Electromagnetic Induction – GCSE Physics
Introduction
- Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electric current by changing the magnetic field around a conductor.
- This fundamental concept links electricity and magnetism and was first discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831.
What Happens in Electromagnetic Induction?
- When a wire or coil is placed in a changing magnetic field, or if a magnet moves near the coil, it causes electrons in the wire to move. This movement of electrons creates an electric current. This is known as induced current, and the voltage produced is called “Induced Electromotive Force (EMF)”.
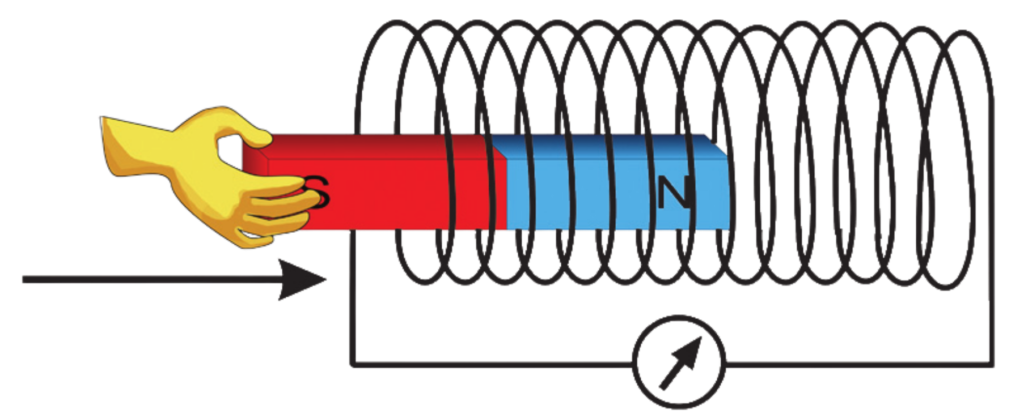
How Induction Occurs in Electromagnets?
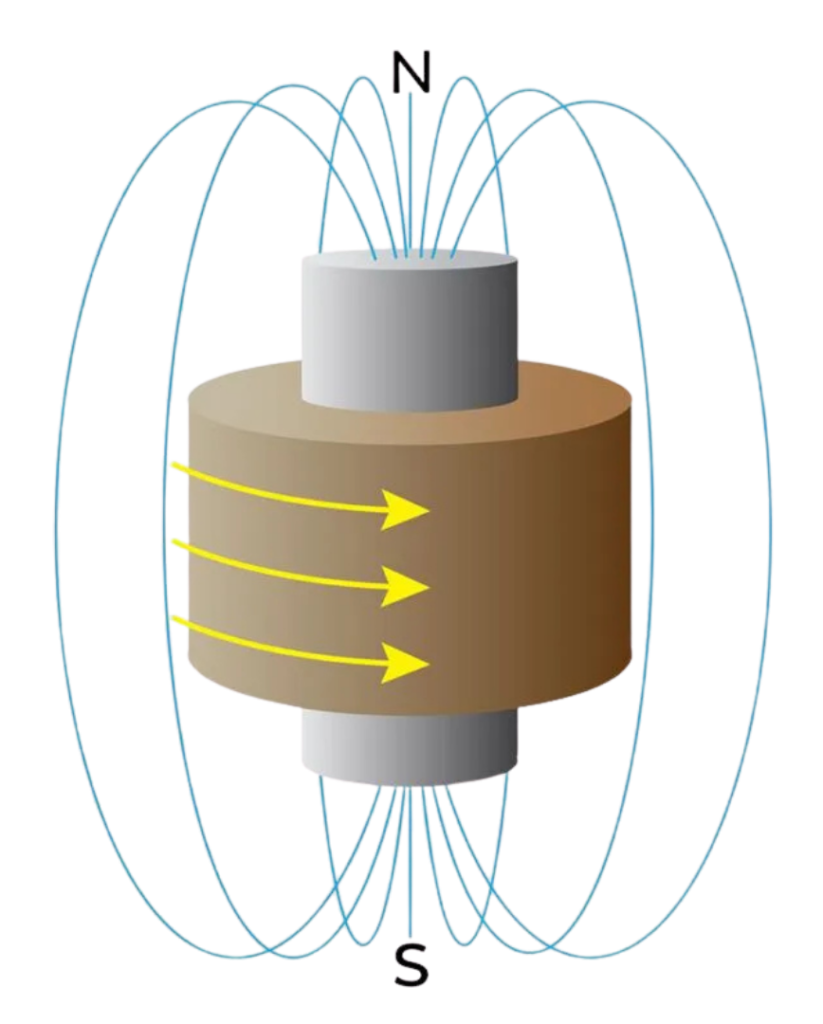
Electromagnet
- An Electromagnet is a type of magnet created when electricity flows through a wire.
