Trigonometry – GCSE Maths
Introduction
- Trigonometry is all about Triangles.
- It is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles—especially right-angled triangles.
Basics of Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the study of the relationship between the angles and sides of triangles.
1. Why do we use it?
To find:
- How long a side is
- What an angle is
—when we have the values of some other parts of the triangle.
2. The Three main Functions:
In a right-angled triangle:
- sin (as: “sine”)
- cos (as: “cosine”)
- tan (as: “tangent”)
They are simply the ratios (fractions) of the given triangle’s sides.
3. All about Triangles:
Triangles are three-sided polygons with several important properties. Here are some key properties of triangles:-
Basic Properties-
- A triangle has three sides, three vertices, and three angles.
- The sum of the interior angles is always 180°.
- The sum of the exterior angles is always 360°.
Side Length Rule (Triangle Inequality Theorem)
There are mainly four types of Triangles that can be distinguished uniquely.
Let us understand about them in detail:
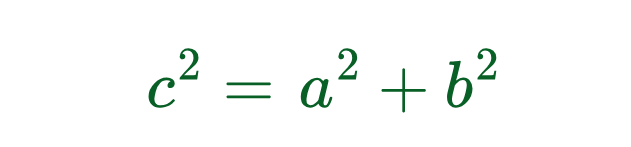
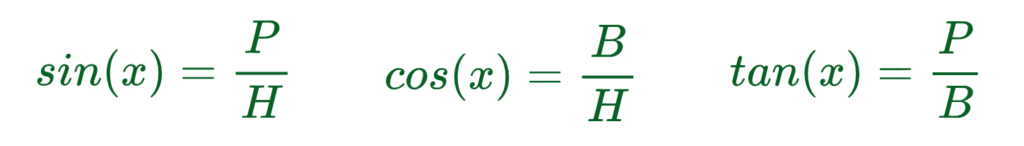
Angles Of Elevation & Depression
Definitions-
- Angle of Elevation: The angle formed between the horizontal line (eye level) and the line of sight when an observer looks upwards at an object.
- Angle of Depression: The angle formed between the horizontal line (eye level) and the line of sight when an observer looks downwards at an object.
Key Points-
- Both angles are measured from the horizontal (eye level).
- They are always between 0° and 90°.
- The angle of elevation and depression are congruent (equal) when the observer and object are at the same horizontal level (i.e., in symmetric positions).
Real Life Applications-
- Angle of Elevation: Used in measuring heights of buildings, mountains, or trees.
- Angle of Depression: Used in aviation (pilots landing planes), navigation, or determining distances between objects at different heights.
