Heat Energy Changes – GCSE Chemistry
Introduction
- Heat is the form of energy that flows from a hotter place to a cooler place, and in chemical reactions, the heat energy is absorbed or released based on the type of reaction.

- Thus, in Chemistry, the change in heat energy refers to the transfer of energy during a chemical reaction, and these energy changes must be read to understand how and why reactions occur, which falls under the branch of chemistry known as Thermochemistry.
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
HEAT TRANSFER:
- Transfer of thermal energy between two objects at different temperature.
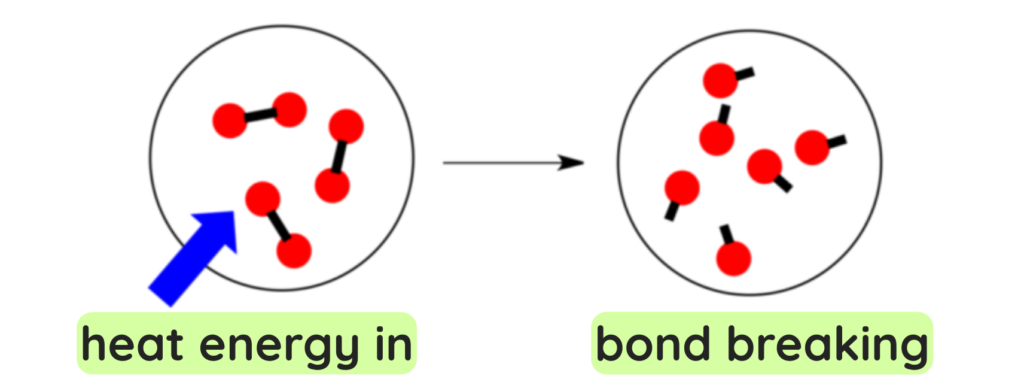
BREAKING OF BONDS (Endothermic):
- Atoms in a molecule are bound together by attractive forces and to break them we need to invest energy, thus this process is always Endothermic.
Example: Photosynthesis
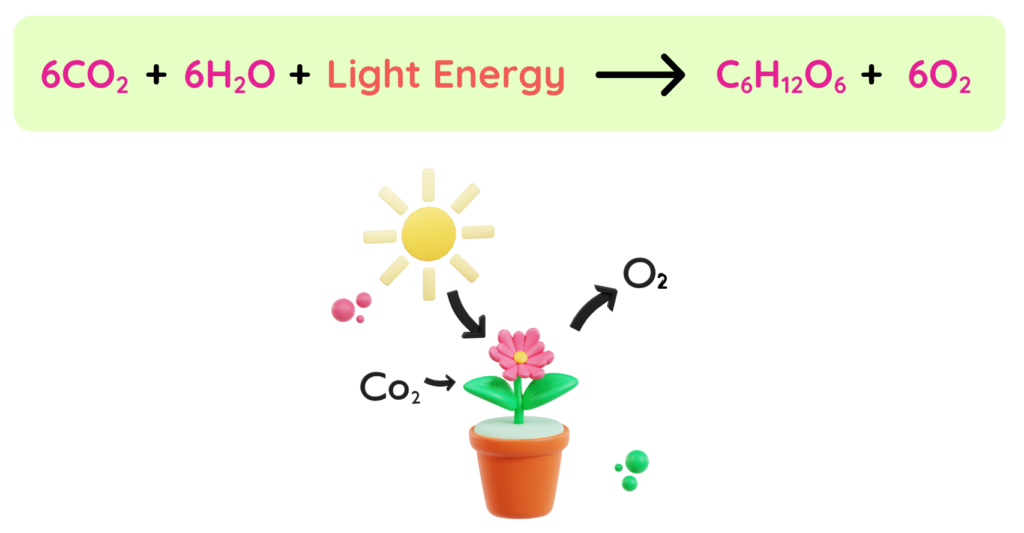
- Plants absorb light energy to convert Carbon dioxide and Water to Glucose. Here, the energy source is sunlight. The energy is used to break the bonds in 6C02 and 6H2O and to form the bonds in C6H12O6 and 6O2 .
