Find The Exact Value of The Trigonometric Function – GCSE Maths
Introduction
- In GCSE Maths, you’re often asked to find sin, cos, or tan of specific angles without a calculator. These specific values are called exact trigonometric values.
- Exact trigonometric values refer to the known and precise values of sine, cosine, and tangent for specific standard angles, without using a calculator.
- These values are written as fractions or square roots, not rounded decimals.
- We study exact trigonometric values to solve non-calculator GCSE exam questions accurately.
Example:
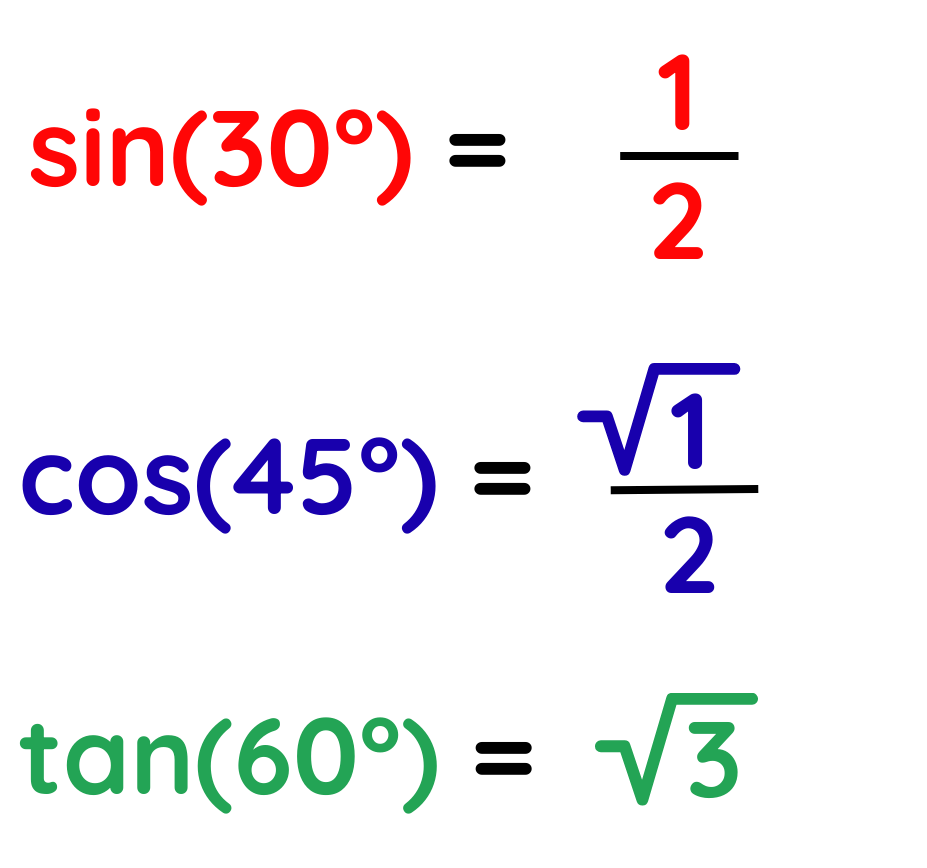
Table of Exact Trigonometric Values
- If we need to calculate exact values of sin, cos, or tan for special angles like 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, or 90°, there’s no need for a calculator.
- We can use a simple trigonometric values table that shows all the exact answers using fractions and square roots.
Let’s draw and understand the full table step by step:
- First, we will find the value of sine, because using the sine values, we can also find the values of functions like cosine and tangent.
- So, to start with this, first we will take the sine value and its corresponding angle on one side. Now, for each angle, we will take a number from 0 to 4, find its square root, and then divide it by 2, like-
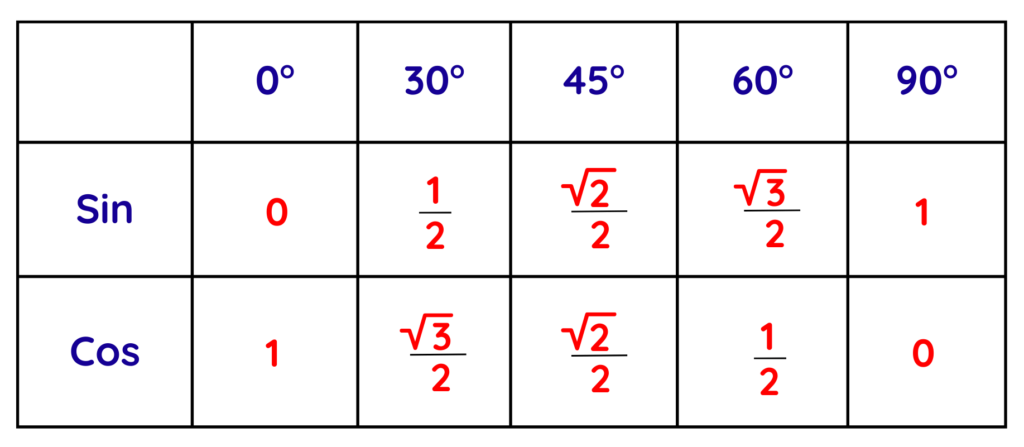
- After solving these values, we will get the sine values for each angle.
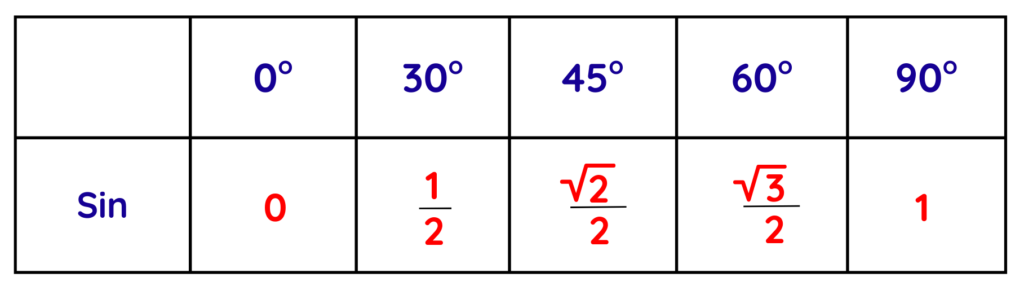
- The cos values are just the reverse order of sine values.

