Resultant Forces – GCSE Physics
Introduction
- Force is a push or pull acting on a body.
- A body needs Force to change its state of motion.
- There are number of Forces acting on a body at a same time, so instead of analyzing multiple forces individually, we use the Resultant Force to predict Motion.
- The Resultant Force is the single Force that replaces multiple forces acting on an object, producing the same effect.
Real-life Scenario:


What is Free Body Diagram?
- A Free Body Diagram is a simplified visual representation of an object to visualize the forces acting on a single object (or body).
- It helps analyze the effects of External Forces.
Examples:
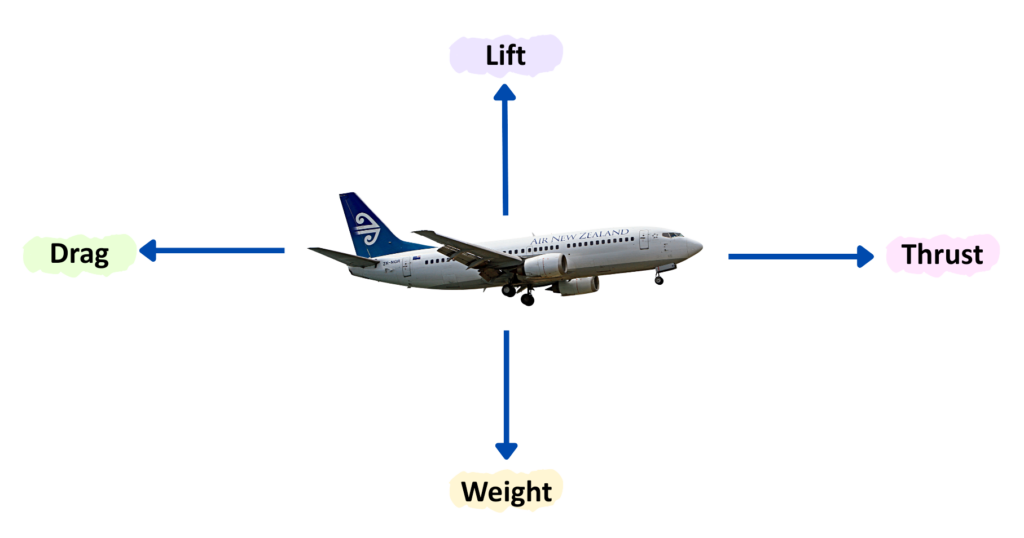
Characteristics:
- The arrow points in the direction that the force is acting.
- The length of the arrow shows how strong the force is:
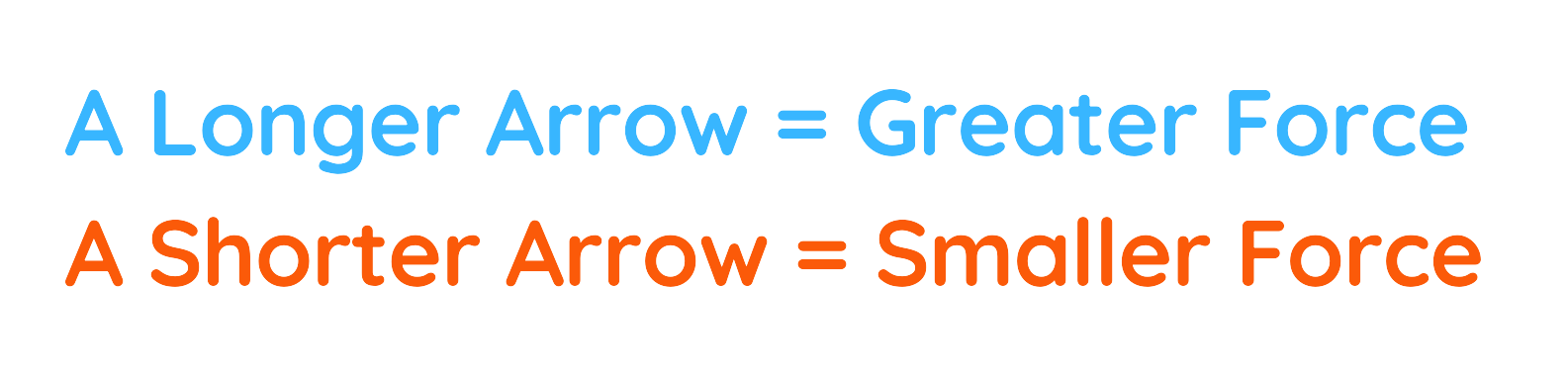
Common Forces in Free Body Diagrams:
- Weight
- Tension
- Friction
- Air Resistance/Drag
What is Resultant Force Equation?
- Resultant Force is the Vector sum of all the individual forces acting on an object.
- It is also called a net force which represent the combined effect of all other forces.
- SI Unit of Force: Newton(N)
Equation 1:
- If F1, F2, F3,….are the forces acting on a body, the Resultant Force FR is calculated using the formula with positive and negative signs used for pair of opposite forces,
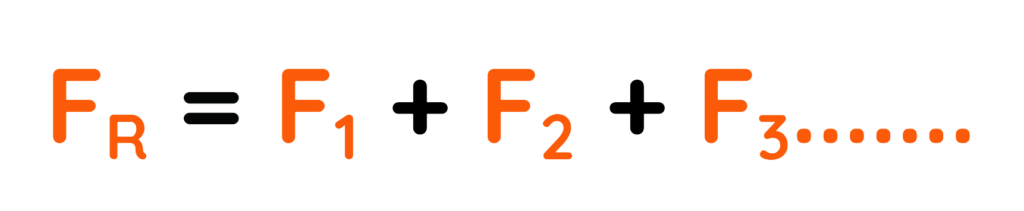
- Where F1, F2, F3, . . . are the Linear Forces acting of the body.
Equation 2:
- If F1 and F2 are the forces perpendicular to each other then their Resultant Force is,

