Extracting Metals – GCSE Chemistry
Introduction
- Metals are shiny, strong and good conductor of heat and electricity making them useful for tools, wires, and structures.
- Metals are naturally found in the Earth’s crust combined with other elements in mineral deposits called ores, which are then extracted through mining and refined for use.
- Some common metals:

Daily-life examples where metals are used:

The Reactivity Series of Metals
- Reactivity is the ability of a substance, especially a metal, to undergo a chemical reaction with other substances like water, acids, or oxygen.
- It shows how easily a metal can lose electrons to form positive ions.
- If a metal reacts quickly, it is highly reactive.
- If it reacts slowly or not at all, it is less reactive or unreactive.
Reactivity Series of Metals:
- The reactivity series is a list of metals that shows how easily different metals react.
- It is arranged in order of their reactivity, from most to least reactive.
- A common series is:

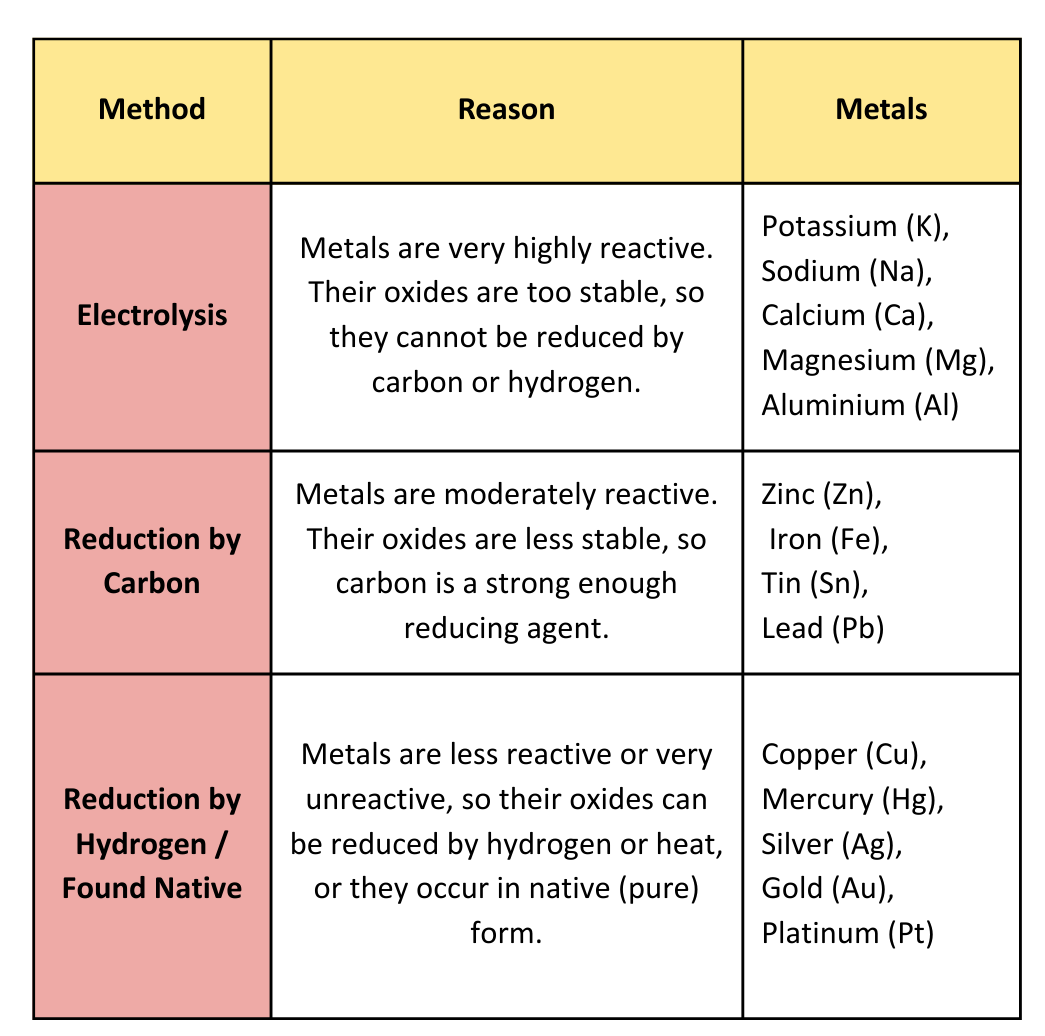
Extraction of Metals:
What are Oxidation and Reduction?