- Now, to find the value of tan, we will again use a method similar to sine. First, we will take the same numbers and find their square roots, but this time, instead of dividing by 2, we will divide by the reverse of these numbers.
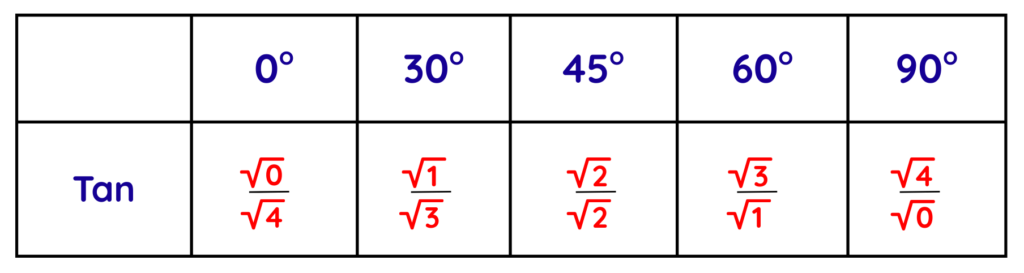
- After solving these values, we will get the tan values for each angle and tan(90°) is undefined because there is division by zero, which is mathematically impossible.
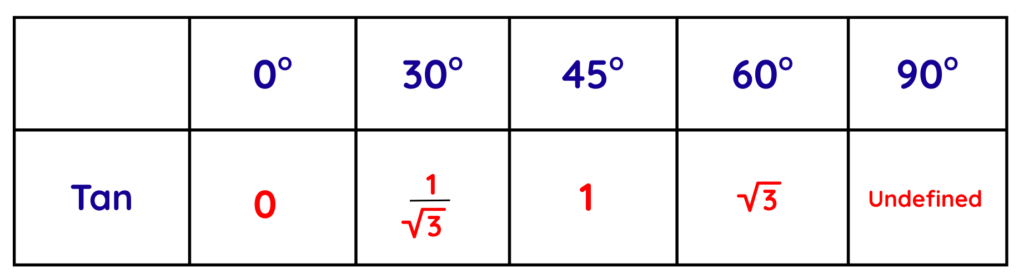
- The final exact trigonometric table is:

