Acids – GCSE Chemistry
Introduction
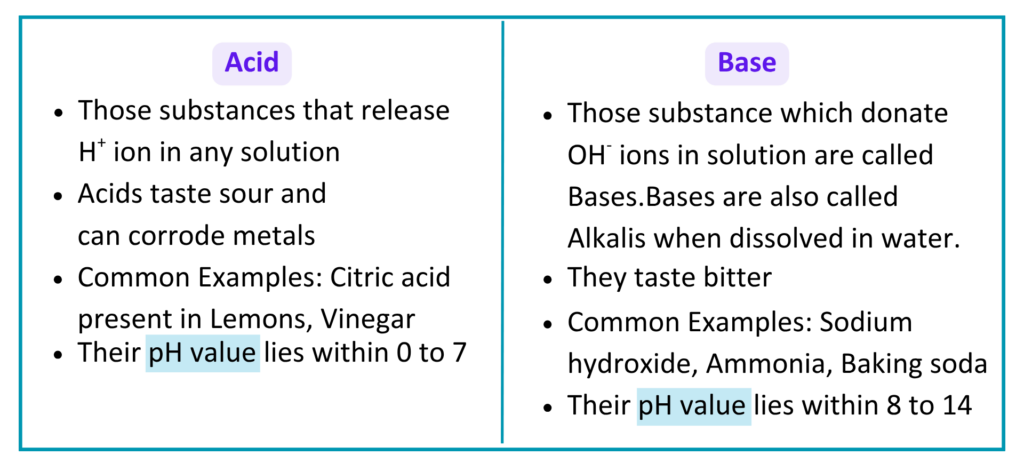

What are Acids and Base?
ACIDS
- An Acid is a substance that releases H+ ions in water. Acids usually have sour taste and can turn blue litmus paper into red.
Examples:

Base
- A base is a substance that releases OH⁻ (hydroxide) ions in water. Bases usually have a bitter taste, feel soapy, and turn red litmus paper blue.
Examples:

Uses of Acids
- The carbonic acid gives fizz to soda drinks.
- Acetic acid(vinegar) is used for pickling.
- HCl is used for concrete cleaning and for pool PH adjustment.
- Acids are also used in batteries and metal works.
Uses of Bases
- The soap and detergent products contain Sodium hydroxide(base).
- Ammonia is common household cleaner and fertilizer raw material.
- Calcium Hydroxide(slaked lime) is used to soften water, to deal with acidic soil and is used in cement.
What is pH Scale and How it is measured?
- pH Scale is a numerical scale that is used to measure how acidic or basic a substance is. This scale’s value ranged from 0 to 14-
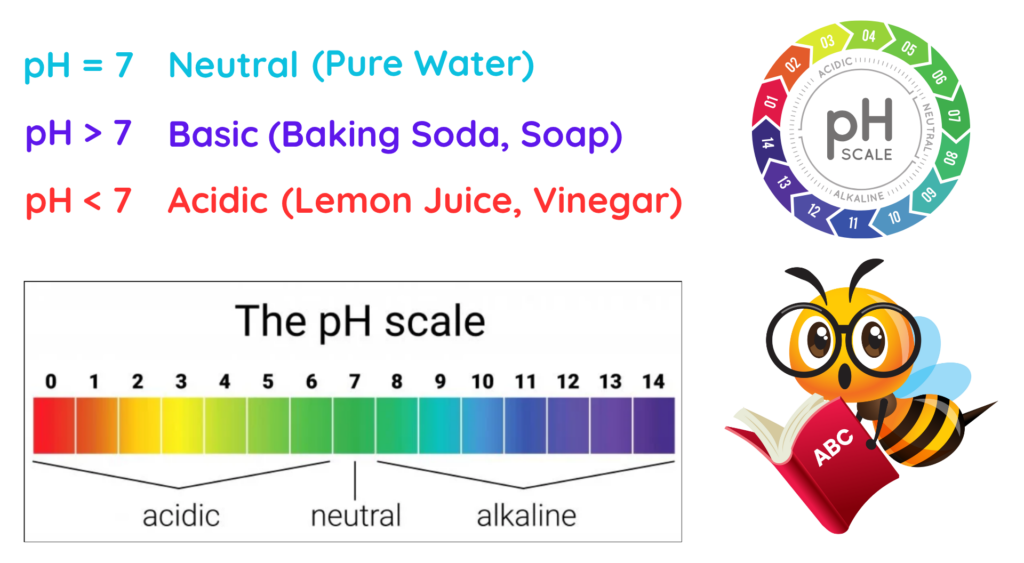
Fact: Bee stings are acidic and has pH between 5 and 5.5
Formula to find the pH of any solution
- The pH of any substance is a measure of how much acidic or a basic that substance is. The formula to measure pH is –

Where, [H+] is the concentration of Hydrogen ions in (Moles per Liter or M)
Steps to calculate PH
- Find the H+ concentration, for strong acids like HCl (Hydrochloric acid). The concentration of acid equals the concentration of H+ ions.