- It works only when the current is ON, making it a temporary magnet.
How Induction occurs:
- Induction in electromagnets happens when a changing magnetic field—created by the electromagnet—induces an electric current in a nearby conductor.
Step by Step Explanation:
- Step #1: Electromagnet creates a magnetic field: When electric current flows through a coil of wire (usually wrapped around an iron core), it becomes an electromagnet and produces a magnetic field.
- Step #2: Change in magnetic field: If the current in the electromagnet changes, the magnetic field around it also changes.
- Step #3: Nearby conductor affected: If there is a wire or coil near this changing magnetic field, the magnetic lines of force cut through the conductor.
- Step #4: Induced current: This change causes electrons in the nearby conductor to move, creating an induced current. This is electromagnetic induction.
Key Facts About Electromagnetic Induction
Key Facts about Electromagnetic Induction
- Discovery: Introduced by Michael Faraday, who demonstrated that moving a magnet near a coil induces an electric current.
- Faraday’s Law: The induced voltage is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux.
- AC-Friendly: Alternating current (AC) is ideal for induction due to its continuous change in direction.
- Contactless Power: Induction enables power transfer without direct electrical connections.
- Efficiency Factors: Induced current increases with faster motion, stronger magnets, or more coil turns.
- Temporary Effect: The induction only occurs as long as the magnetic field is changing.
Uses of Electromagnetic Induction
- Used in electric generators to produce electricity
- Powers transformers to change voltage levels
- Drives induction motors in fans, pumps, and machines
- Enables wireless charging in smartphones and devices.
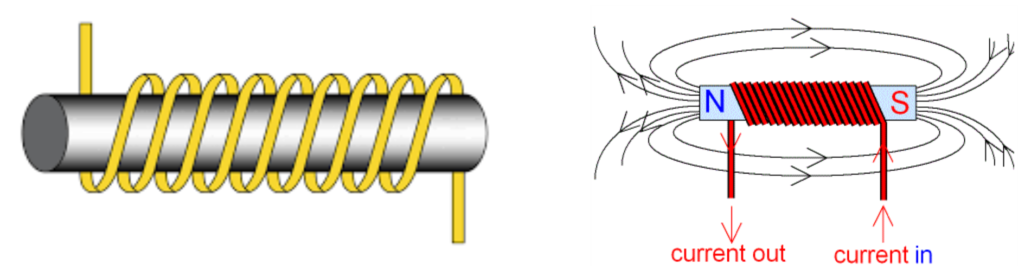
What Do You Mean By EM Coil And EM Currents?
EM Coil
- An EM coil is a wire wound in loops or spirals, often around an iron core, used to create or respond to magnetic fields.
- When current flows through the coil, it acts like a magnet (called an electromagnet).
- When the magnetic field around the coil changes, it can also generate current by induction.
- EM coils are essential in inductors, motors, speakers, and wireless chargers.
EM Current
- EM currents refer to electric currents produced due to electromagnetic induction. These are not regular currents from a battery, but are induced when a magnetic field around a conductor changes.
- When a magnet moves near a coil, or the coil moves in a magnetic field, electrons in the wire start moving.
- This motion creates an induced current, called an electromagnetic (EM) current.
- EM currents are used in generators, transformers, and induction motors.
