Hydrocarbons - GCSE Chemistry
Introduction
- In organic chemistry, the study of hydrocarbons is important for understanding all carbon compounds.
- They show how carbon and hydrogen combine to form the simplest organic structures, which later give rise to complex substances such as alcohols, acids, fuels, medicines, and plastics.
- In this blog, we’ll study the two main classes of hydrocarbons — alkanes and alkenes — along with their important reactions and properties.
Uses of Hydrocarbons
- Fuels — in the form of petrol, diesel, and LPG for transport and cooking.
- Used in manufacturing medicines and cosmetic products.
- Provide energy through combustion in industries and power plants.
- Act as lubricants in engines and machinery.
What are Hydrocarbons?
- Hydrocarbons are organic substances composed only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms.
- Based on the type of bonding between carbon atoms, hydrocarbons are classified into two major categories:
Alkanes –
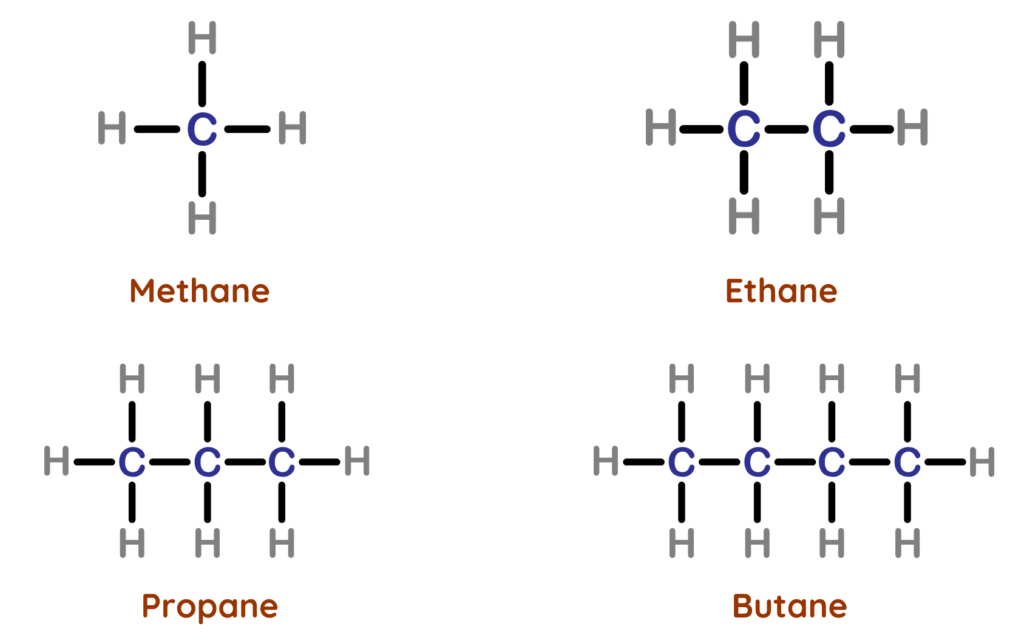
- Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons where each carbon forms four single covalent bonds.

- They are quite stable and unreactive, mainly reacting through combustion.
Example:
Alkanes –
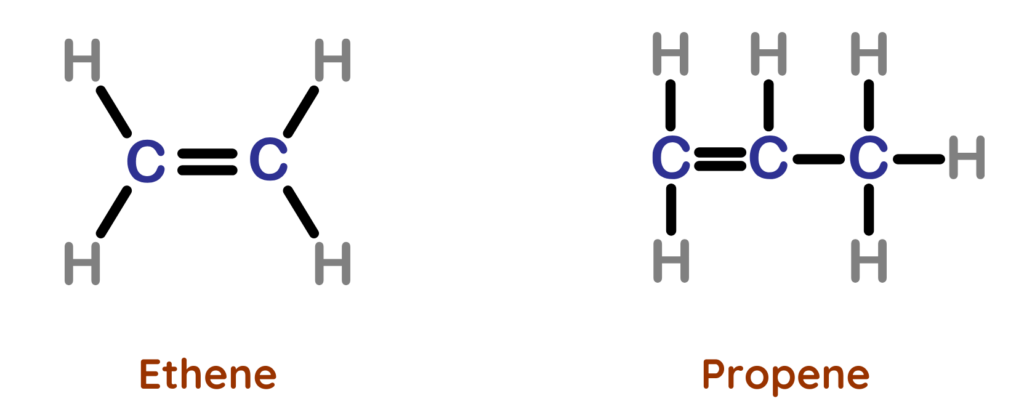
- Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds.

