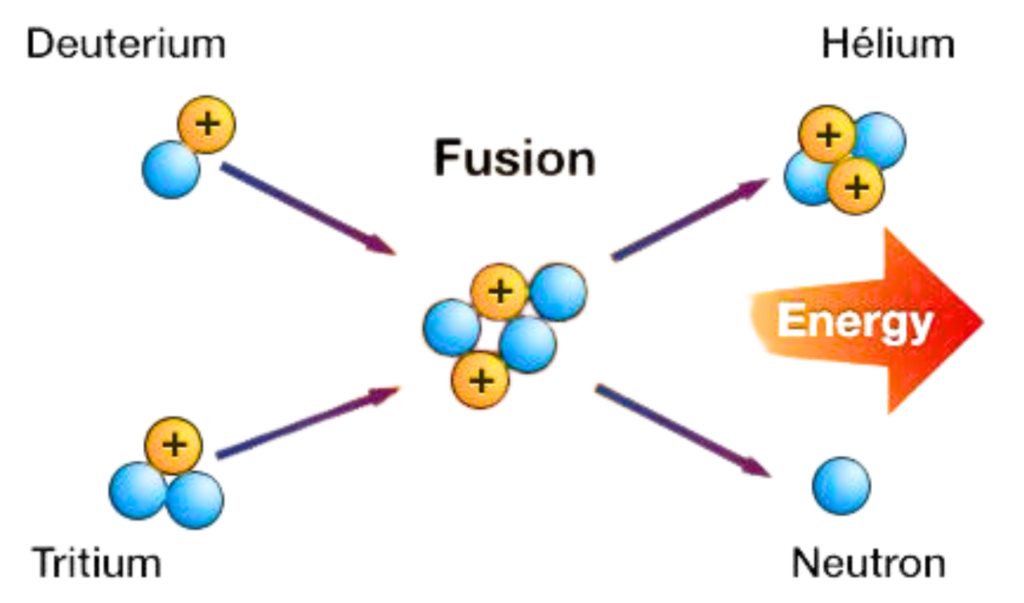
How it works:
- At extremely high temperatures and pressures, two hydrogen nuclei (deuterium and tritium) overcome their repulsion and combine.
- This forms helium and releases energy.
- Some mass is converted into energy, based on Einstein’s formula:
E = mc2
where,
- E = energy,
- m = mass lost,
- c = speed of light.
Where it Happens:
- In the core of stars, including the Sun.
- Under research in labs on Earth (e.g., ITER project) for clean energy.
- 📌 Equation Example:
D + T → He +n + Energy
Practical Applications of Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear fusion is the process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing enormous energy. Though it’s not yet commercially used on Earth, fusion powers the Sun and stars and is under active research for clean energy.
The Sun and Other Stars
- The most natural and perfect example of nuclear fusion.
Example:
- In the Sun, hydrogen nuclei (protons) fuse to form helium and release energy.
- This energy reaches Earth as sunlight and heat.
- Fusion keeps stars shining for billions of years.
4H → He + Energy
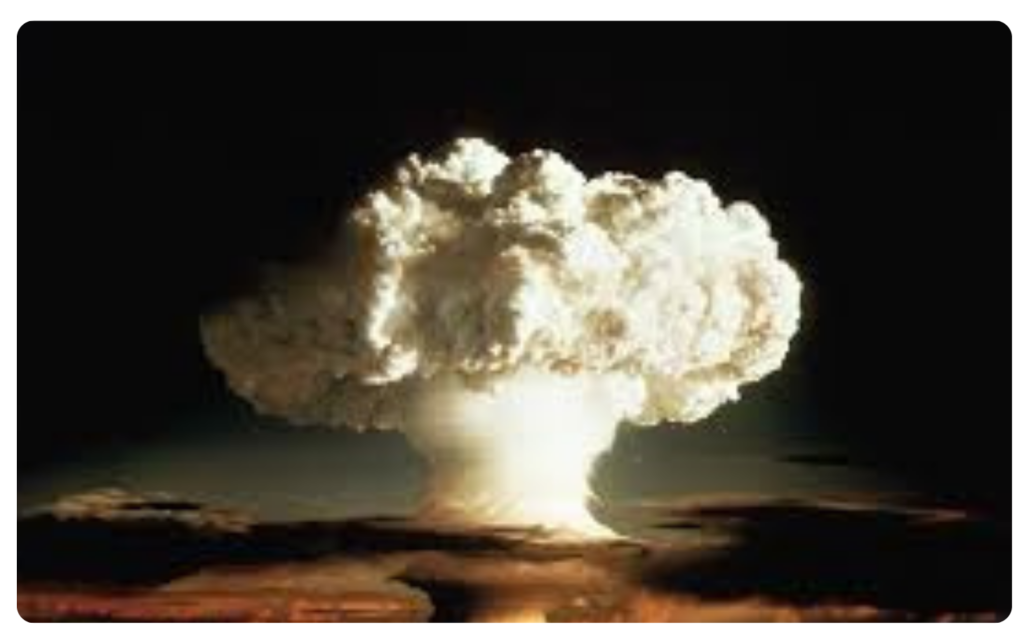
Hydrogen Bomb (Fusion Bomb)
- Fusion is used in thermonuclear weapons, where it releases even more energy than fission bombs.