- For weak acids and bases you may need to use an equilibrium expression or the Ka (Acid Dissociation constant).
Example:
Calculating PH Values
- HCl (Hydrochloric Acid) is a strong acid(dissolves completely)
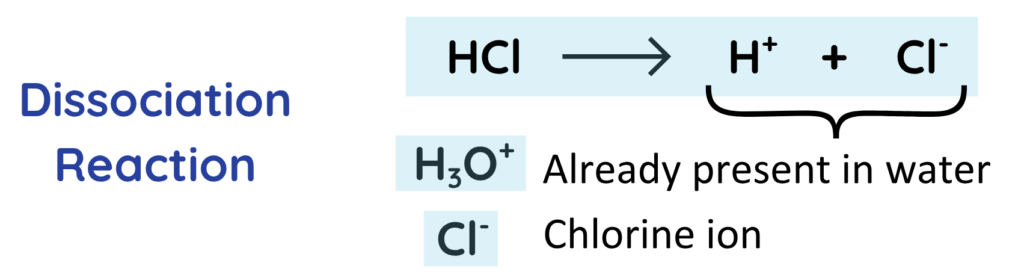
- This reaction is responsible for the acidic nature of Hydrochloric Acid
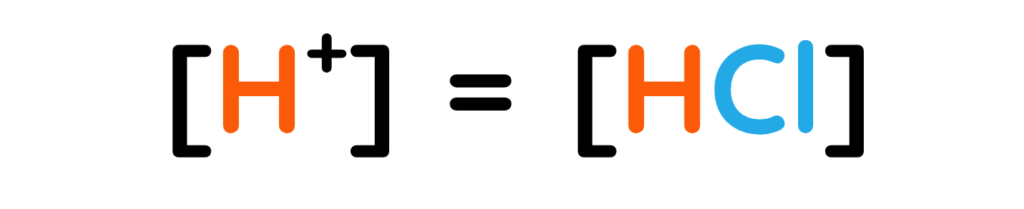
The concentration of Hydrogen ions is same as the concentration of Hydrochloric acid.