- Oxidation and reduction are the reactions which always happen together in a redox reaction.
- They involve moving electrons from one substance to another.
Oxidation
- Oxidation is the gain of oxygen by a substance or the loss of electrons during a reaction.

Where:
- Mg = Magnesium
- O = Oxygen
Reduction
- Reduction is the loss of oxygen by a substance or the gain of electrons during a reaction.
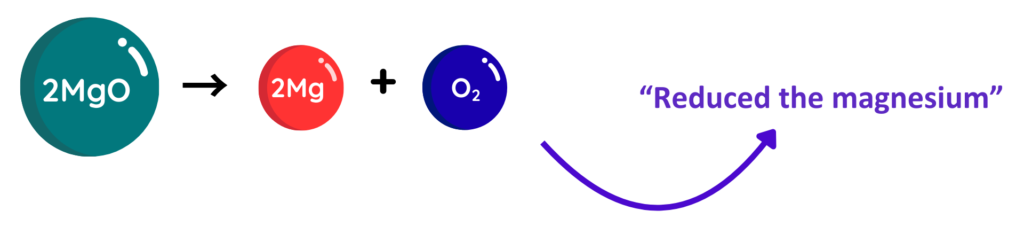
Where:
- Mg = Magnesium
- O = Oxygen
How are Oxidation and Reduction used to Extract Metals?
- Most metals are found in nature combined with oxygen or other elements, not as pure metals.
- To get the pure metal, we need to remove the oxygen from these compounds.
- This is done using a process called reduction.
- In simple words, reduction helps us take away oxygen, so we get the pure metal we need.
- We can use carbon or hydrogen as reducing agents to take away the oxygen.
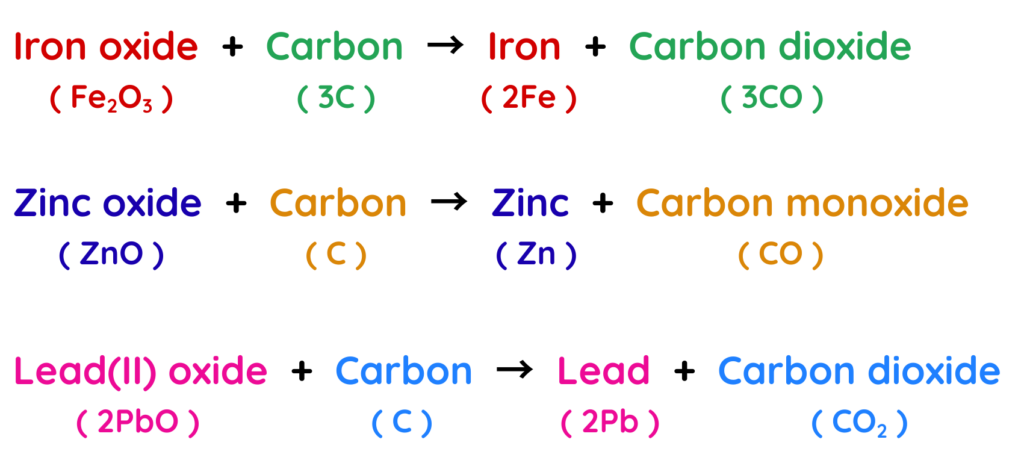
Extraction of Metals from Oxides using Carbon:
- Metals below carbon in the reactivity series are – zinc, iron, lead, copper and these metals can be extracted from their oxides using carbon.
- Carbon removes oxygen from the metal oxide to form pure metal, while carbon itself gets oxidised to carbon dioxide.
