Atomic Structure – GCSE Physics
Introduction
- An Atom is the fundamental building block of all matter. It generally represents the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties.
- Despite their incredibly small size, atoms form the foundation of all substances in the universe, from the air we breathe to the stars in the sky.
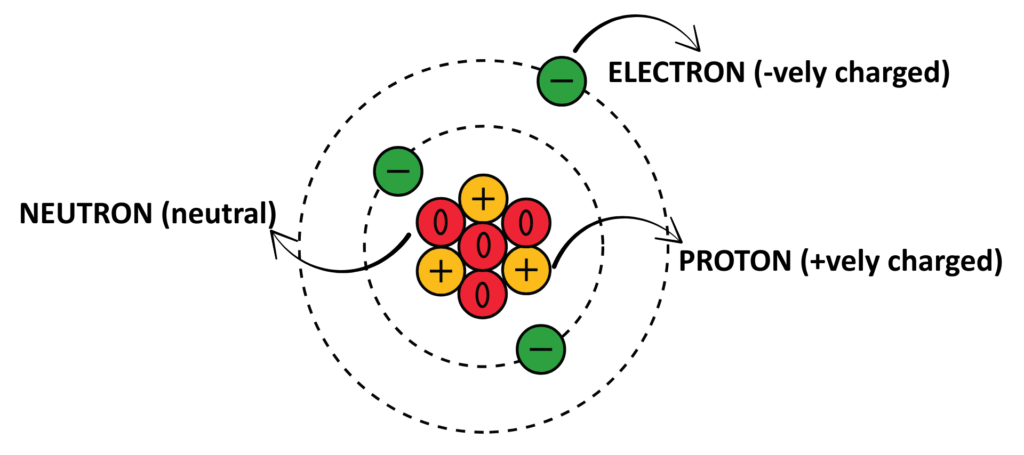