Step by Step Procedure-
- Step#1: Draw a Diagram
- Step#2: Identify known and unknown values
- Step#3: Choose the Right Trigonometric Ratio
- Step#4: Solve for the Unknown
- Step#5: Check for Angle of Depression
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
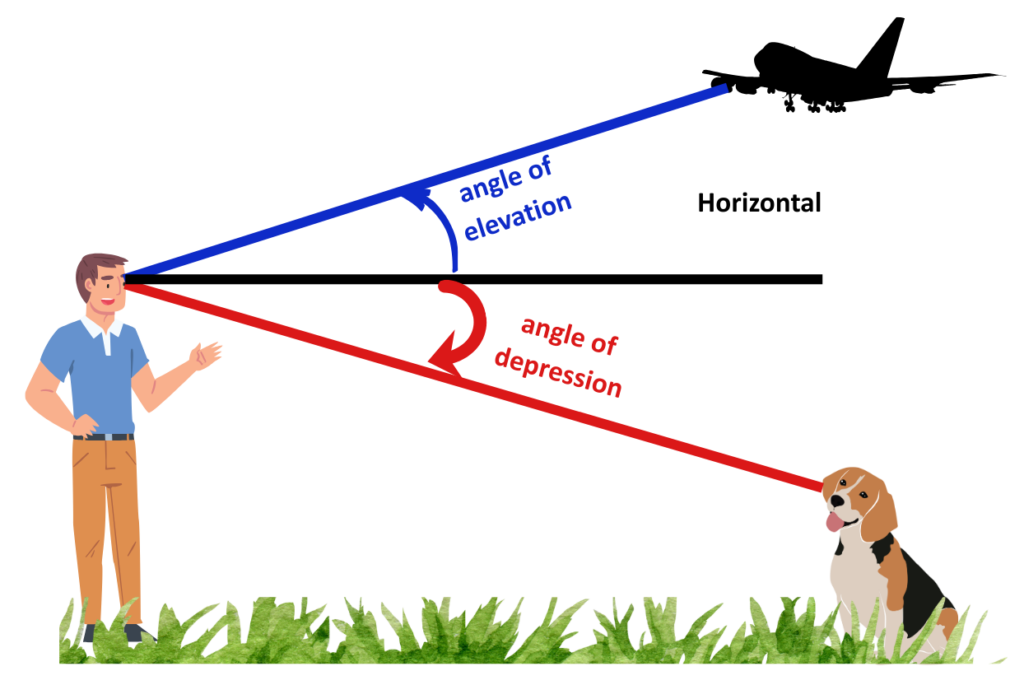
Example: “A bird sits on a tree 10m high. A man 20 m away looks up at the bird.”
Solution:
Step#1: Draw a Diagram-
- Sketch the scenario based on the problem statement.
- Label-
- The observer’s eye level (horizontal line).
- The line of sight (angle of elevation or depression).
- The height (vertical side) and distance (horizontal side).
Step#2: Identify Known & Unknown Values-
- Given:
- Distance from observer to object (adjacent side).
- Height (opposite side).
- Angle (if given).
- Find:
- The missing side or angle.
Example:
- Given:

- Find: Angle of Elevation (θ).
Step#3: Choose the Right Trigonometric Ratio-
- SOH-CAH-TOA helps decide which ratio to use:
- Sine (sinθ) = Opposite / Hypotenuse
- Cosine (cosθ) = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
- Tangent (tanθ) = Opposite / Adjacent
In our example:
- We have opposite (height) = 10m and adjacent (distance) = 20m.
- Use tangent-

Step#4: Solve for the Unknown-
- If finding an angle, use inverse trig functions (tan⁻¹, sin⁻¹, cos⁻¹).
- If finding a side, rearrange the formula.
Example (continued):
- To find θ:
- θ = tan−1(0.5) ≈ 26.57°
Step#5: Check for Angle of Depression-
- If the problem involves looking downward, the steps are the same, but the angle is measured below the horizontal.
Key Fact:
- Angle of elevation from point A to B = Angle of depression from B to A (they are equal due to alternate angles).
Therefore,
Angle of Elevation = Angle of Depression
Hence,
Angle of depression ≈ 26.57°
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
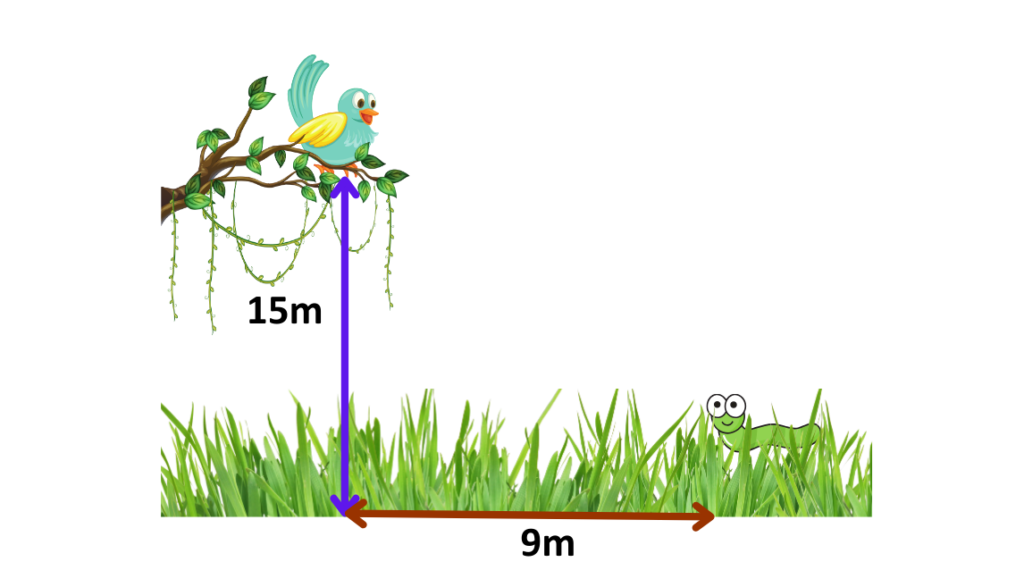
Example: A bird is perched on a 15-meter-high tree. It spots a worm on the ground 9 meters away from the base of the tree. What is the angle of depression from the bird to the worm?