Examples:
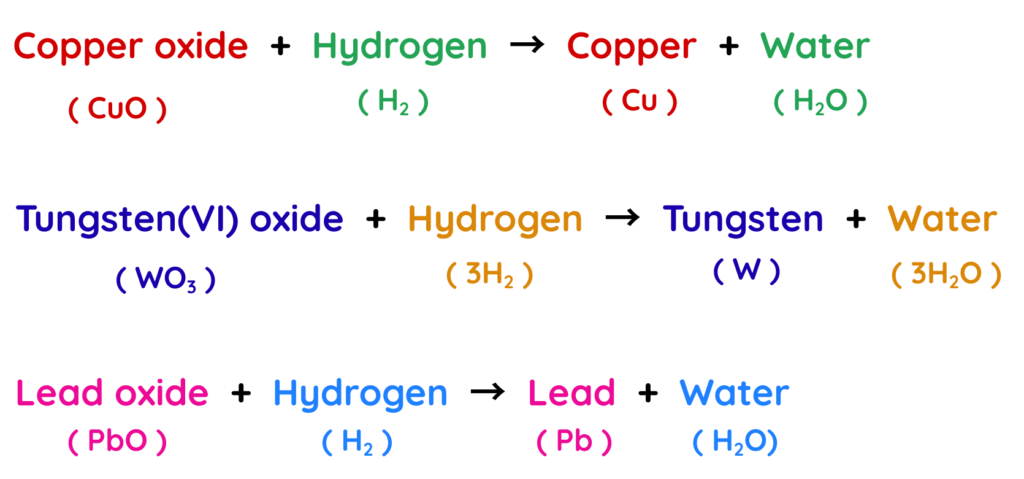
Extraction of Metals from Oxides using Hydrogen:
- Metals below hydrogen in the reactivity series are – copper, silver etc. are less reactive and so these metals can be extracted from their oxides using hydrogen.
- Hydrogen removes oxygen from the metal oxide to form pure metal, while hydrogen itself is oxidised to water.
Examples:
For Highly Reactive Metals:
- Metals like aluminium and sodium are very reactive, so they are high up in the reactivity series.
- They form strong bonds with oxygen, making very stable compounds.
- Carbon is not reactive enough to remove the oxygen from these metals, so we cannot use carbon to extract them.
- We need to use other methods like electrolysis to get these metals
Note: To Learn about Electrolysis, please tap on the link: Electrolytic processes
What Are The Methods of Preventing Rusting?
- There are different methods we can use to prevent rusting. Here they are:
Painting and Plastic Coating
- A layer of paint or plastic is used on car bodies, fences, etc., which keeps out air and water.
Oiling or Greasing
- It is commonly used for machine parts and bicycle chains.
- The oil prevents water and oxygen from reaching the metal.
Galvanising
- When iron is coated with a layer of zinc, it is called galvanising.
- The zinc protects the iron by forming a barrier, and even if it is scratched, zinc reacts more easily than iron, so it prevents rusting.
Electroplating
- Using electricity, a thin layer of another metal such as chromium or silver is coated onto iron or steel.
- This protects it from rust and also makes it look better.
Alloying
- When iron is mixed with other metals, such as chromium and nickel, it makes stainless steel.
- This process is called alloying, and the steel does not rust easily, so it is used in cutlery, sinks, and medical tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
It is a list of metals arranged from most reactive to least reactive, helping us understand how metals react with water, air, acids, and how they are extracted.
Solution:
Because metals react with oxygen in air, forming stable metal oxides over time.
Solution:
Less reactive metals (like iron, zinc, lead, copper) are extracted from their oxides using carbon or hydrogen, which remove oxygen from the metal oxide (reduction).
Solution:
Highly reactive metals (like aluminium, sodium, potassium) are extracted using electrolysis, as they are too reactive for carbon to reduce their oxides.
Solution:
When a metal gains oxygen or loses electrons during a reaction.
Solution:
When a metal loses oxygen or gains electrons during a reaction, usually when extracting metals from their oxides.