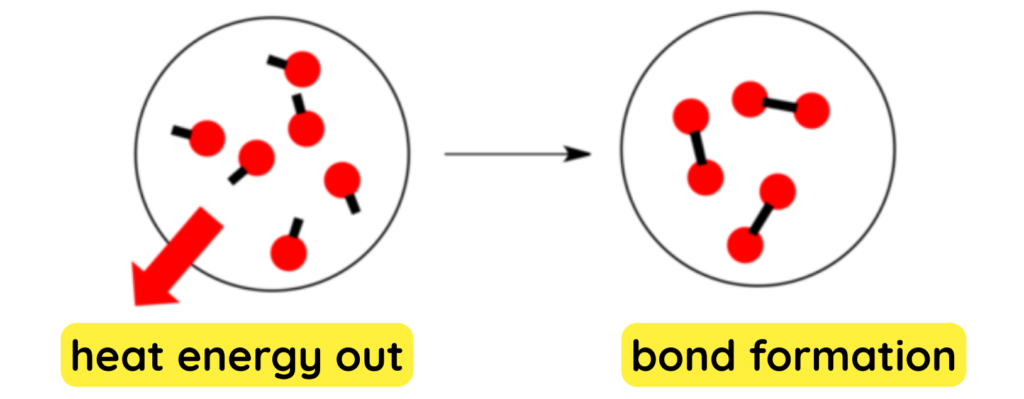
BREAKING OF BONDS (Exothermic):
- When atoms come together they settle into lower energy and the extra energy from the arrangement then is released to the surroundings.
Example: Wood
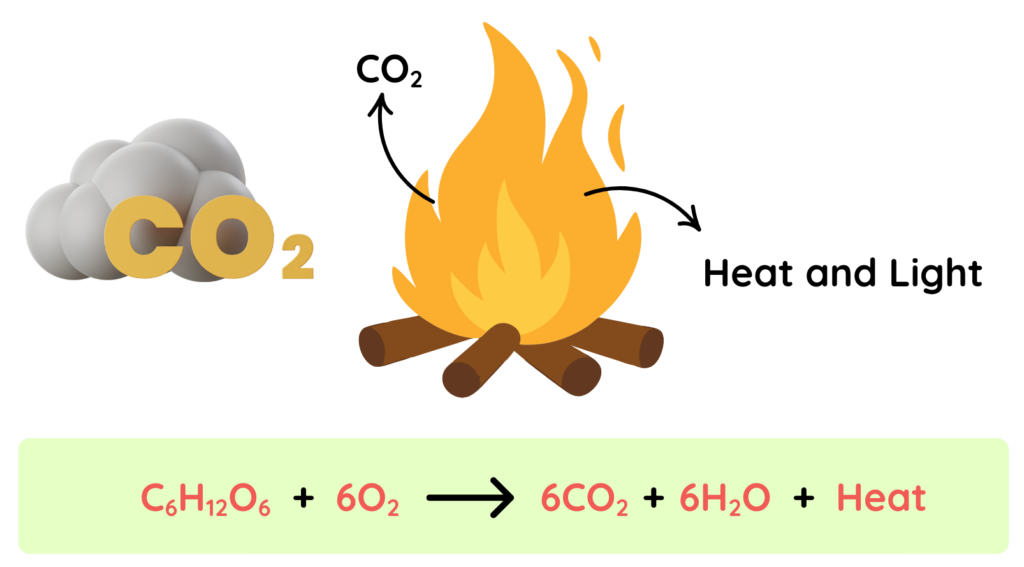
- Burning of wood is an irreversible chemical reaction, where wood reacts with Oxygen in the presence of heat and produce new substance like ash, Carbon dioxide, Water vapors and heat and light energy is released.
Net Energy Change: (ΔH)
- By calculating the net energy change in the chemical reaction, we can determine whether the reaction is Endothermic or Exothermic. The formula is given as –

- If ΔH is negative: Reaction is Exothermic
- If ΔH is positive: Reaction is Endothermic
- A reaction is called Exothermic if the energy released from breaking of bonds is greater than the energy required to form new bonds.