- If [HCl] = 0.001M
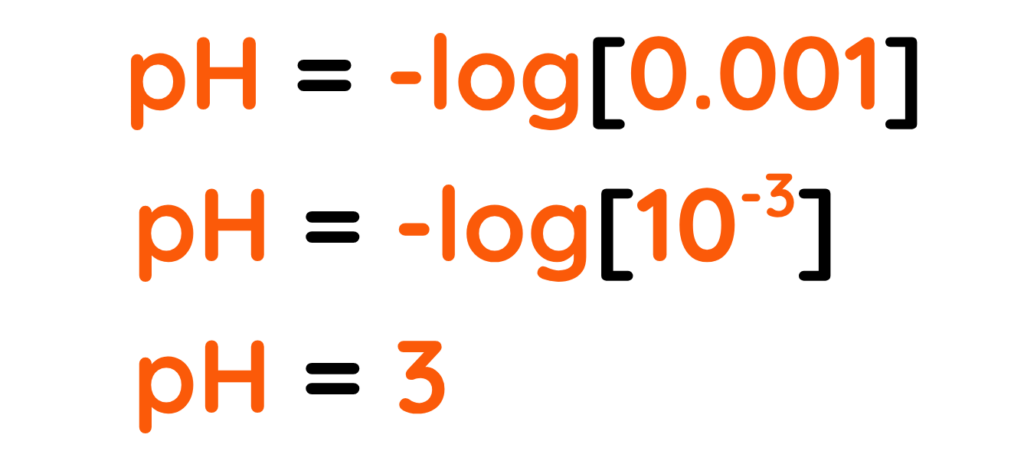
Concept of Dilute and Concentrated Solution
Dilute or Concentrated ≠ Acidic or Basic
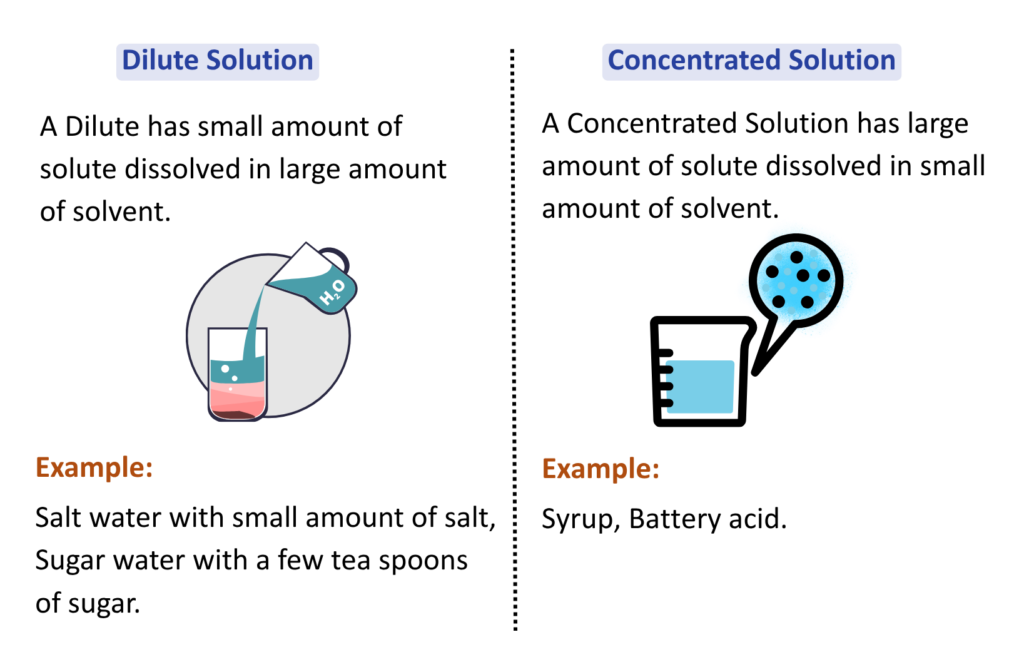
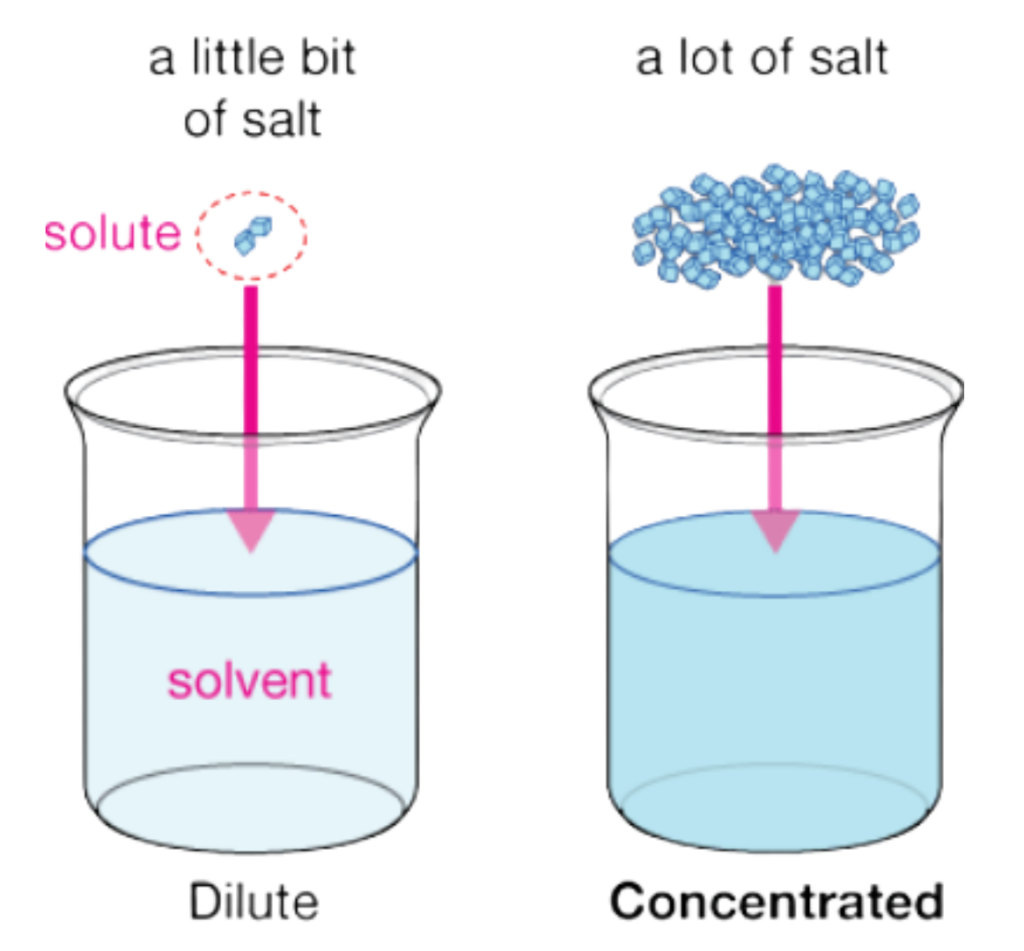
- The terms Dilute and Concentrated describe the amount of solute dissolved in a given quantity of solvent, not the chemical strength or nature of the solute.