Using Exact value with SOHCAHTOA
- SOHCAHTOA is also a way to remember how sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan) relate to the sides of a right-angled triangle.
SOH-CAH-TOA Stands For –
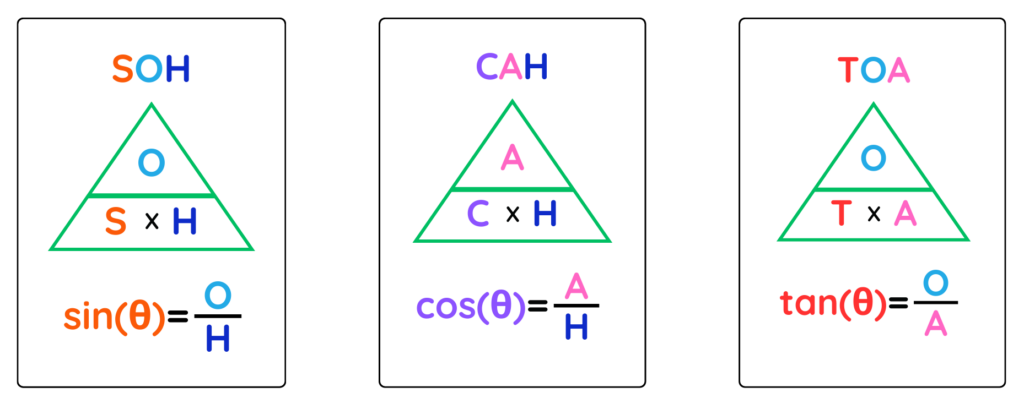
Note: To Learn more about SOH-CAH-TOA, please click on the link: How to Use SOHCAHTOA
Steps to Find Missing Side or Angle by SOHCAHTOA (Using Exact Trig Values):
- Step #1: Identify the Trigonometric function from given values.
- Step #2: Plug the known values into the formula.
- Step #3: Solve it.
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Find the length of the opposite side if the angle θ = 30° and the hypotenuse = 8.
Solution:
Step #1: Identify the Trigonometric function.
Given
- Angle = 30°
- Hypotenuse = 8
We will use,

Step #2: Plug the known values into the formula.

Step #3: Solve it.