Examples:
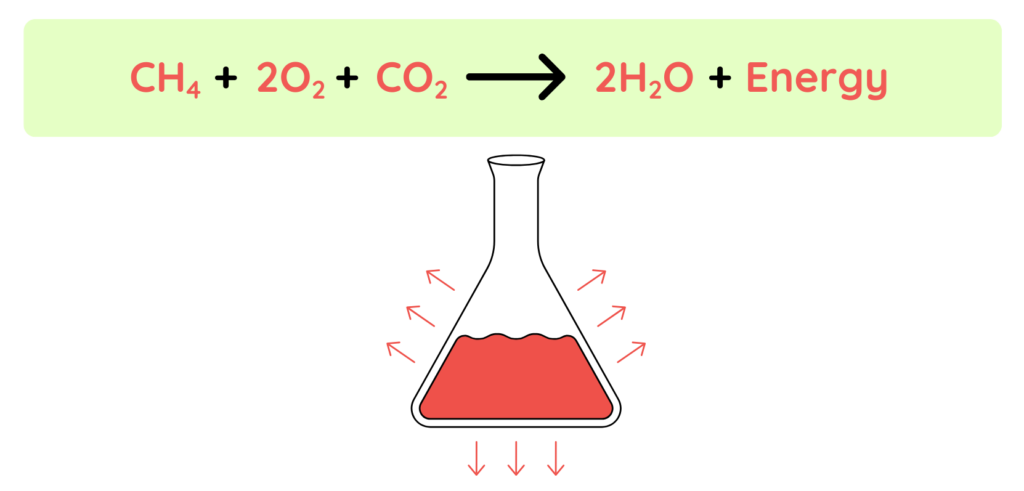
Energy release: -890 kj/mol
- As we can see it is given that the energy release is negative that means the reaction is Exothermic reaction.
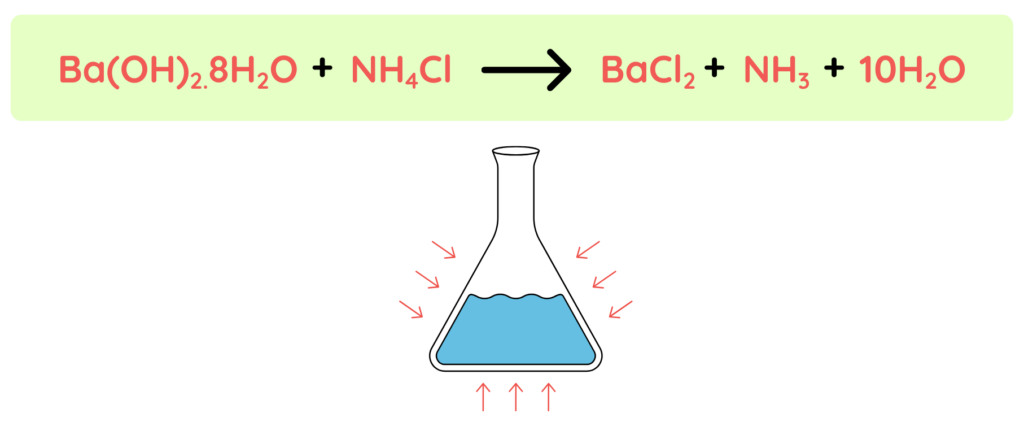
Energy absorbed: +30kj/mol
- As we can see it is given that the energy absorbed is positive that means the reaction is Endothermic reaction.
Enthalpy Change in terms of Activation Energy
- The minimum extra energy needed for reactants to reach the transition state and transfer into products in a chemical reaction, is called as Activation energy.
- Activation Energy(Ea)is crucial to determine how fast a reaction occurs.