- This consequence can also be calculated geometrically using other methods.
How to Calculate Resultant Force?
Method #1:
- If force acts on a same direction, then the Resultant force is,
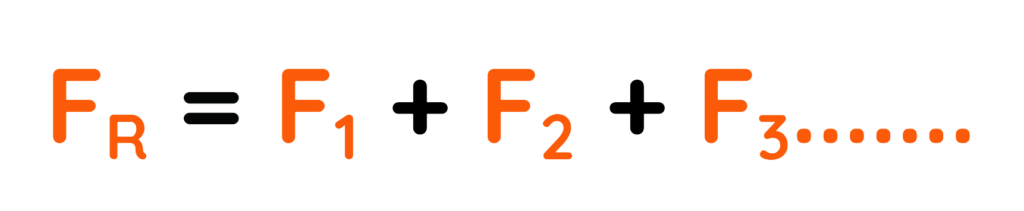
Method #2:
- If force acts on a opposite direction, then the Resultant force is,

 Solved Example: Method 1
Solved Example: Method 1
Problem: If Person A pushes a car in the East direction with a Force of 200 N, and Person B also pushes the car in the same direction with a Force of 300 N, what will be the Resultant Force?
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- Person A applies Force F1 : 200N
- Person B applies Force F2 : 300N
Step #2: Then the Resultant Force will be:
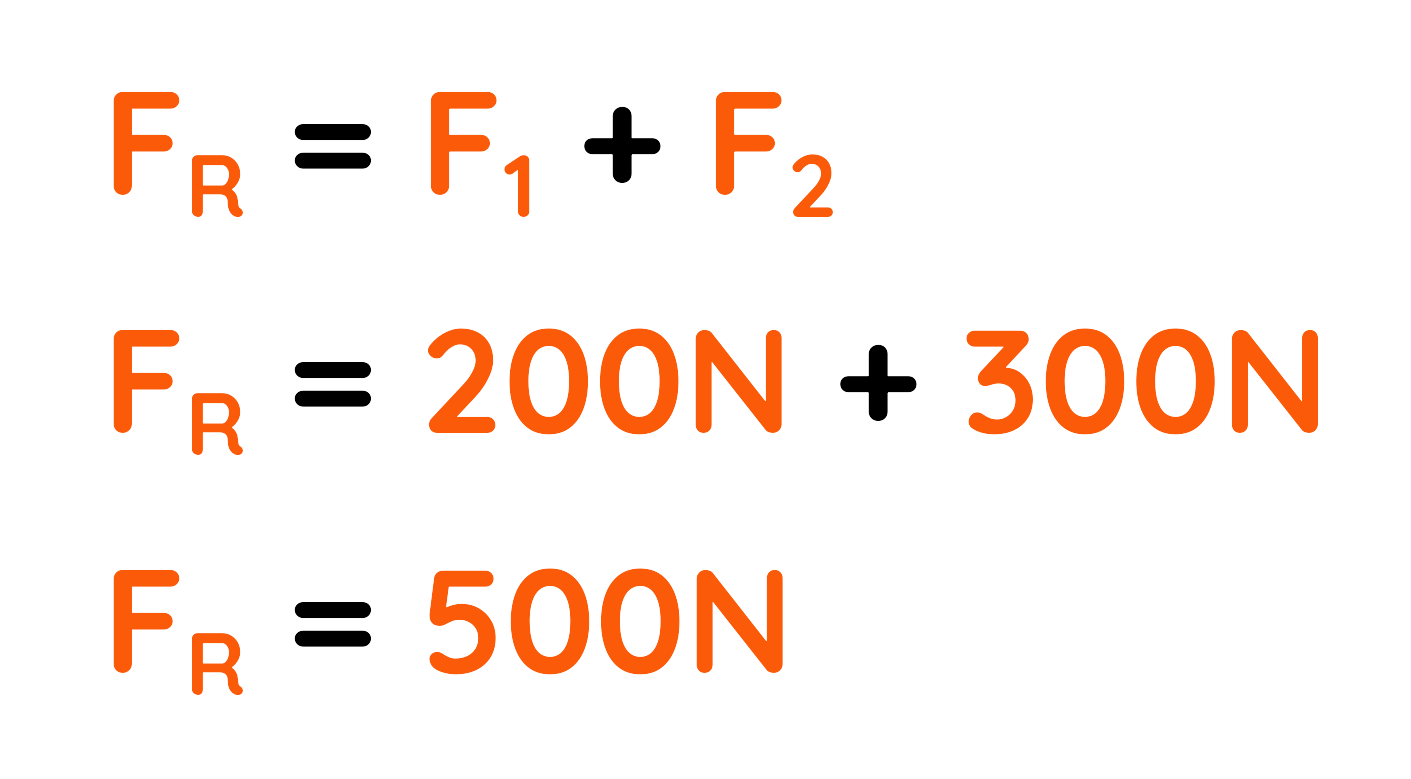