Structure Of An Atom
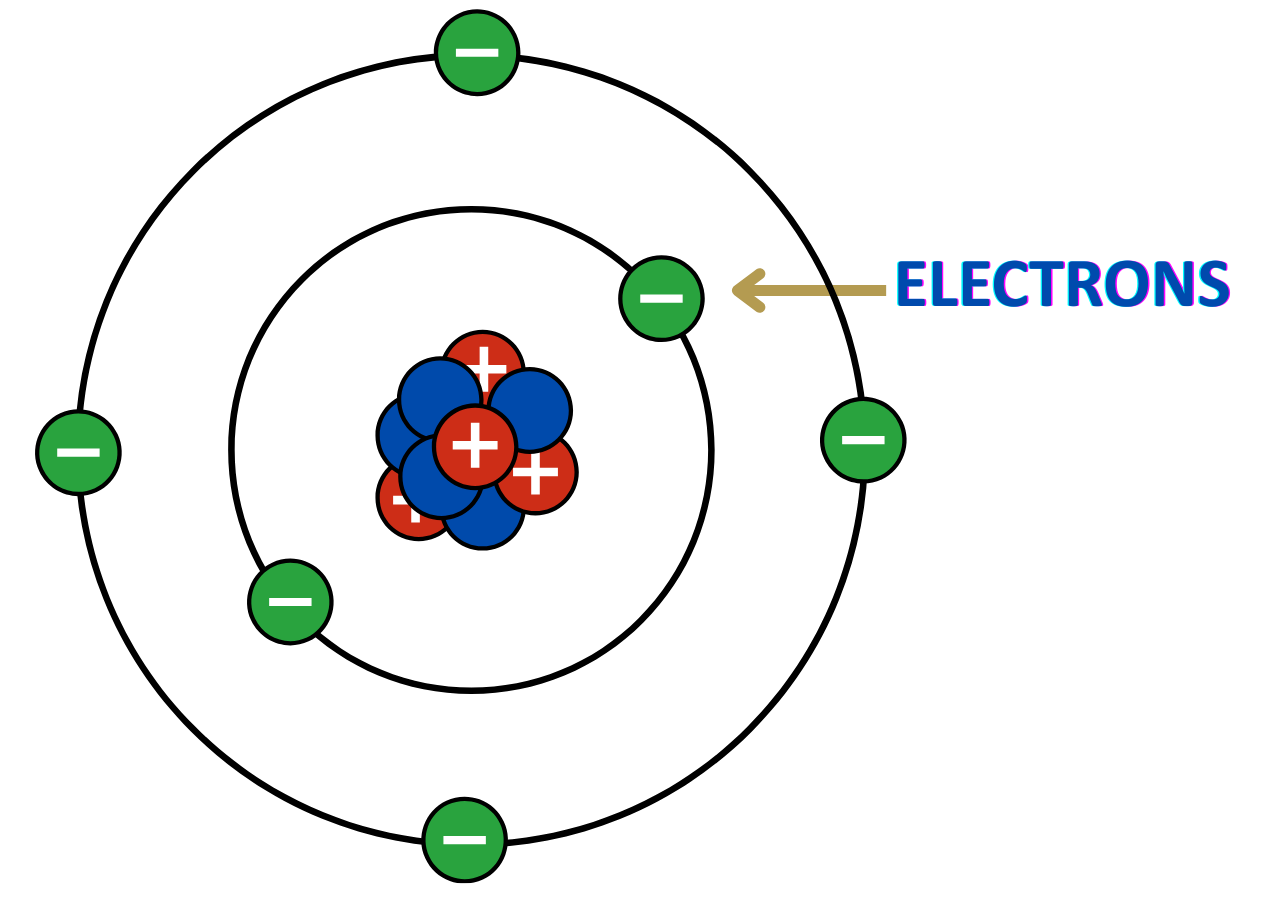
- The Structure of an atom describes how its fundamental particles—protons, neutrons, and electrons—are arranged, forming the basis of all matter in the universe.
Related terminology
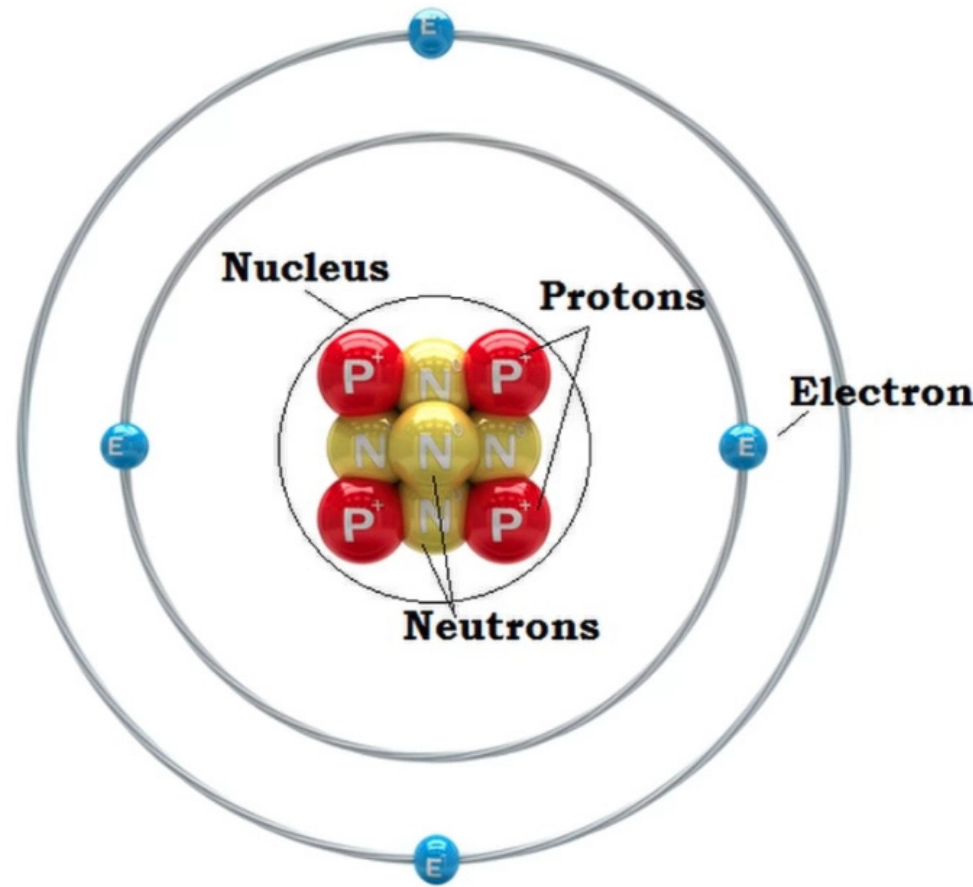
1. Nucleus:
- Located at the center of the atom; contains most of the atom’s mass.
