Stem Cells - GCSE Biology
Introduction
- Cells with the ability to divide repeatedly to produce more similar cells that also differentiate are called stem cells.
- These are unspecialized, that is, they do not have a specific function.
- They give rise to cells that specialize in different functions.
- For example, stem cells develop into pancreatic cells and help in digesting sugar.
- Another example, cells in the lungs are designed to exchange gases.
Real-life Examples

Where are Stem Cells Found?
- Stem cells are found in both plants and animals.
- In plants, stem cells are present in meristems.
- It includes the regions of apical meristem (root and shoot), lateral meristem (sides of stem and root), and intercalary meristem (base of leaves and internodes).
- In animals, these cells are found in early-stage embryo and are called embryonic stem cells.
- Apart from this, these can be observed in most adult tissues, known as adult stem cells.
What are the Functions of Stem Cells?
- The major functions of stem cells are – Differentiation, tissue growth, and repair.
- Stem Cells differentiate into specialized cells in both plants and animals.
- After growth, they are found as adult stem cells that, in humans, allow tissue growth.
- Cells that get old or are damaged need replacement. Stem cells replace these cells to repair the tissue.
Advantages of Using Stem Cells in Medicine
- Diseases caused by damaged cells can be treated using stem cells.
- Treatment of diseases such as type I diabetes. E.g., Bone marrow transplantation to cure a blood disease.
- Study of stem cells can help appropriate drug development for humans.
- With this, there is no need to test drugs on humans, as can be done in lab settings.
- For example, testing on transparent young zebrafish.
Risk of Using Stem Cells In Medicine
- Continued division after replacement of damaged cells can lead to cancer.
- Using stem cells to treat a disease involves putting them in the body of the patient. The immune system of the body usually kills these cells.
- The reason the immune system kills these cells is that they are treated as foreign particles.
- It is known as rejection.
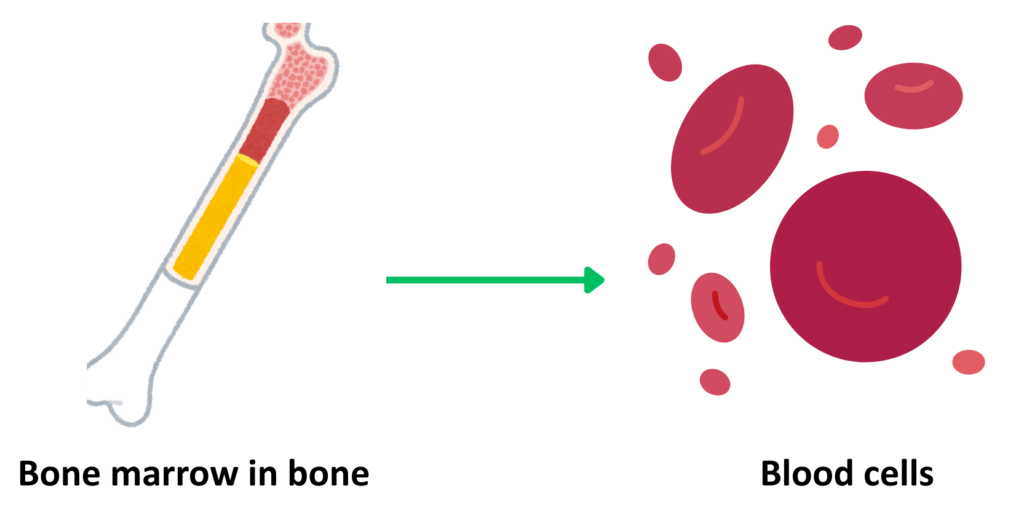
Function of Stem Cells in Bone Marrow
- Stem cells are present in the middle of those bones in the body that are long, like the femur.
- During their whole life, they divide continuously and produce new blood cells.
- Stem cells can only give birth to those specialized cells that are in the tissue surrounding them.
- Since blood stem cells are found in bone marrow and blood cells surround them, they produce blood cells only.