- In brief: A Small amount of solute in a large amount of solvent.
- Concentrated Solution: A Large amount of solute in a smaller amount of solvent. These terms tell us how much solute is present, but not how weak or strong the solute is in terms of chemical behaviour.
Examples to Clarify
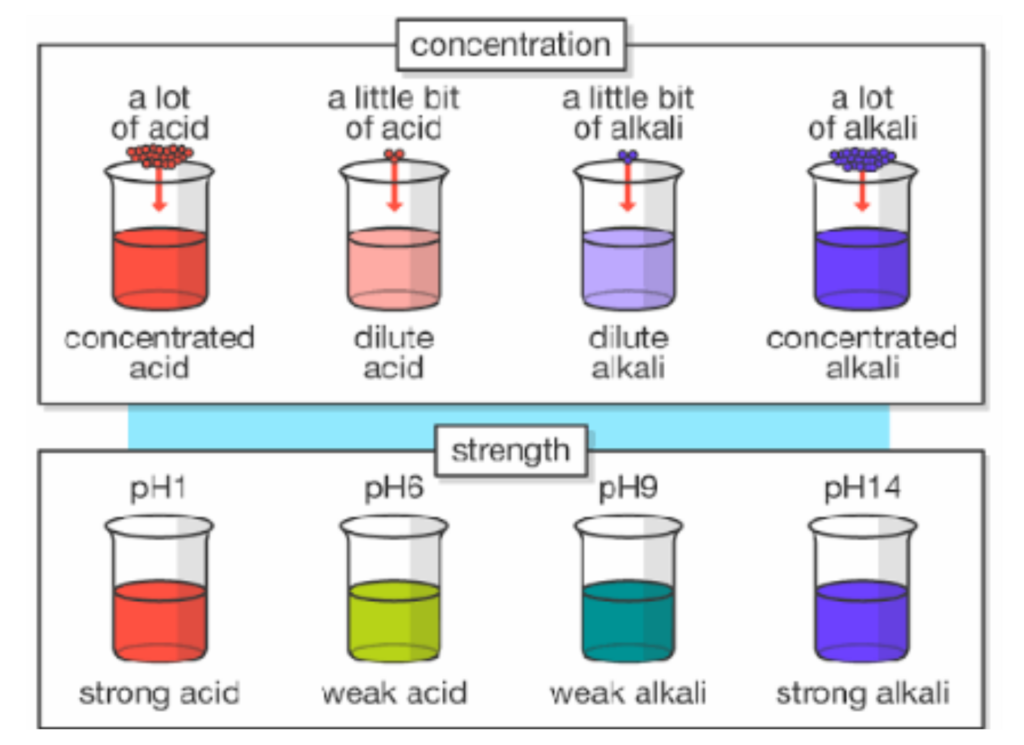
- Dilute Acid: Small amount of Hydrochloric acid in large amount of water. Still an acid but weak and not dangerous.
- Concentrated Acid: A large amount of HCl in little amount of water. Still an acid but stronger and much corrosive.
- Dilute Base: A small amount of Sodium Hydroxide(NaOH) in water. Still a base but mild.
Examples of Acid and Base Reaction
- The reaction between Acid and base is called Neutralisation reaction. Often when an acid and base react salt and water is formed.
