Venn Diagram: Step-by-Step Examples
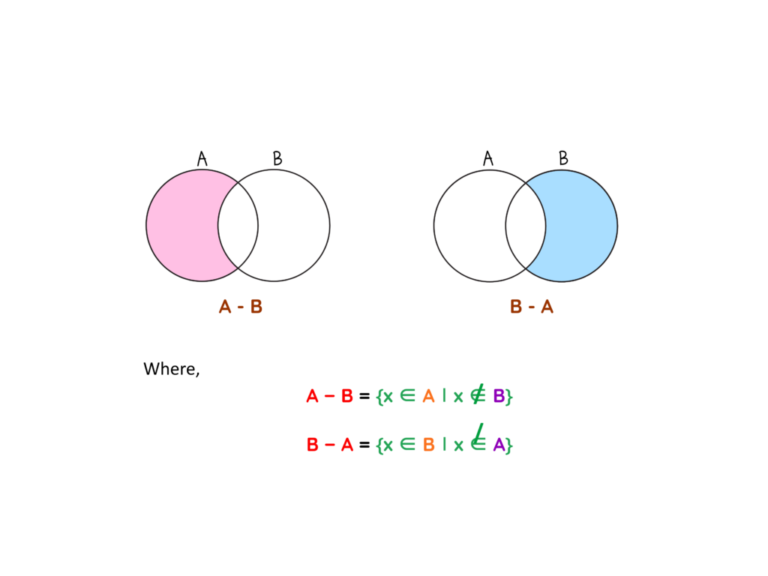
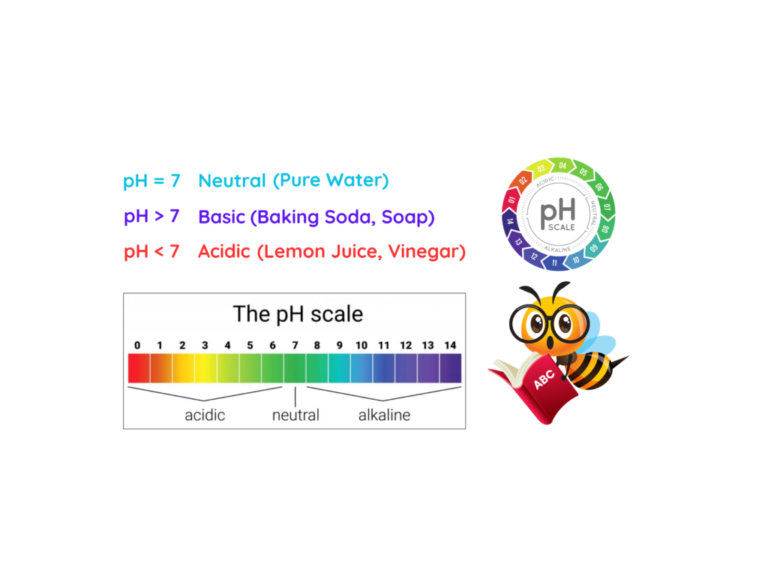
Venn Diagram – GCSE Maths Practice Questions Downloads Introduction A Venn diagram is a simple method to compare and group items using overlapping circles. It is fundamental tool in mathematics, logic, and problem-solving. Venn diagrams make complex data simple by showing it visually. What is Venn Diagram? A Venn diagram is a visual way to…