- This double bond is their functional group and the reason for their higher reactivity.
Example:
Why are Alkanes Saturated Hydrocarbons?
- Alkanes are called Saturated Hydrocarbons because each carbon atom forms only single bonds (C–C) and is bonded to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible.
- Since their carbon atoms are fully “saturated” with hydrogen, no more atoms can join unless a bond is broken.
- This is why alkanes are not very reactive and do not react with bromine water or undergo addition reactions.
Why are Alkenes Unsaturated Hydrocarbons?
- Alkenes are called unsaturated hydrocarbons because they contain at least one double bond (C=C) between carbon atoms.
- The double bond means that more atoms can join the molecule without breaking existing single bonds.
- This makes alkenes more reactive than alkanes.
- They react with bromine water, which turns from orange to colorless, and can undergo addition reactions.
How do Alkenes React with Bromine?
- The reaction in which an alkene reacts with bromine is called an addition reaction.
- The double bond in the carbon molecule breaks, and each carbon atom bonds to one bromine atom, forming a saturated compound.
- This happens because alkenes are more reactive due to their double bond, which easily opens to add new atoms.
Example:
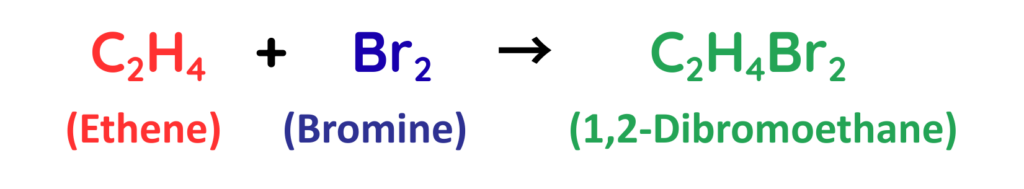
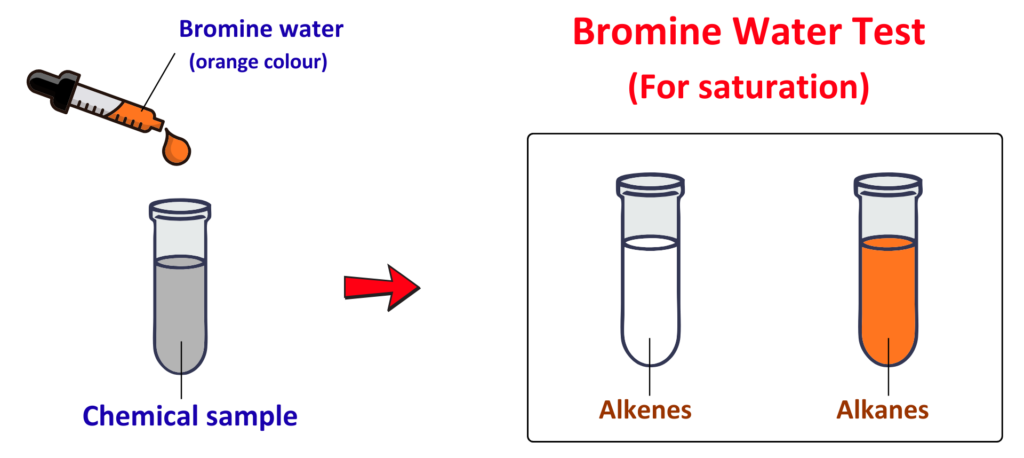
How does Bromine Water Test distinguish Alkanes and Alkenes?