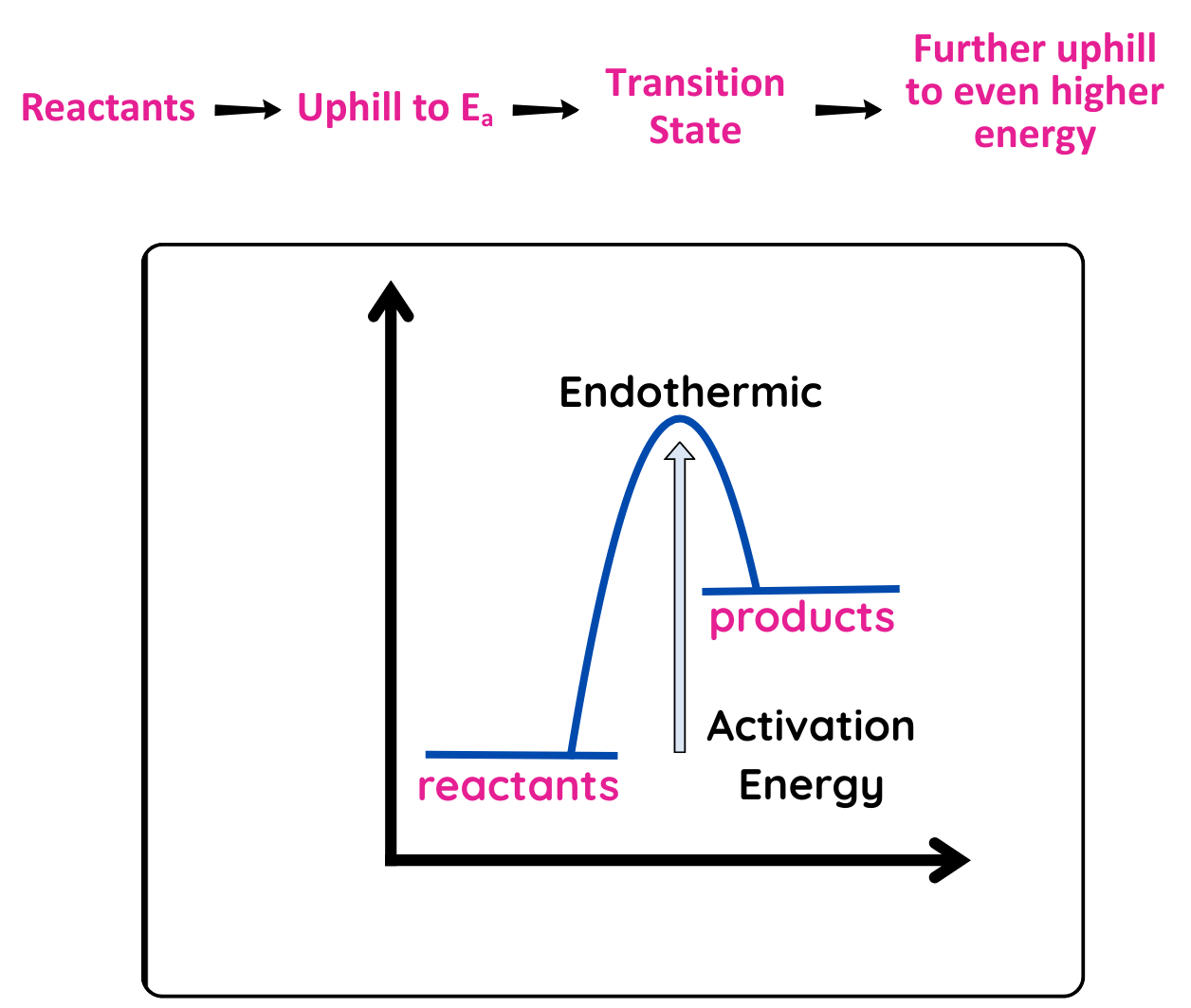
Endothermic Reaction (ΔH < 0):
- Release energy(products are lower in energy than the reactants)
- Ea: You still need to input energy to reach transition state, often supplied by heat. Once it reaches transition state, energy is released and the reaction continuous itself.