Comparison of Adult Stem Cells with Embryonic Stem Cells
- Differences between Embryonic Stem Cells and Adult Stem Cells

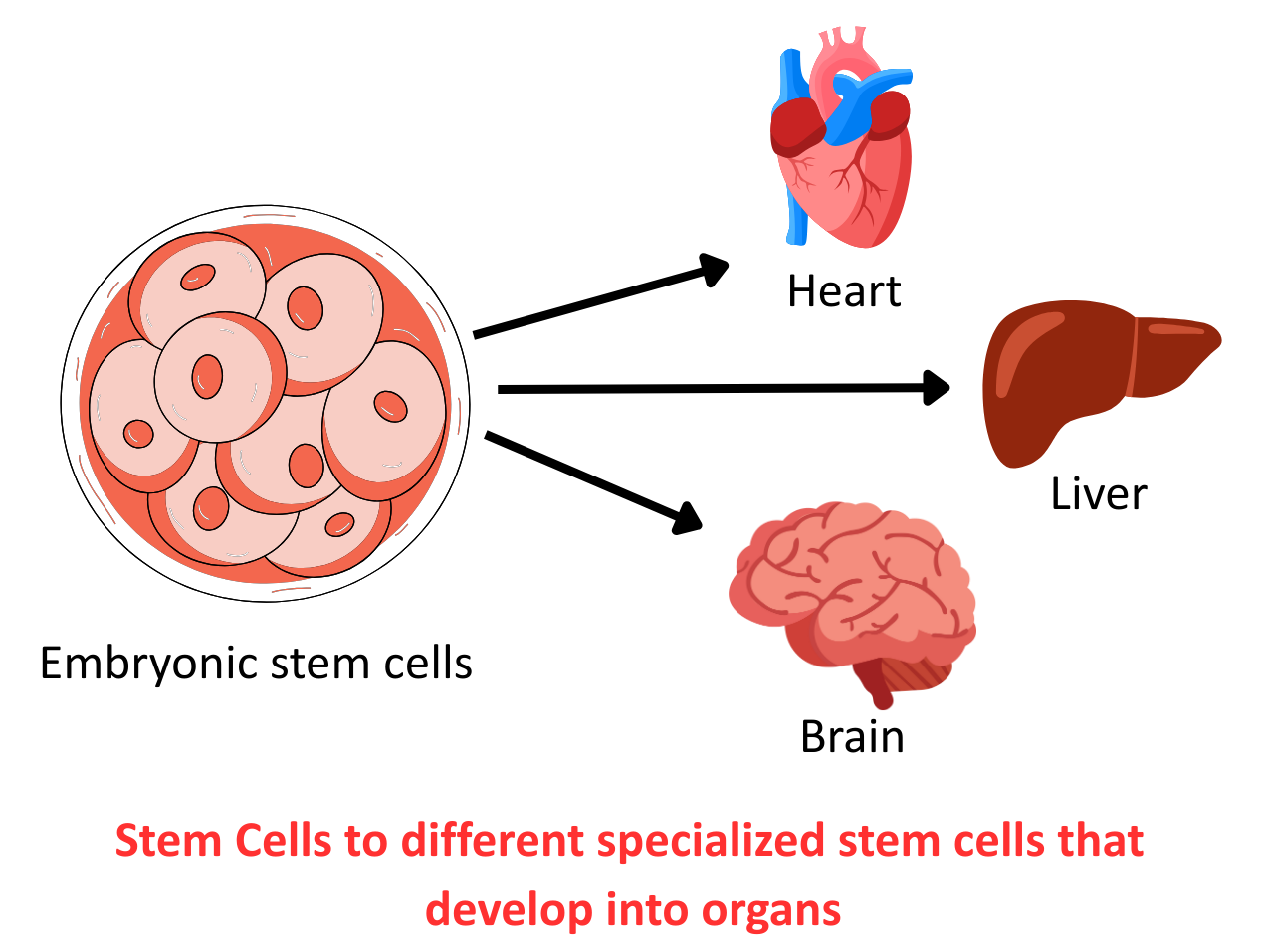
- Stem Cells to Different Specialized Stem Cells that Develop into Organs
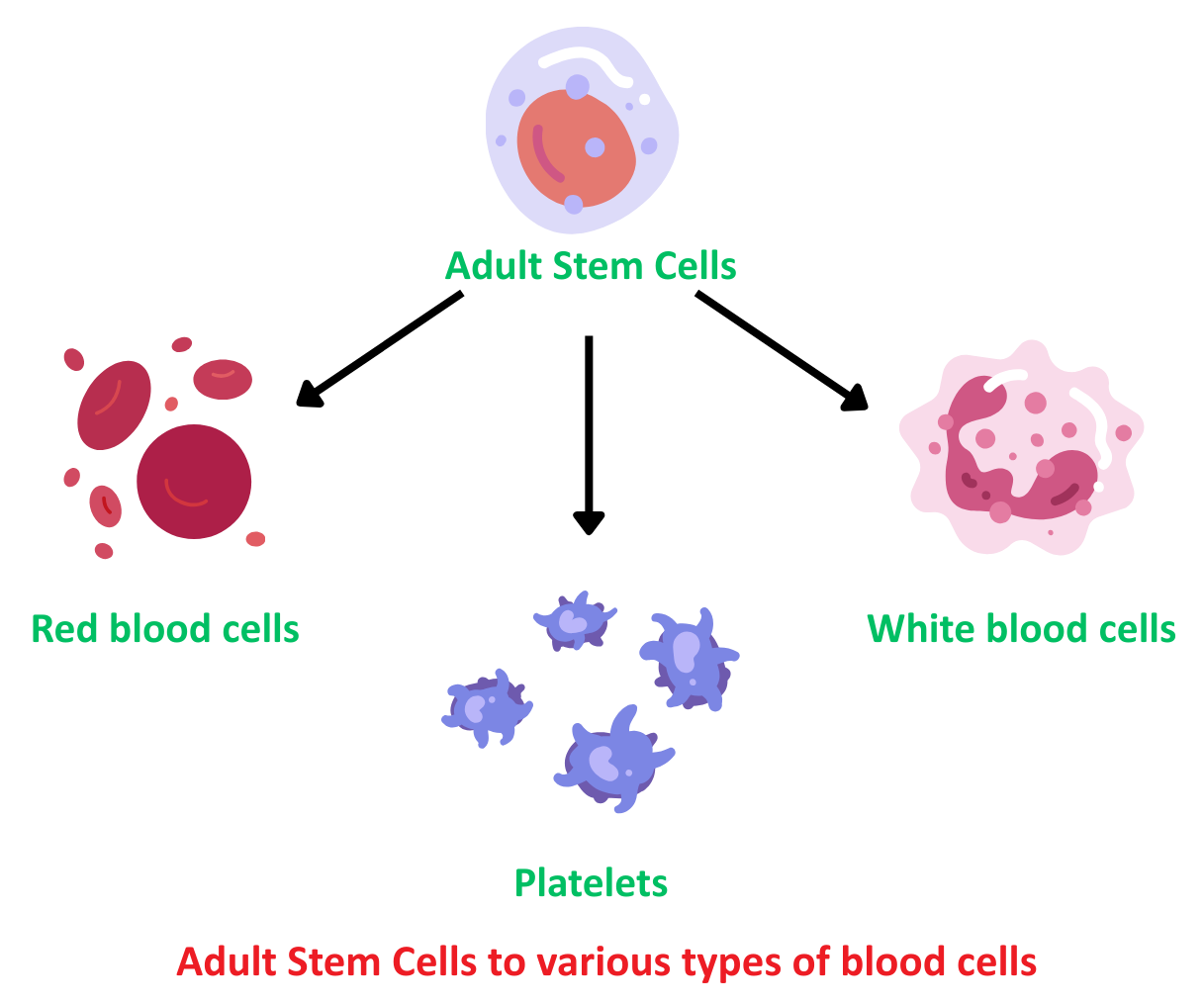
- Adult Stem Cells to Various Types of Blood Cells
Roles of Meristems in Plant Growth
- In plants, the roots and shoots are the areas where growth happens.
- Meristems are stem cells found in these regions.
- The cells in meristems divide continuously by mitosis.
- These take part in elongation as the length of the cells increases.
- Refer to 7.Plant Meristem Elongation in Cell Differentiation & Specialization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that undergo division to make more similar cells and differentiate into specialized ones.
Solution:
In animals, there are two types of stem cells. These include embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
Solution:
Stem cells are used for the treatment of diseases, replacement of damaged cells, and drug research.
Solution:
Usage of stem cells in medicine involves the risk of cancer and rejection by immune system.
Solution:
Adult stem cells are responsible for tissue growth and cell repair.