Final Answer: 500N
 Solved Example: Method 2
Solved Example: Method 2
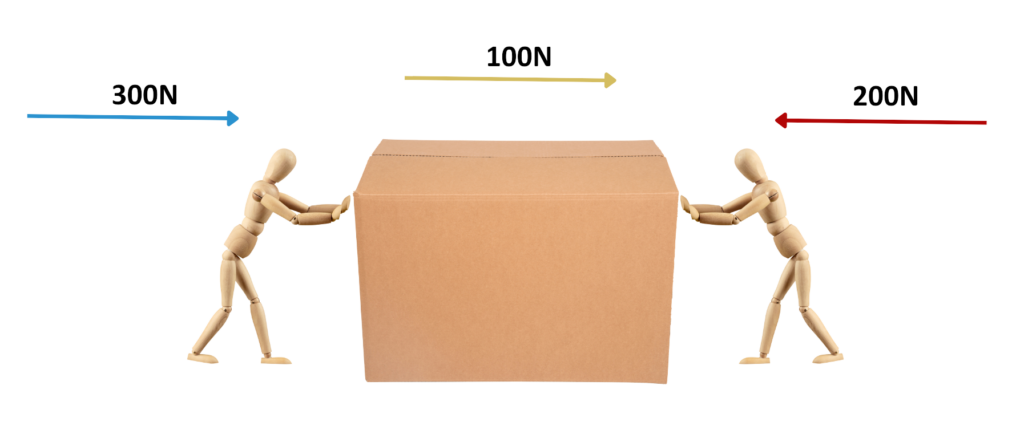
Problem: If Person A pushes a box to the Left with a Force of 200 N, and Person B pushes the same box to the Right with a Force of 300 N, what is the Resultant Force on the box?
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- Person A applies Force F1 : 200N
- Person B applies Force F2 : 300N
Step #2: Then the Resultant Force will be:
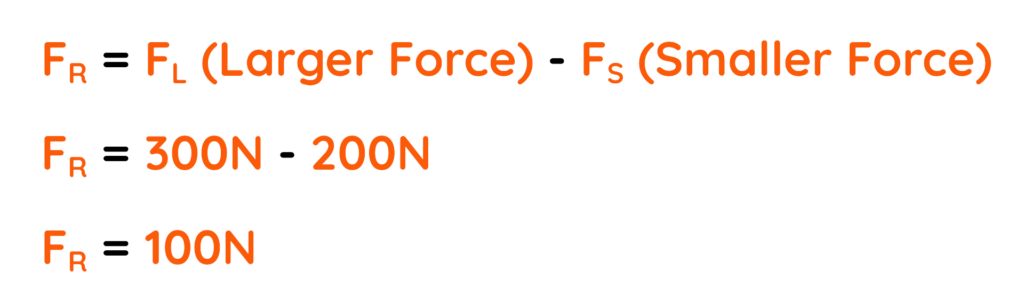

Final Answer: 100N
What are Balanced and Unbalanced Force?
Balanced Force:
- Forces acting on an object are equal in Magnitude but opposite in Direction.
- They cancel each other out, so the Resultant Force is Zero.

Characteristics:
- No change in Motion.
- Object or Body remains at rest or continues at Constant Velocity.
Examples:


Unbalanced Force:
- Forces acting on an object are not equal in Unbalanced Force.
- They do not cancel each other out, so the Resultant Force is non-zero.
Characteristics:
- Change in Motion.
- Object or Body accelerates (speed up, speed down or change direction).
Examples:


Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
A Resultant Force is the overall force acting on an object after all individual Forces are combined.
Solution:
- Add Forces in the same direction
- Subtract it they act in opposite directions. This gives the net force.
Solution:
- Resultant force = Larger Force – Smaller Force (if opposite)
- Resultant force = Sum of Forces fil same direction
Solution:
A drawing that shows the size and direction of each force using arrows.
Solution:
When the Resultant Force is not zero this causes movement or change.
Solution:
The object is Balanced. It either stays still or keeps moving at Constant Speed.
Solution:
A Rocket producing 13,000 N thrust and 5,000 N weight then,
Resultant Force is,
FR = FL (Larger Force) – FS (Smaller Force)
FR = 13,000 – 5000 = 8,000 N upwards