Examples
- Hydrogen Bromide reacts with Potassium Hydroxide to form water and Potassium Bromide. Potassium Bromide is formed from the K+ ions from the base(KOH) and OH– ions from the acid HBr.

- Hydrochloric acid reacts with Ammonia to form Ammonium Chloride(salt). Ammonium Chloride is made up of NH4+ cations from the base NH3 and Cl– anions from the acid HCl.

Some Uses of Acid Base Reactions

- Let us discuss some specific types of Acid Base reaction in which type of base used changes and acid remains the same –
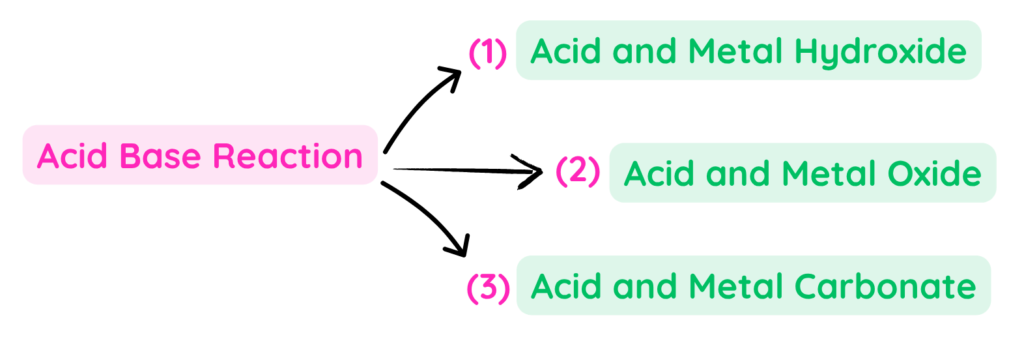
1. Acid and Metal Hydroxide:
- When an Acid reacts with metal hydroxide, a salt and water are formed. These are a type of double displacement reactions.
Examples
- Hydrochloric acid reacts with Sodium Hydroxide to form Water and Sodium Chloride.

- Here, Hydrochloric Acid reacts with Aluminium Hydroxide to from Water and Aluminium Chloride.
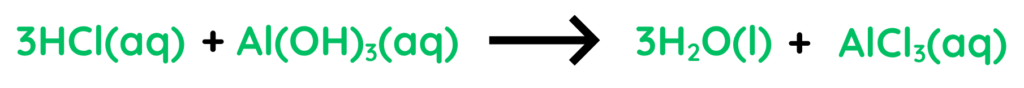
Properties
- It is an Exothermic reaction.
- The reaction do not produce any gas.
- Both soluble and insoluble metal hydroxides can react with acids.
2. Acid and Metal oxide:
- When an Acid reacts with metal oxide, a salt and water are formed.
Examples
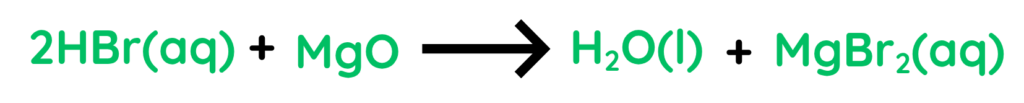
- Reaction of Hydrogen Bromide and Magnisium oxide gives us Water and Magnisium Bromide.
- Hydrochloric Acid reacts with Aluminium Oxide and forms Water and Aluminium Chloride.
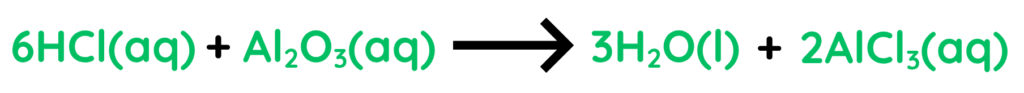
Properties
- It is an Exothermic reaction.
- The reaction do not produce any gas.
3. Acid and Metal Carbonates:
- When an Acid reacts with metal carbonate, Carbon Dioxide and Water are formed.
Examples
- Nitric Acid reacts with Sodium Carbonate and forms Nitrate, Carbon dioxide and water.

- Sulfuric acid reacts with Sodium carbonate to form Nitrate, Carbon dioxide and water.

Properties
- The reaction is mildly Exothermic.
- In the reaction of acid and carbonates the CO2 gas is produced. The gas can be tested by passing it through limewater which turns milky/cloudy if there is CO2.
Formation of Water from its ions
- We know that Water(a compound) consists of two elements, Hydrogen and Oxygen (constituents).