Now,
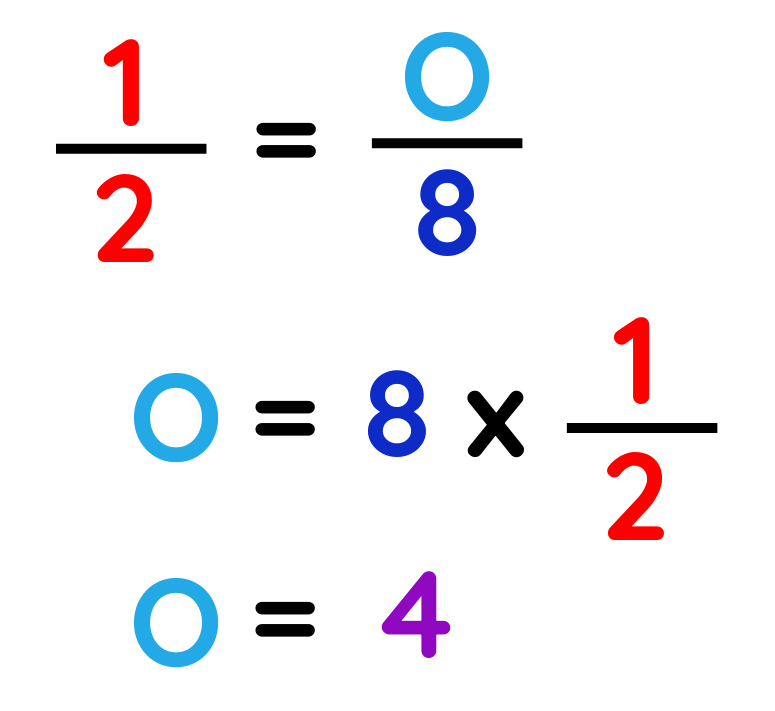
Final Answer: 4
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Find the adjacent side if the angle θ = 60∘ and the hypotenuse = 10.
Solution:
Step #1: Identify the Trigonometric function.
Given
- Angle = 60°
- Hypotenuse = 10
We will use,
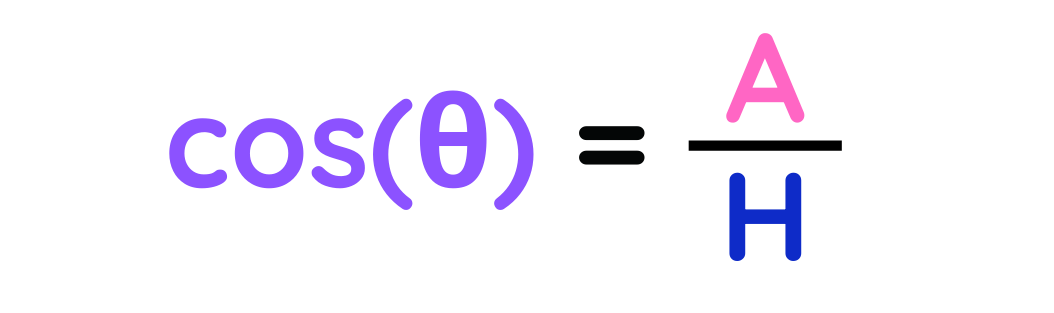
Step #2: Plug the known values into the formula.

Step #3: Solve it.
Using exact trigonometric table,

Now,
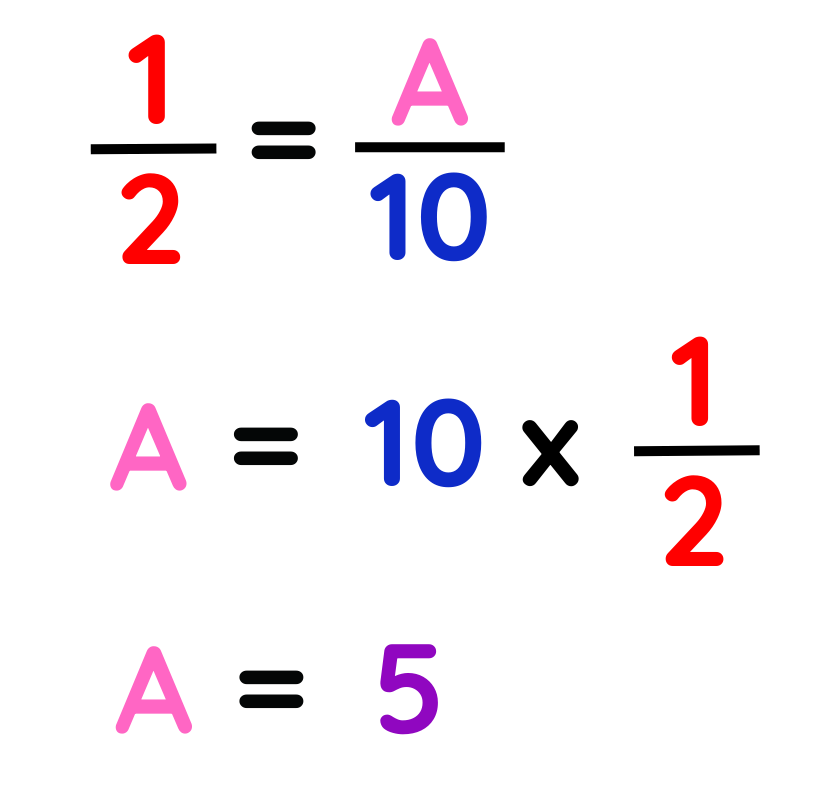
Final Answer: The adjacent side = 5 units
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Find the angle θ if the opposite side = 5 and the adjacent side = 5.
Solution:
Step #1: Identify the Trigonometric function.
Given
- Opposite side = 5
- Adjacent side = 5
We will use,

