Brain Diagram - GCSE Biology
Introduction
- The brain is mostly composed of neurons, also known as nerve cells.
- The brain of an adult consists of approximately 86 billion neurons.
- These neurons are interconnected with each other and with the other parts of the body.
- This interconnection allows information processing and body control.
- Without a functioning brain, a person dies.
Real-life uses:

Diagram of the Brain

Main Parts of the Brain
- Main parts of the brain include the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata.
Cerebellum:
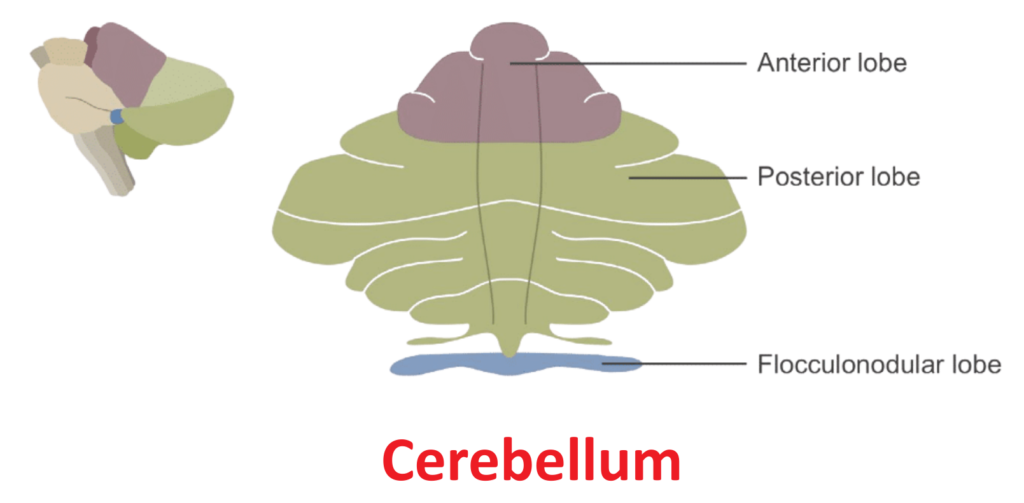
- It is present at the base of the brain.
- It consists of two equal parts.
- The body’s balance and posture are controlled by the cerebellum.
- It works to ensure smooth movements. For this, it precisely coordinates when and how the muscles contract.
Medulla Oblongata:
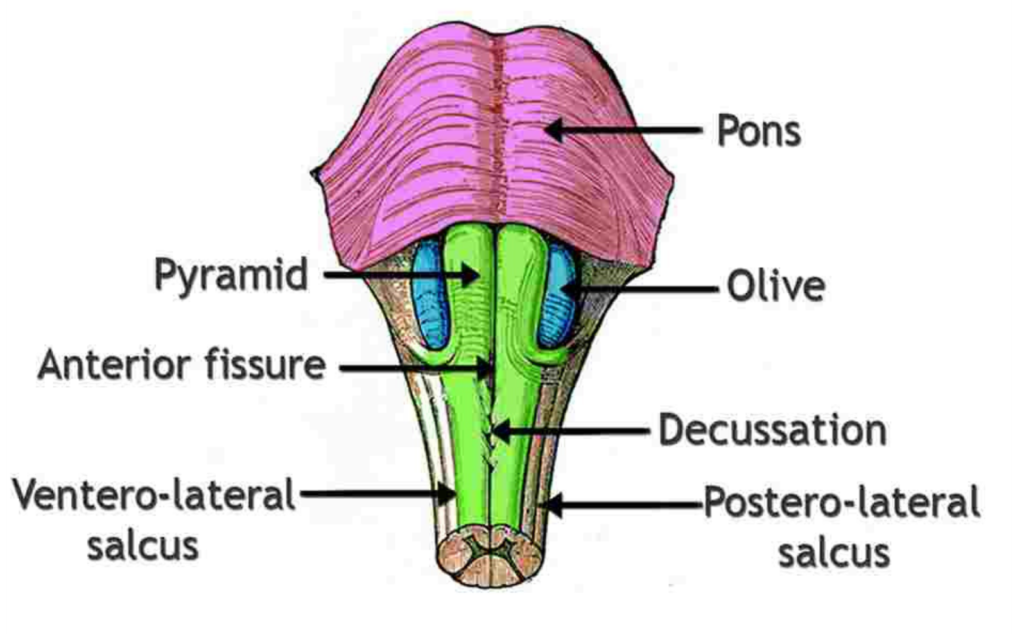
- It is located between the brain and the spinal cord, and connects them.
- It is mainly responsible for involuntary tasks like controlling heart rate and breathing rate.
- Essential reflexes, including vomiting, sneezing, and swallowing, are carried out by the medulla oblongata.
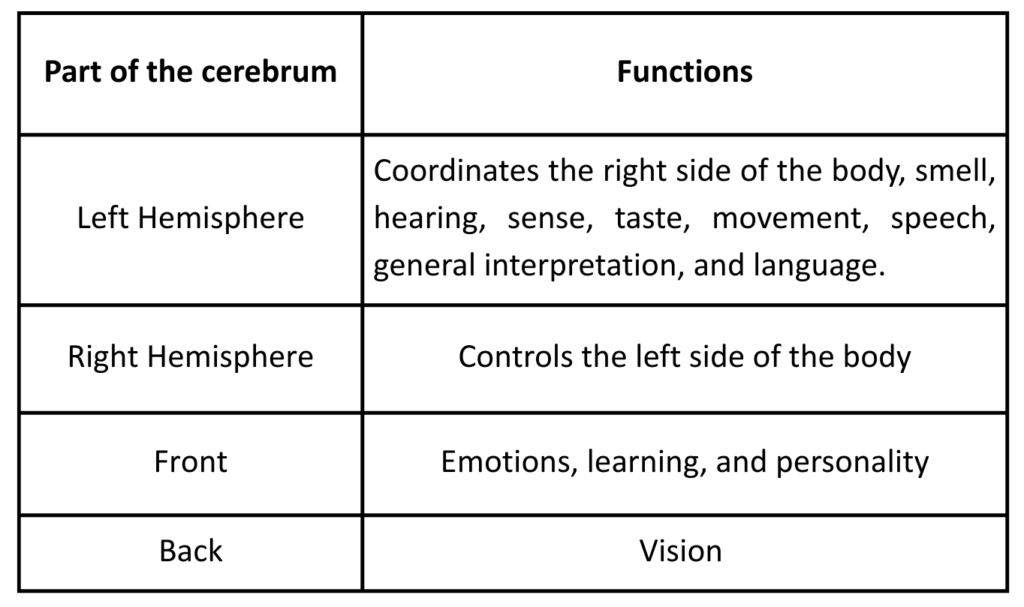
Cerebrum:
- It is the most widespread part of the brain, having two hemispheres.
- The front and top of the brain are its parts.
- The cortex with the underlying white matter makes up the cerebrum.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
The Central Nervous System (the brain and spinal cord) is made of Nervous tissue.
Solution:
The human brain is divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
Solution:
The stem cells of a three-week-old embryo begin to differentiate and give rise to nerve cells.
Solution:
The right cerebral hemisphere sends the impulse to the midbrain and then to the left hemisphere. From here, it descends to the medulla, the spinal cord and finally reaches the left hand.
Solution:
The medulla oblongata is called the brain’s “automatic pilot” as it controls the vital involuntary functions: breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, vomiting, digestion, and sneezing without conscious thought.
Solution:
No, the cerebral cortex and cerebrum are not the same. The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum.
Table of Content