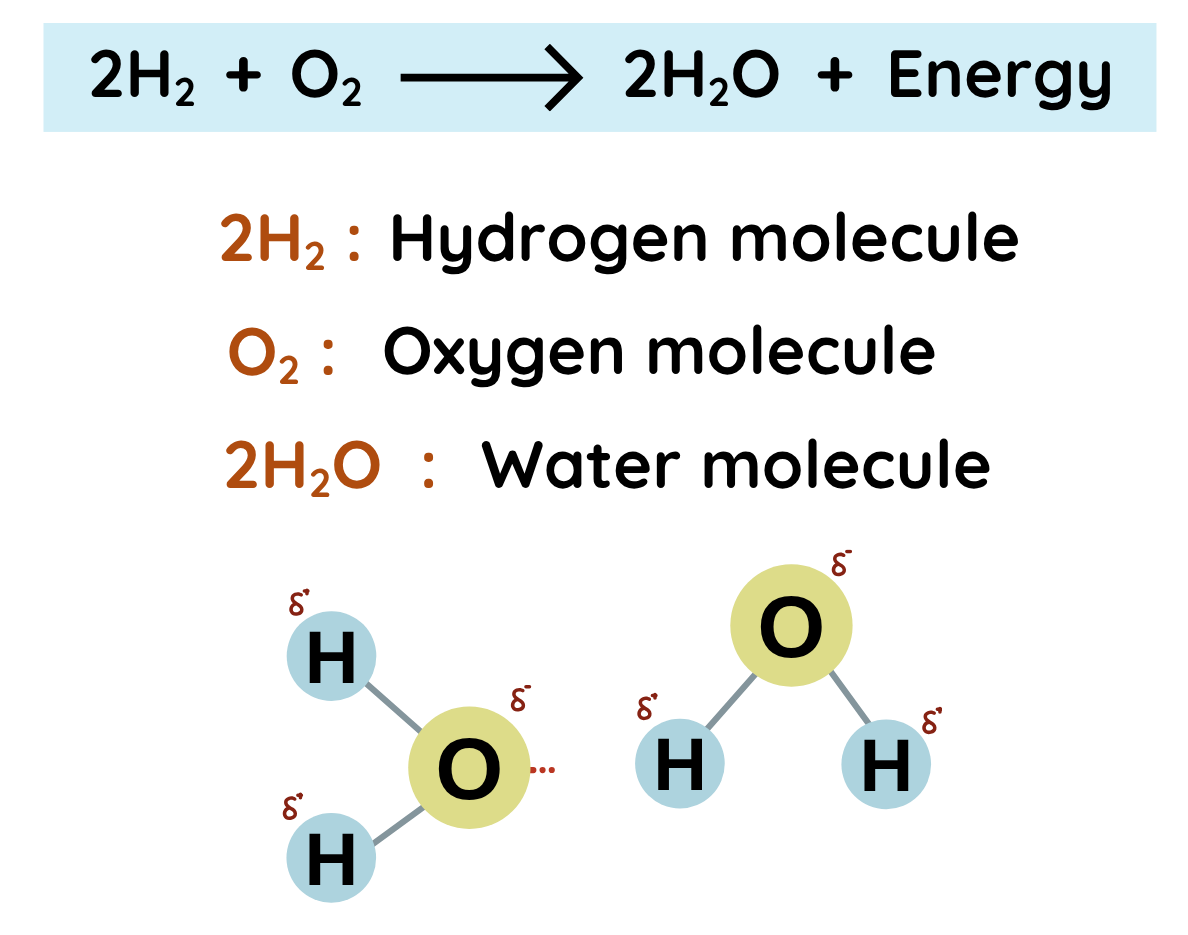
Activation Energy:
- The energy required to reach at the stage of breaking bonds within Hydrogen and Oxygen Molecules.
Bond Breaking:
- The energy required to break the bonds present in reactants.
Energy Release:
- Energy is released in the form of Water and Light, and that is why Hydrogen is used as fuel in rocket
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Acids donate H+ ions on the other hand bases donate OH– ions when dissolved in a solution.
Solution:
It is the reaction of Acid and Base and is called neutralisation reaction as the ions from acid and base combine and form water.
Solution:
Maintaining the PH level is crucial for proper functioning of many systems in our everyday life including human body.
Solution:
pH = – log+10[H+]
Solution:
The concept of dilute and concentrated solution tells us how much strong an acidic or basic solution is.