- Bromine water test is a simple way to distinguish between alkanes and alkenes.
- Bromine water is orange-brown in color.
Working/Procedure:
- Take two test tubes — one with an alkane and one with an alkene.
- Add a few drops of bromine water to each test tube.
- Gently shake or stir both tubes.
Result:
For Alkanes:
- Do not react with bromine water because they are saturated hydrocarbons.
- The orange color stays the same.
For Alkenes:
- Undergo an addition reaction with bromine water because they are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- The orange color turns colorless.
How Do Hydrocarbons Undergo Combustion?
- Both alkanes and alkenes burn in oxygen in a reaction called combustion.
- This reaction releases energy as heat and light, which is why hydrocarbons are widely used as fuels.
1. Complete Combustion:
- Hydrocarbons burn completely when there is enough oxygen.
- In this process, the carbon and hydrogen atoms are oxidised, forming carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
Example:
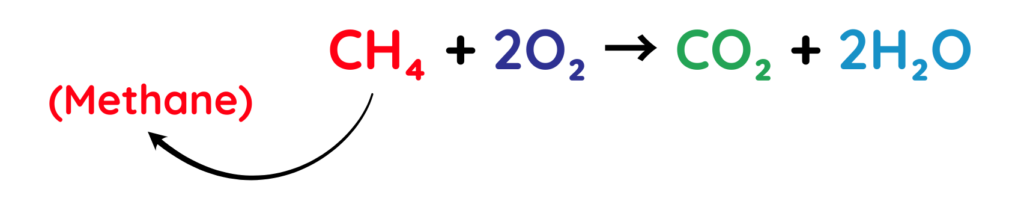
2. Incomplete Combustion:
- Hydrocarbons burn incompletely when there is not enough oxygen.
- In this process, carbon monoxide (CO) is formed instead of carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Example:
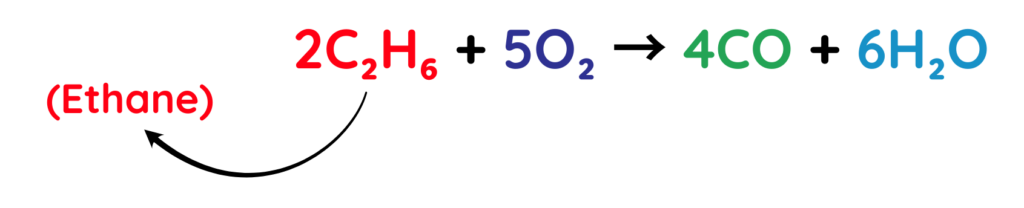
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
- Hydrocarbons are compounds made only of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- They are the basic fuels like methane and petrol.
- Example: CH₄ is the simplest hydrocarbon.
Solution:
- Alkanes contain only single bonds between carbon atoms.
- This means no more atoms can be added, so they are called saturated.
- Example: Ethane (C₂H₆).
Solution:
- Alkenes contain a C=C double bond, which can open and add more atoms.
- Because they are not fully bonded with hydrogen, they are unsaturated.
- Example: Ethene (C₂H₄).
Solution:
The double bond in alkenes breaks open during the reaction. Bromine atoms add across the double bond, forming a colourless product.
Solution:
- Alkenes decolourise brown bromine water because they react with it.
- Alkanes do not react, so the brown colour stays the same.
Solution:
Hydrocarbons burn in oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. This reaction releases heat energy, which is why fuels are useful.
Solution:
Alkanes burn completely when oxygen is enough. This produces a blue, clean flame with no smoke.
Solution:
Alkenes burn less completely because of their double bond. This forms carbon particles, which give a yellow, smoky flame.
Solution:
Alkanes follow the formula CₙH₂ₙ₊₂. This fits all single-bonded hydrocarbons like methane and ethane.
Solution:
Alkenes follow the formula CₙH₂ₙ. This matches hydrocarbons with one double bond such as ethene and propene.