2. Protons:
- Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
- The number of protons = atomic number.
3. Neutrons:
- Neutral particles also located in the nucleus.
- Protons + Neutrons = Mass number.
4. Electrons:
- Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells.
5. Electrically Neutral:
- In a stable atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
6. Atomic Stability:
- The arrangement of electrons determines the atom’s chemical reactivity and bonding behavior.
Atomic Particles Of An Atom
- There are three subatomic particles of an atom that are:
- Protons
- Neutrons
- Electrons
- These three subatomic particles work together to define the structure, properties, and behavior of every atom.
Let us understand about them in a more detailed way.
Protons:
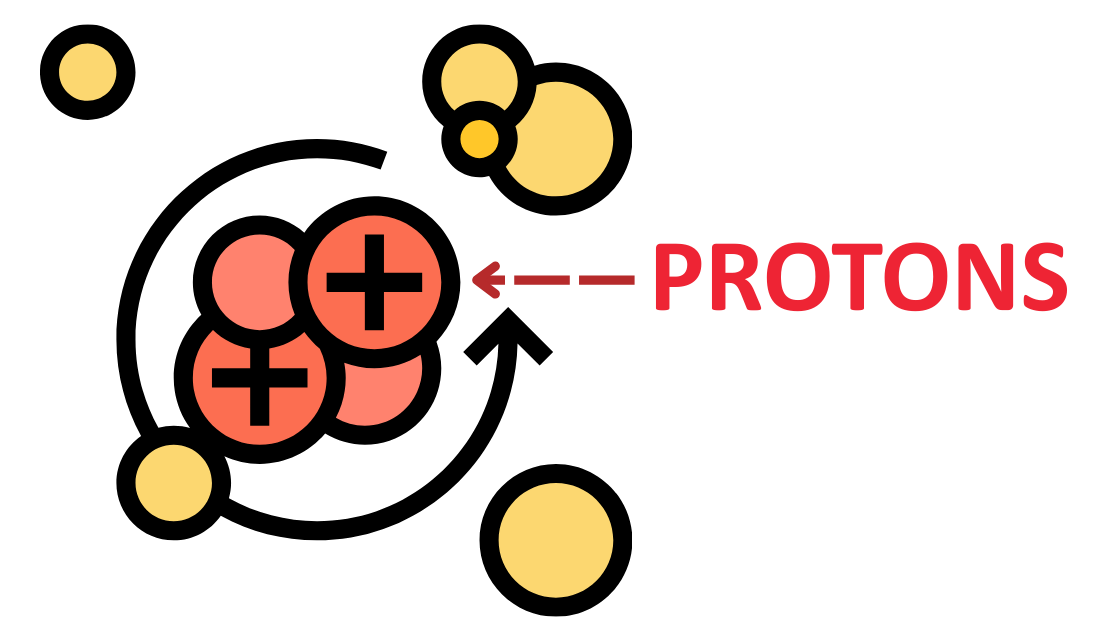
Definition:
- Protons are positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Charge:
- Each proton carries a +1 elementary charge (+1e).
Mass:
- Approximately 1 atomic mass unit (1 amu) or 1.67 × 10-27 kg, slightly less than a neutron.
Role in Atomic Identity:
- The number of protons in an atom defines the atomic number and thus the type of element.