Step #2: Plug the known values into the formula.
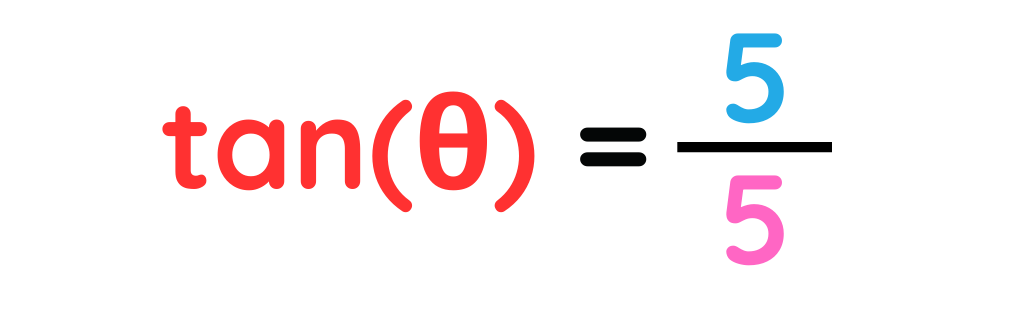
Step #3: Solve it.
Using exact trigonometric table,

We know:
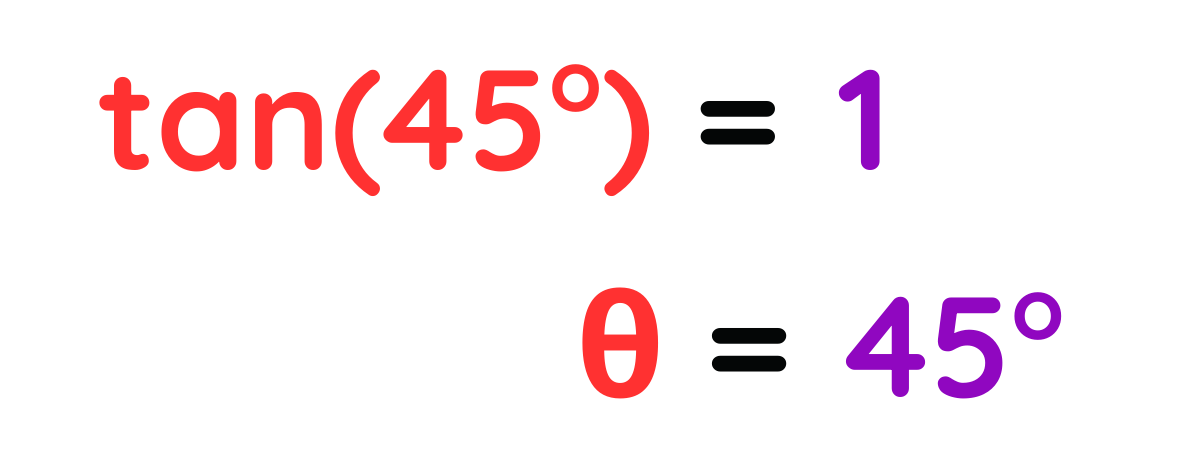
Final Answer: The angle θ = 45°