Solution:
Step#1: Draw a Diagram-
- Sketch the scenario based on the problem statement.
- Label:
- The observer’s eye level (horizontal line).
- The line of sight (angle of elevation or depression).
- The height (vertical side) and distance (horizontal side).

Step#2: Identify Known & Unknown Values-
- Given:
- Distance from observer to object (adjacent side).
- Height (opposite side).
- Angle (if given).
- Find:
- The missing side or angle.
Example:
- Given:
- Distance (adjacent) = 9m
- Height (opposite) = 15m
- Find: Angle of depression(θ).
Step#3: Choose the Right Trigonometric Ratio-
- SOH-CAH-TOA helps decide which ratio to use:
- Sine (sinθ) = Opposite / Hypotenuse
- Cosine (cosθ) = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
- Tangent (tanθ) = Opposite / Adjacent
In our example:
- We have opposite (height) = 15m and adjacent (distance) = 9m.
- Use tangent-

Step#4: Solve for the Unknown-
- If finding an angle, use inverse trig functions (tan⁻¹, sin⁻¹, cos⁻¹).
- If finding a side, rearrange the formula.
Example (continued):
- To find θ:
- θ = tan−1(1.67) ≈ 59.3°
Step#5: Check for Angle of Elevation-
- If the problem involves looking downward, the steps are the same, but the angle is measured below the horizontal.
Key Fact:
- Angle of elevation from point A to B = Angle of depression from B to A (they are equal due to alternate angles).
Therefore,
Angle of Elevation = Angle of Depression
Hence,
Angle of depression ≈ 59.3°
Triangles Exact Values
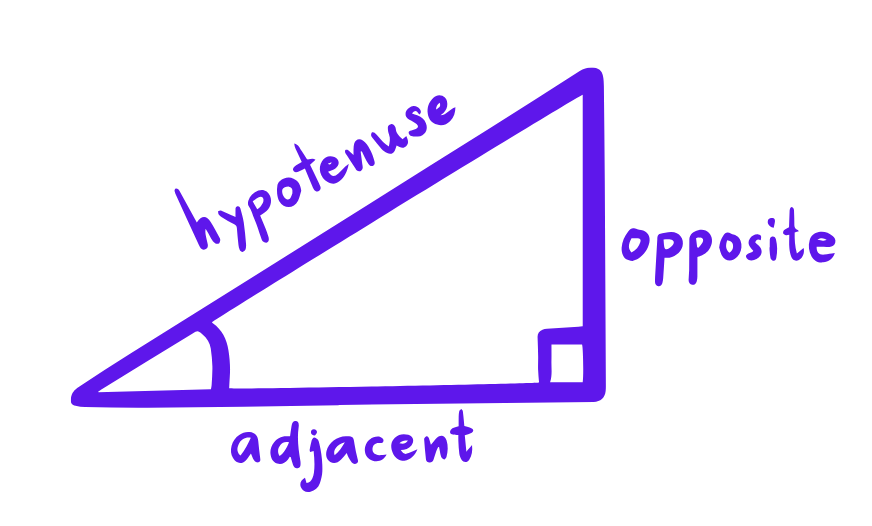
Let us understand about some important ratios in brief: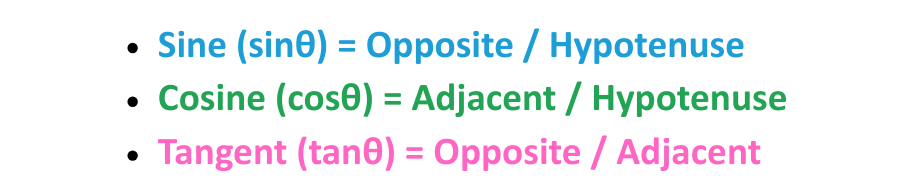
- Opposite = side opposite the angle
- Adjacent = side next to the angle (not the hypotenuse)
- Hypotenuse = the longest side (opposite the 90° angle
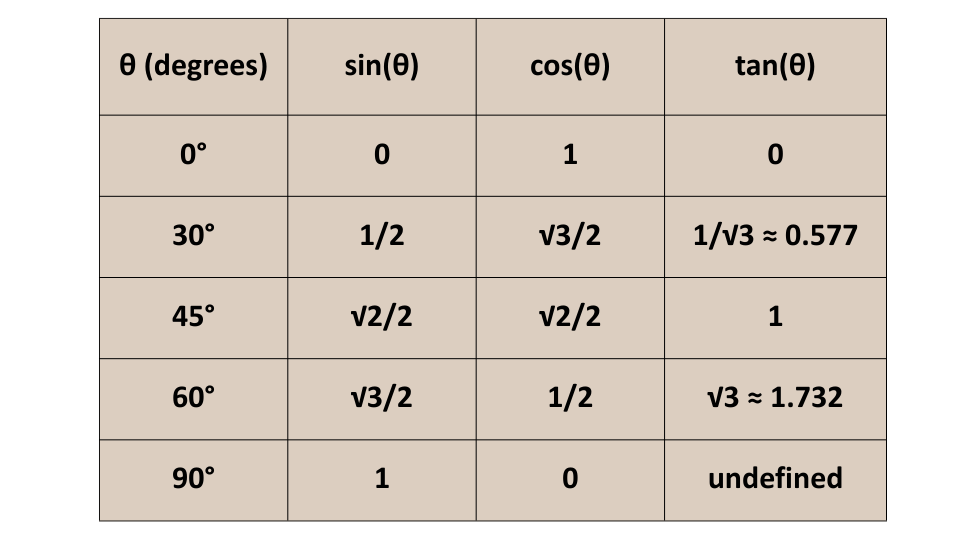
- Tip: We have to summarize this table given above to solve each of the question accurately.
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Example: In a right triangle, the angle is 30° and the adjacent side is 6 units. Find the opposite side.
Solution: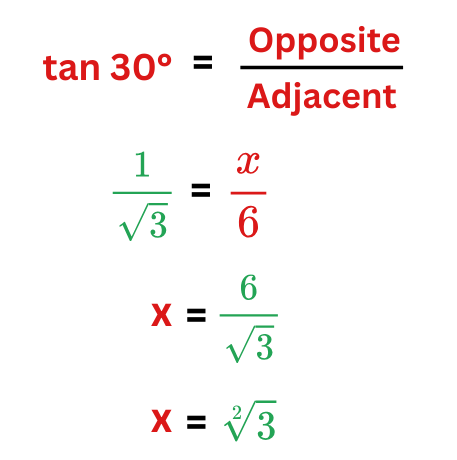

 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Example: In a right triangle, the angle is 30° and the opposite side is 9 units. Find the opposite side.