Energy Diagram:
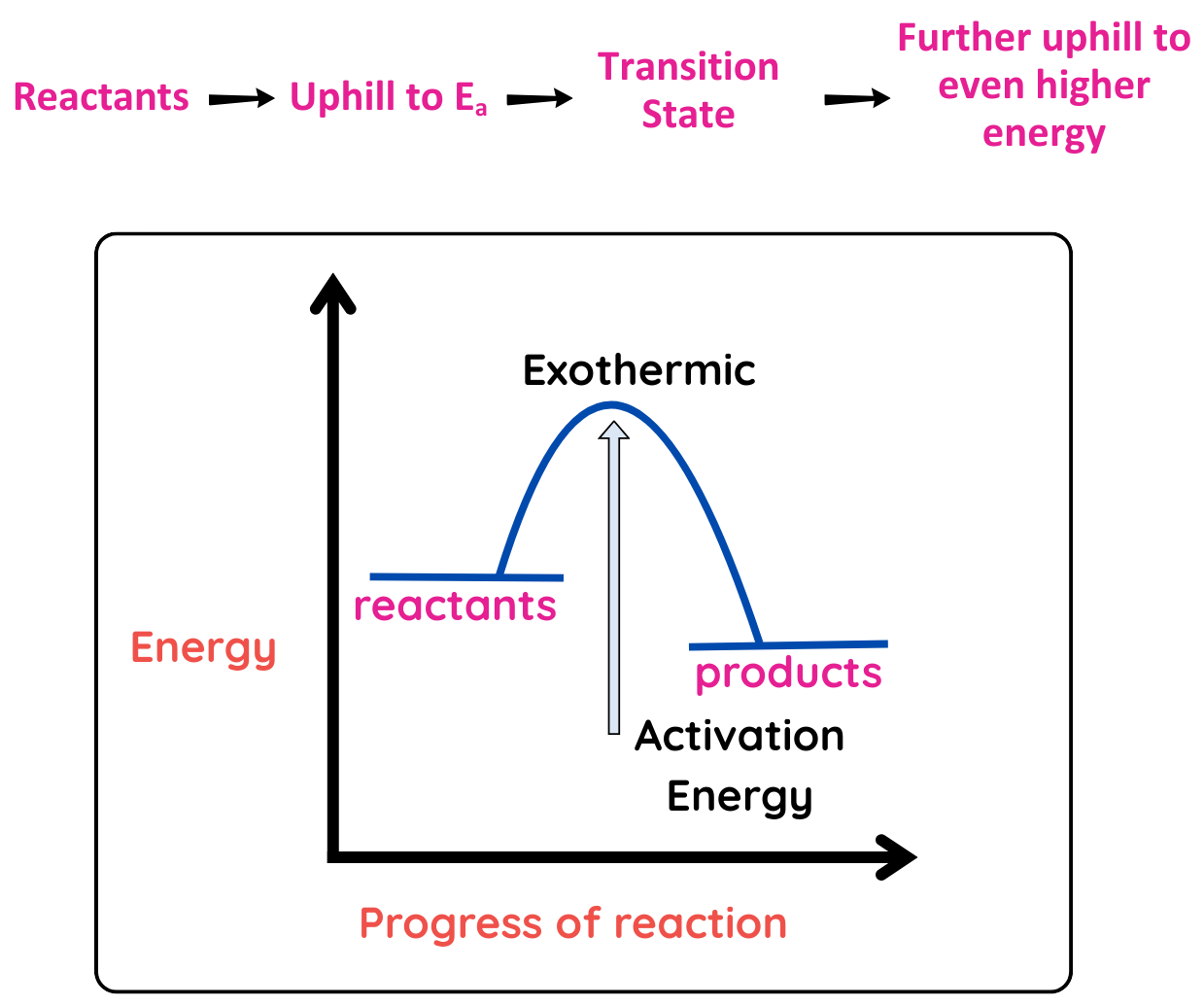
Exothermic Reaction (ΔH < 0):
- Absorbs energy (products are higher in energy than the reactants)
- Ea: You still need to input energy to reach transition state, often supplied by heat. Once it reaches transition state, energy is released and the reaction continuous itself.
Energy Diagram:
Real Life Examples
Example:
Explain the consequences of burning waste material used in daily life? Discuss the concept of recycling.

Answer:
- Here are a few examples of daily used materials: they include plastic bottles, Cans, and food. The major issue arises when our environment is polluted and these bottles or polyethene enter the food chain. Many animals like cows, dogs and cats use these materials as food, and eventually they die. Thus, our society must follow the rules and regulations of the government.
Recycling:
- Plastic water bottles and polyethene can reused in multiple ways where recycling becomes more reliable than to burn these wastes.

Frequently Asked Questions
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required for any reaction to occur. It is important because it determines how easily and quickly a reaction can happen. If Activation energy is lower it means the reaction can happen easily.
Heat energy change refers to the amount of heat released or absorbed during the reaction. It indicates weather the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
Activation energy of a reaction can be lowered by using a catalyst which provides an another way for reaction to occur in lesser energy required.
Examples of Endothermic reactions – Photosynthesis, melting ice, cooking an egg.
Examples of Exothermic reactions – Combustion, respiration.
Bond energy is the specific amount of energy required to break a bond and Activation energy is the amount of energy required for any reaction to occur. The key difference is that bond energy relates to individual bond but activation energy refers to overall energy barrier for a reaction to occur.