- (e.g., 1 proton = hydrogen, 6 protons = carbon)
Neutrons
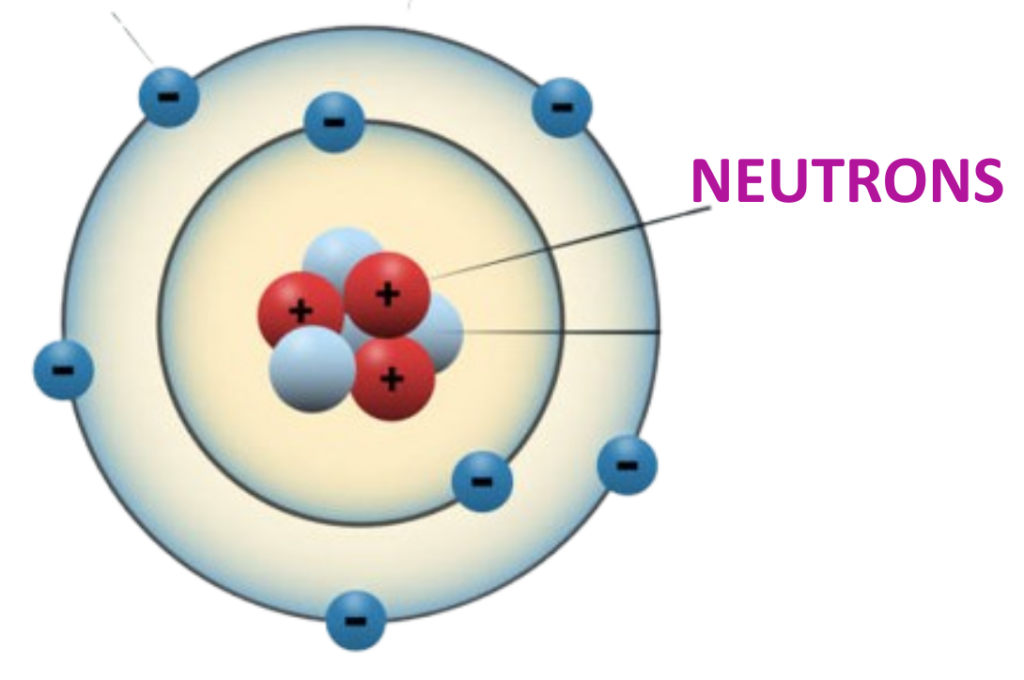
Definition:
- Neutrons are neutral subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Charge:
- Neutrons carry no charge (they are electrically neutral).
Mass:
- Neutrons have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (1 amu).
Role in Atomic Stability:
- Neutrons contribute to the mass of the atom and play a key role in maintaining the stability of the nucleus by reducing the repulsion between positively charged protons.
Isotopes:
- Neutrons help define the isotope of an element. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.
- (e.g., Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of Carbon.)
Electrons
Definition:
- Electrons are tiny, negatively charged subatomic particles found in atoms.
Charge:
- Each electron carries a -1 elementary charge.
Mass:
- Electrons have a very small mass (9.11 × 10⁻³¹ kg), about 1/1836 the mass of a proton.
Location in Atom:
- They orbit the nucleus of an atom in regions called electron shells or energy levels.
Role in Atoms:
- Electrons determine how atoms interact chemically — they are involved in bonding and reactions.
Electricity and Current:
- Moving electrons in a conductor create electric current.