Solution:
Given:
- Angle = 30°
- Adjacent side = 6 units
We know that,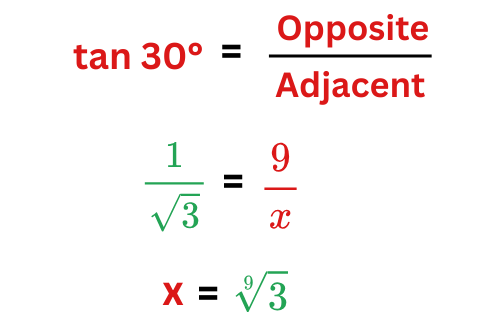
So, therefore we got an answer to our question that is:
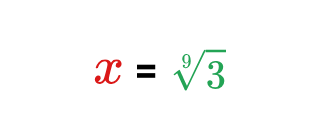
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: A shed roof makes an angle of 41° with the horizontal. Given that the width of the shed is 6 m and the length of its slope is 4 m. Calculate the height of the roof.
Solution:
Given:
- Angle (θ) = 41° (between the roof and the horizontal)
- Slope length (L) = 4 m (the hypotenuse of the right triangle formed by the roof)
- Width (W) = 6 m (total horizontal span of the shed)
The width of the shed (6 m) is the total span, but the roof slope only covers half of this (since it’s a symmetrical shed roof).
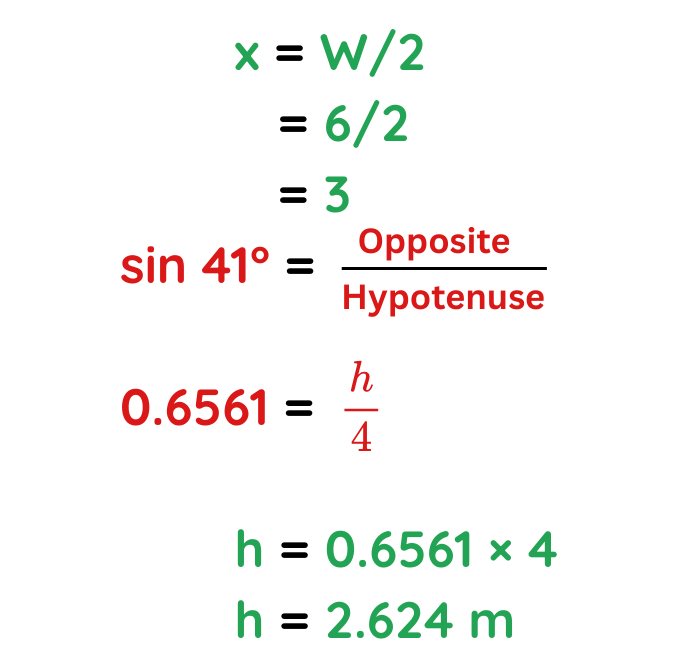
The height of the roof is approximately 2.624 meters.
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
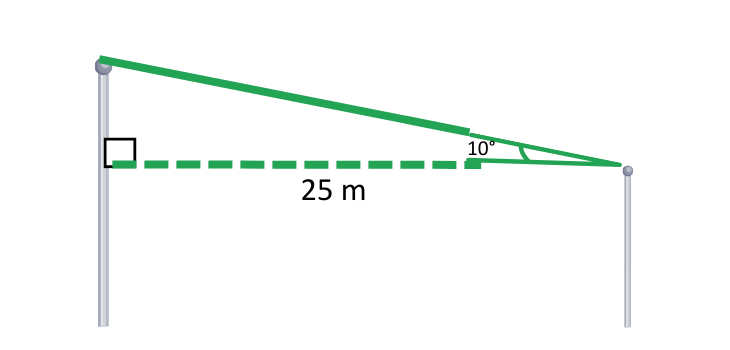
Problem: A zip wire runs between two poles 45m apart. The zip wire is at an angle of 10° to the horizontal. Calculate the length of the zip wire.