Example:
- Tsar Bomba (1961) – Largest hydrogen bomb ever tested by Russia.
- Works by fusing deuterium and tritium after triggering with a fission bomb.

Nuclear Power Plant
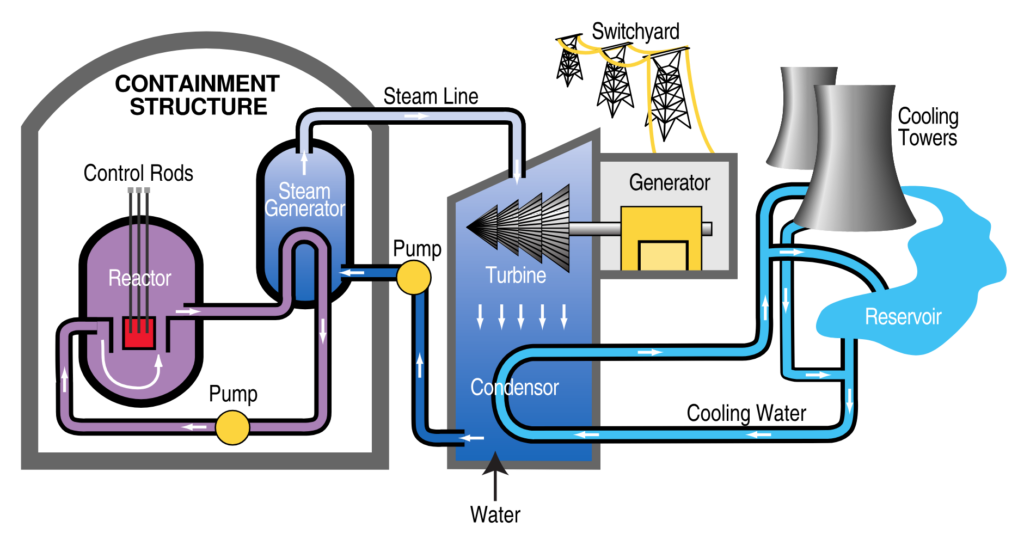
- A Nuclear Power Plant is a facility that generates electricity through controlled nuclear fission reactions, typically using uranium or plutonium as fuel.
- These plants produce large amounts of energy with relatively low greenhouse gas emissions, making them a key part of the clean energy debate.
How it works:
Nuclear Fission:
- Uranium-235 (or plutonium-239) atoms are split in a reactor core, releasing heat.
- This process is sustained by a chain reaction, controlled using neutron-absorbing materials (like control rods).
Heat Generation:
- The fission reaction heats water in the primary coolant loop, which remains under high pressure to prevent boiling.
Steam Production (via Heat Exchanger):
- The hot coolant transfers heat to a secondary water loop, turning it into steam (in a steam generator).
Electricity Generation:
- The steam drives a turbine, which spins a generator to produce electricity.
- After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled back into water in a condenser (often using a cooling tower or nearby water source).
Waste & Safety Systems:
- Spent fuel (radioactive waste) is stored on-site in cooling pools or dry casks.
- Multiple safety systems (containment structures, emergency cooling) prevent radiation leaks.
Types of Nuclear Reactors:
- Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) – Most common; uses high-pressure water as coolant/moderator.
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) – Simpler design; steam is produced directly in the reactor.
- Advanced Reactors –
- Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) – Produce more fissile material than they consume.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) – Compact, scalable designs for flexible deployment.
- Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs) – Use liquid fuel for potentially safer operation.
Difference between Nuclear Fission and Fusion

Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
- Two smaller nuclei (called fission fragments)
- 3 neutrons (on average)
- Energy (in the form of heat and radiation)
Solution:
Yes, in hydrogen bombs and experimental reactors (like ITER), but not yet in a controlled, power-generating way.
Solution:
- Uranium-235
- Plutonium-239
Solution:
- Deuterium (from water)
- Tritium (produced from lithium)
Solution:
Because fusion needs extremely high temperatures and pressures (like those inside stars), it is very hard to control.
Researchers are working on it (e.g., ITER project), but it’s not ready for electricity production yet.
Solution:
- Fission-based nuclear energy is not renewable (limited uranium)
- Fusion-based energy could be considered nearly unlimited and clean, but it’s not yet available for use