Examples of Structures of Some Elements
- Here’s some examples of elements along with their atomic structures.
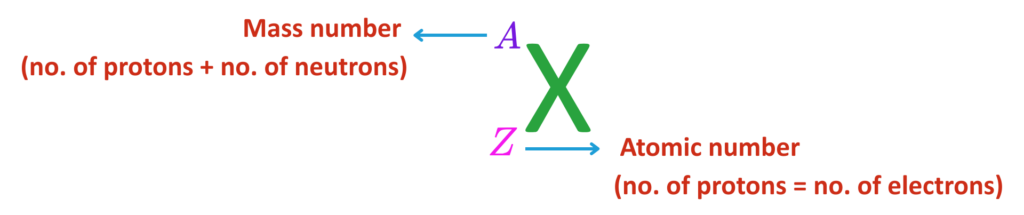
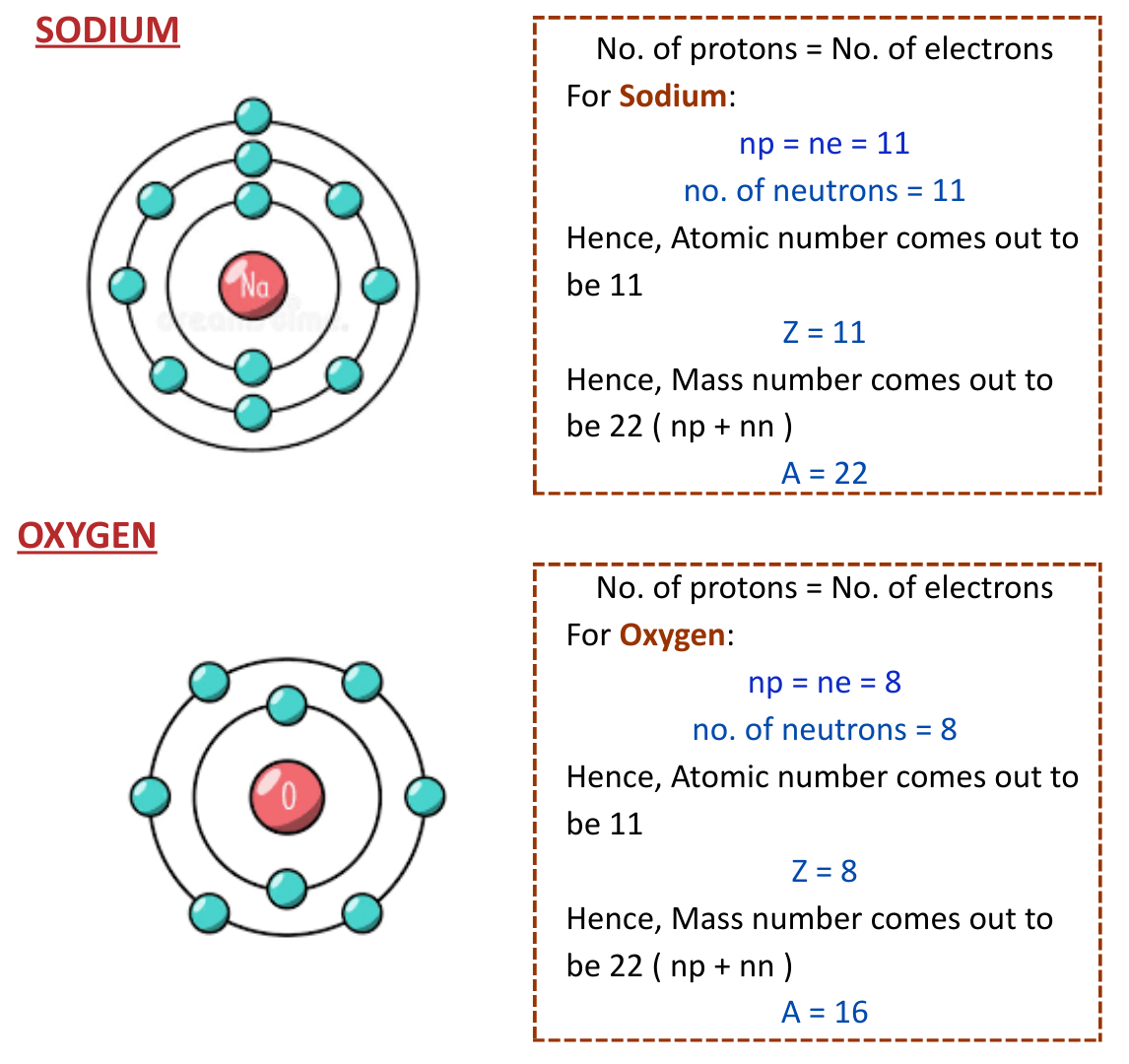
Isotopes
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Basically, isotopes contains same atomic number but they differ in mass number due to uneven number of neutrons.
Key Points:
- Same Element: Same number of protons (same atomic number)
- Different Mass: Due to different numbers of neutrons
- Examples:
- Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14 are all isotopes of carbon.
- All have 6 protons
- Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, Carbon-13 has 7, Carbon-14 has 8
- It can be explained diagrammatically as:
- Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14 are all isotopes of carbon.
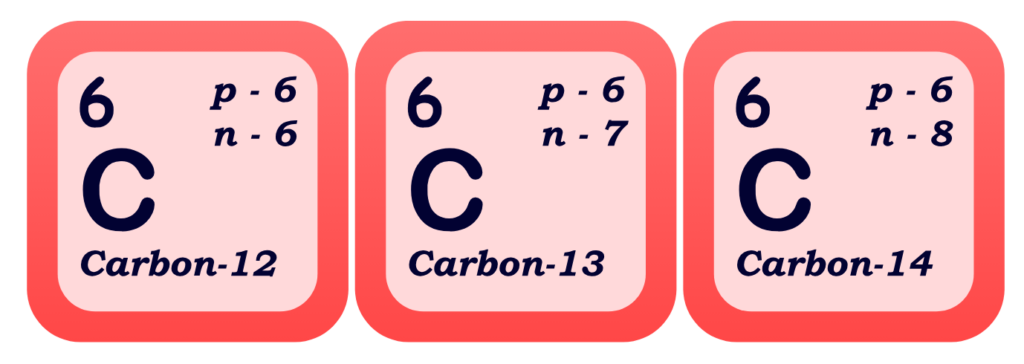
- Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive (they decay over time, releasing radiation)
Uses of Isotopes:
- Medical: Radioactive isotopes in cancer treatment and diagnostic imaging (e.g., iodine-131)
- Archaeology: Carbon-14 dating of ancient artifacts
Ionisation Energy
- Ionisation energy (also spelled ionization energy) is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion in its ground state.