Solution:
Given:
- Angle (θ) = 10° (between the zip wire and the length)
- Width (W) = 25 m (Distance between two poles)
The width of the shed (6 m) is the total span, but the roof slope only covers half of this (since it’s a symmetrical shed roof).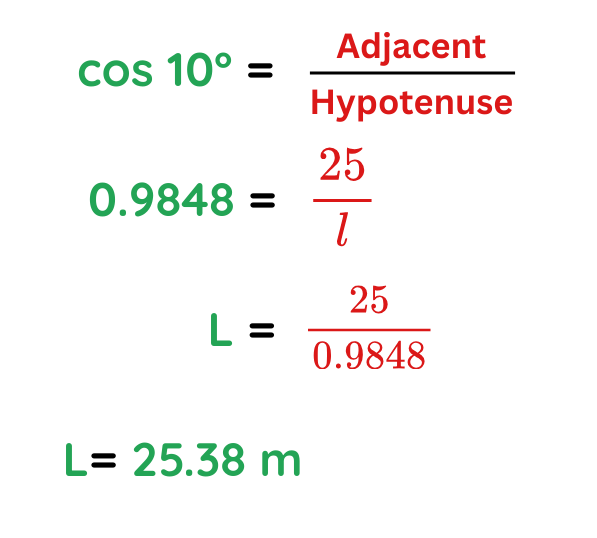
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
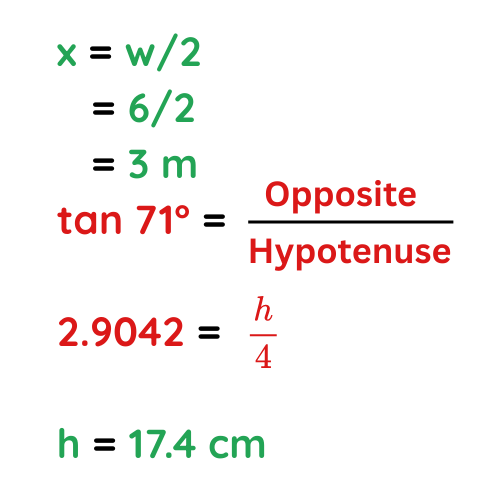
Problem: Triangle ABC is an isosceles. Calculate the height of the given triangle.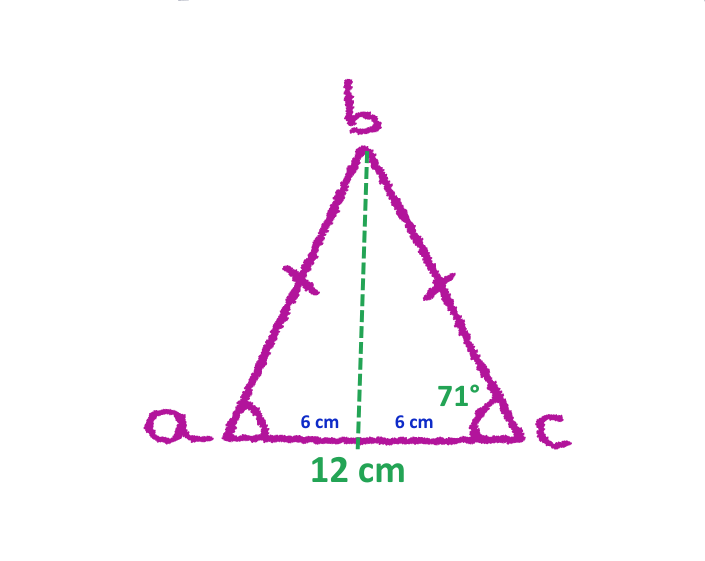
Given:
- Angle (θ) = 71° (between the two sides)
- Side length = 12 cm (Distance between two poles)
The width of the shed (6 m) is the total span, but the roof slope only covers half of this (since it’s a symmetrical shed roof).