Faraday’s Law of Induction
Introduction:
- Faraday’s Law states that:
“An electric current is induced in a conductor whenever it experiences a change in the magnetic field around it”.
Faraday’s Law of Induction
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction states:
- A voltage (or electromotive force) is induced in a coil when it experiences a change in magnetic field. The faster the change, the greater the induced voltage.
Mathematically:

where:
- EMF = induced voltage
- N = number of turns in the coil
- Φ (phi) = magnetic flux
- dΦ/dt = rate of change of magnetic flux.
What Does Faraday’s Law Say?
Faraday’s First Law:
- Whenever a magnetic field passing through a coil or conductor changes, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the conductor. If the circuit is closed, this EMF causes an electric current to flow.
Faraday’s Second Law:
- The magnitude of the induced EMF is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil.
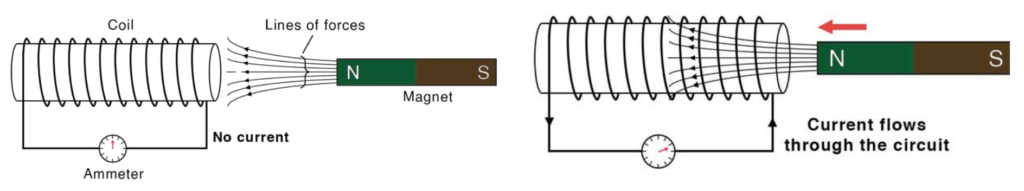
There must be 3 Scenarios that can happen in an Electromagnet
- Magnet moving in
- Current flows
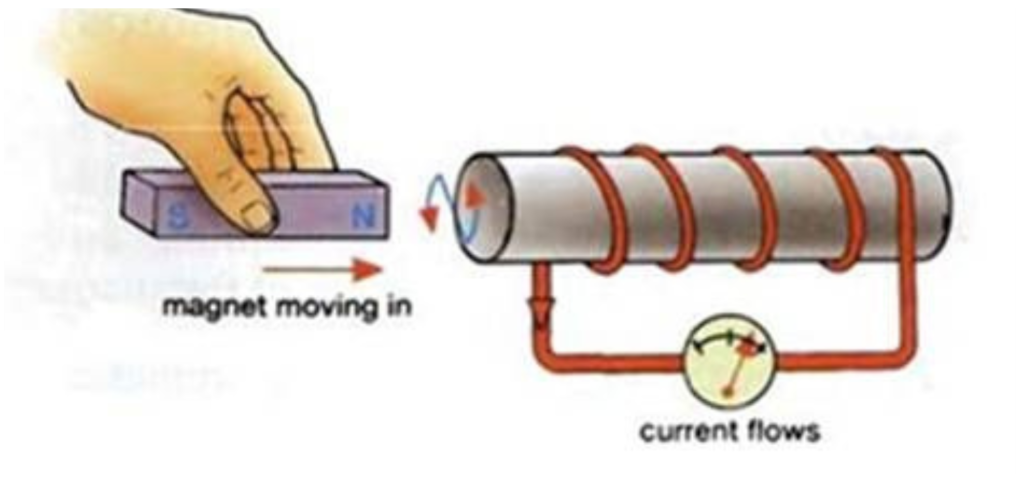
- Magnet inside the coil
- No Current flows
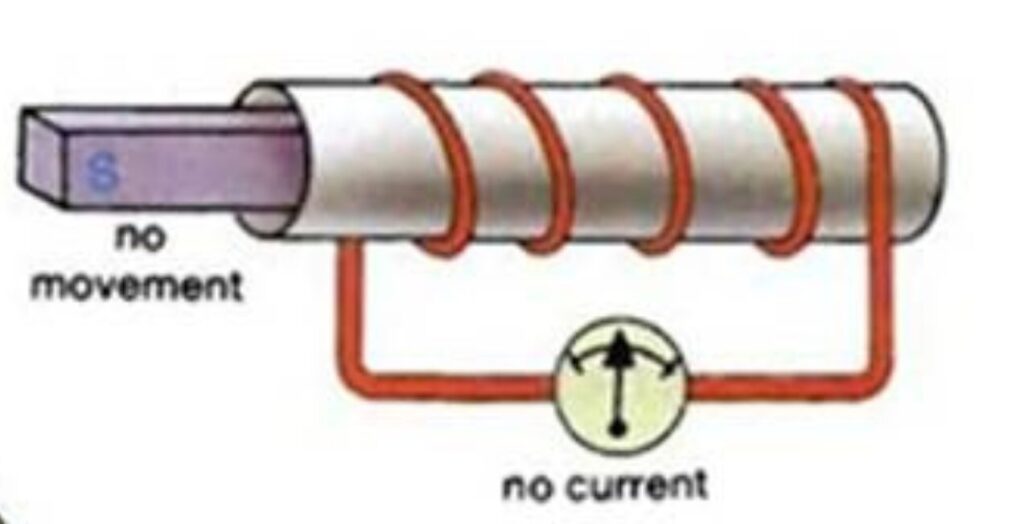
- Magnet outside the coil
- Current flows in opposite direction
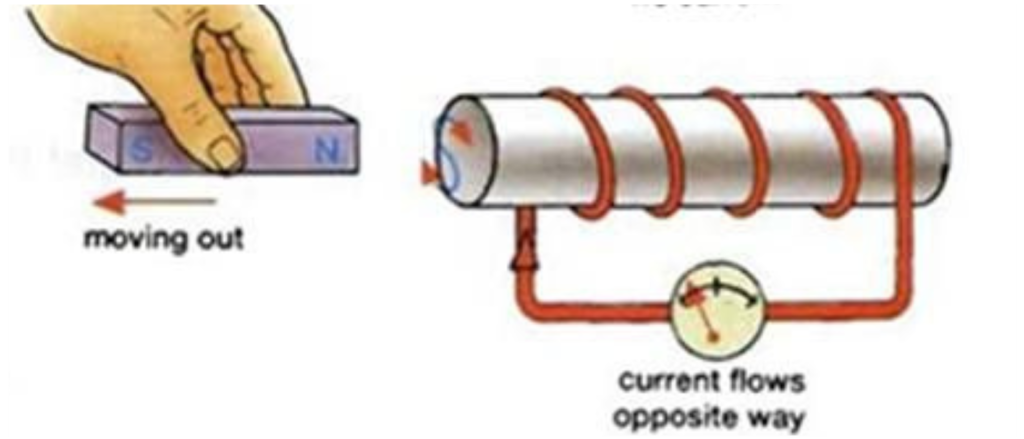
Applications of Faraday’s Law of Induction
- Faraday’s laws are the foundation of modern electrical and electromagnetic systems. They are used in devices and technologies that generate, transfer, or use electricity efficiently.
Electric Generators:
Faraday’s law is the working principle of generators.
- When a coil rotates in a magnetic field, the changing magnetic flux induces current.
- Used in power stations to produce electricity on a large scale.
Transformers:
Used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another.
- A changing current in the primary coil induces voltage in the secondary coil.
- Helps step up or step down voltage for safe power transmission.
Wireless Chargers:
Used to charge phones and other gadgets without cables.
- A coil in the charger generates a changing magnetic field.
- This induces current in the device’s receiving coil.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Magnetic flux is the total magnetic field passing through a given area. It depends on the field strength, area size, and angle between them.
Solution:
- Increase the number of coil turns
- Use a stronger magnet
- Move the magnet or coil faster
- Use a soft iron core inside the coil
Solution:
Alternating current constantly changes direction, which creates a changing magnetic field, making it ideal for continuous induction in devices like transformers and motors.
Solution:
Soft iron enhances the magnetic field and helps direct it more efficiently through the coil, increasing the amount of induced EMF.
Solution:
Induction occurs when there is a change in magnetic flux—this can happen by moving a magnet, moving the coil, or changing the strength of the magnetic field.
Solution:
No. Only a changing magnetic field can induce current. A static field does not produce EMF.