- It is a measure of how strongly an atom holds onto its electrons.
Key Concepts:
- First Ionisation energy: Energy needed to remove the first electron from a neutral atom.
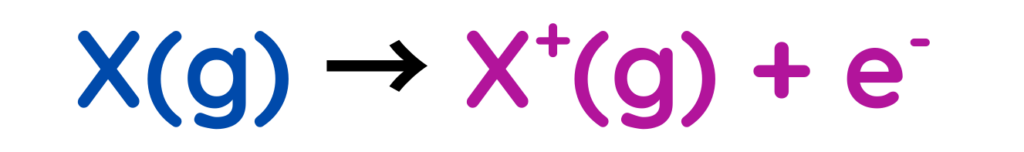
- Second Ionisation energy: Energy required to remove a second electron from a positive ion.
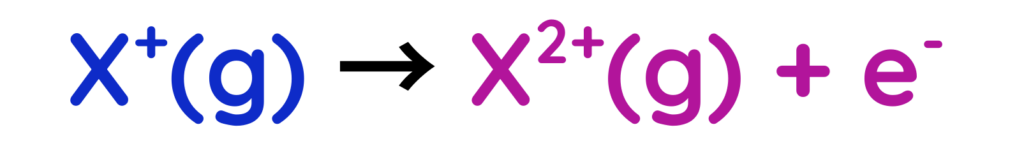
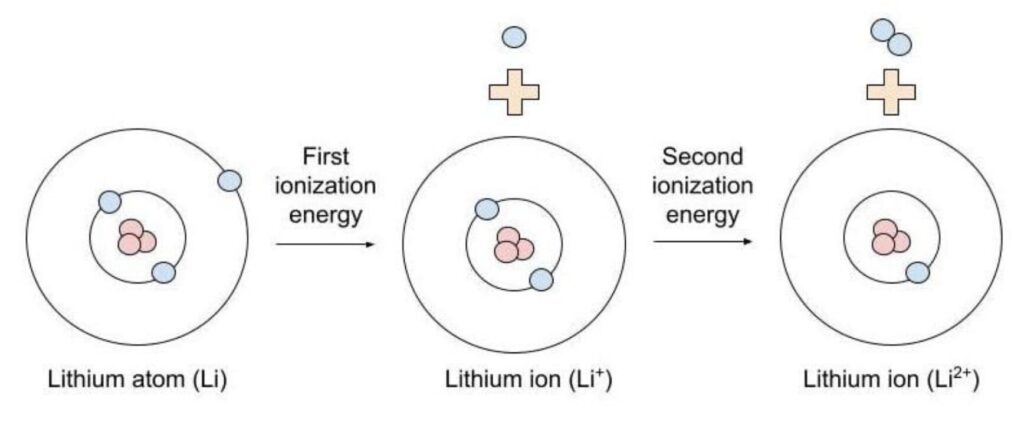
Factors Affecting Ionisation Energy:
- Nuclear charge (more protons = higher ionisation energy)
- Atomic radius (larger radius = lower ionisation energy)
- Electron shielding (more inner shells = lower ionisation energy)
- Electron configuration (full or half-full subshells can affect stability)
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons in orbitals around the nucleus.
Solution:
- Proton: Positive charge (+1), found in the nucleus
- Neutron: No charge (neutral), found in the nucleus
- Electron: Negative charge (–1), found in orbitals around the nucleus.
Solution:
The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in an atom. It determines the element.
Solution:
The mass number (A) is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Solution:
Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons (different mass numbers).
Solution:
Ionisation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion.
Solution:
Electrons occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus. Each level can hold a certain number of electrons (e.g., 2 in the first, 8 in the second).

