Venn Diagram – GCSE Maths
Introduction
- A Venn diagram is a simple method to compare and group items using overlapping circles.
- It is fundamental tool in mathematics, logic, and problem-solving.
- Venn diagrams make complex data simple by showing it visually.
What is Venn Diagram?
- A Venn diagram is a visual way to show relationships between different sets.
- It uses circles to represent sets, and the overlapping areas show what the sets have in common.
Example
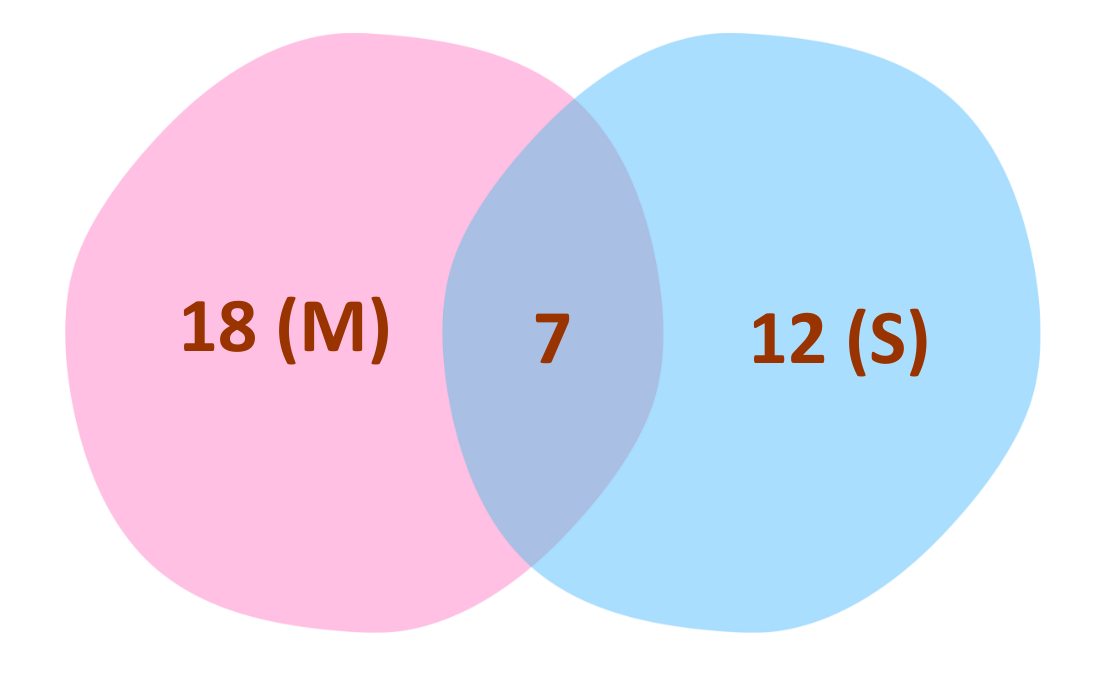
Suppose in a class of 30 students:
- 18 like Math (M)
- 12 like Science (S)
- 7 like both Math and Science
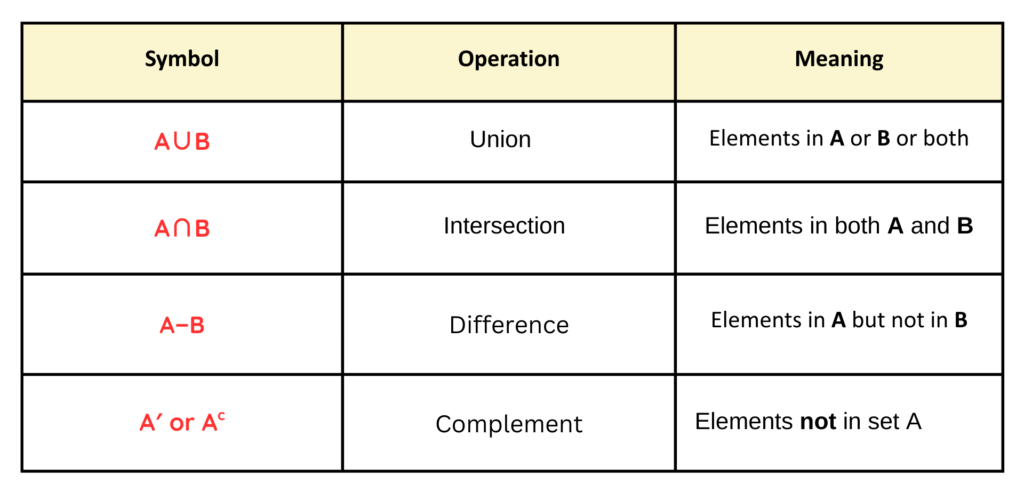
Set Operations in Venn Diagrams
Venn diagrams visually represent different set operations.
- Curly brackets { } show a set of values.
- ∈ means ‘is an element of’.
Common Set Operations in Venn Diagrams:
Union of Set:
- The Union of set represents that all elements that belong to either A or B or both.
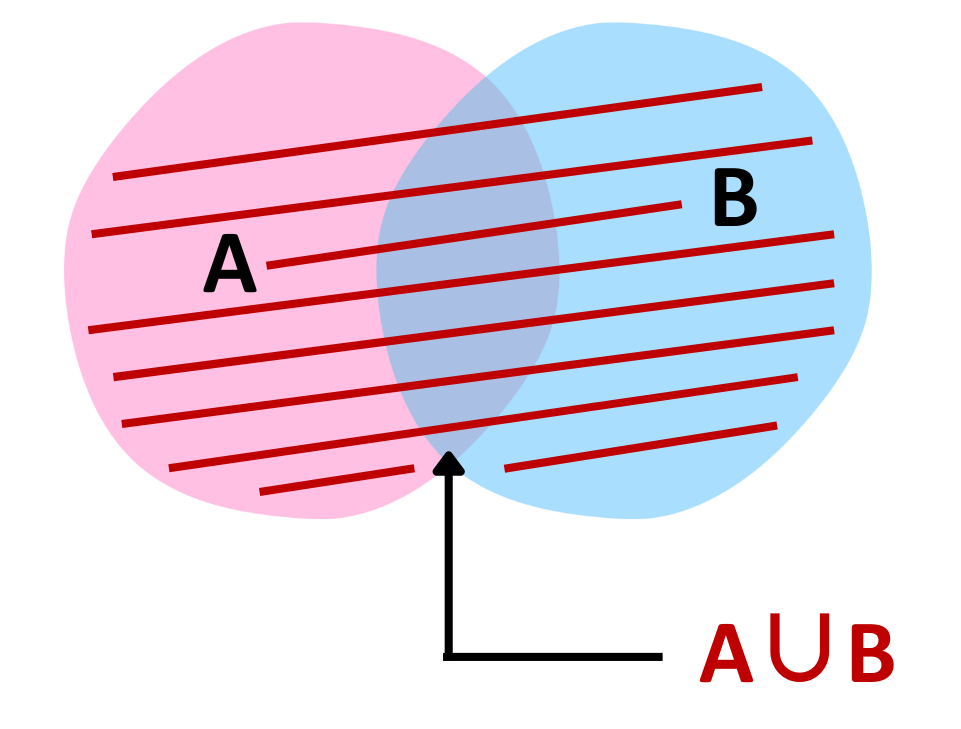
where,

Intersection of Set:
- The Intersection of set represents that only elements that belong to both A and B.
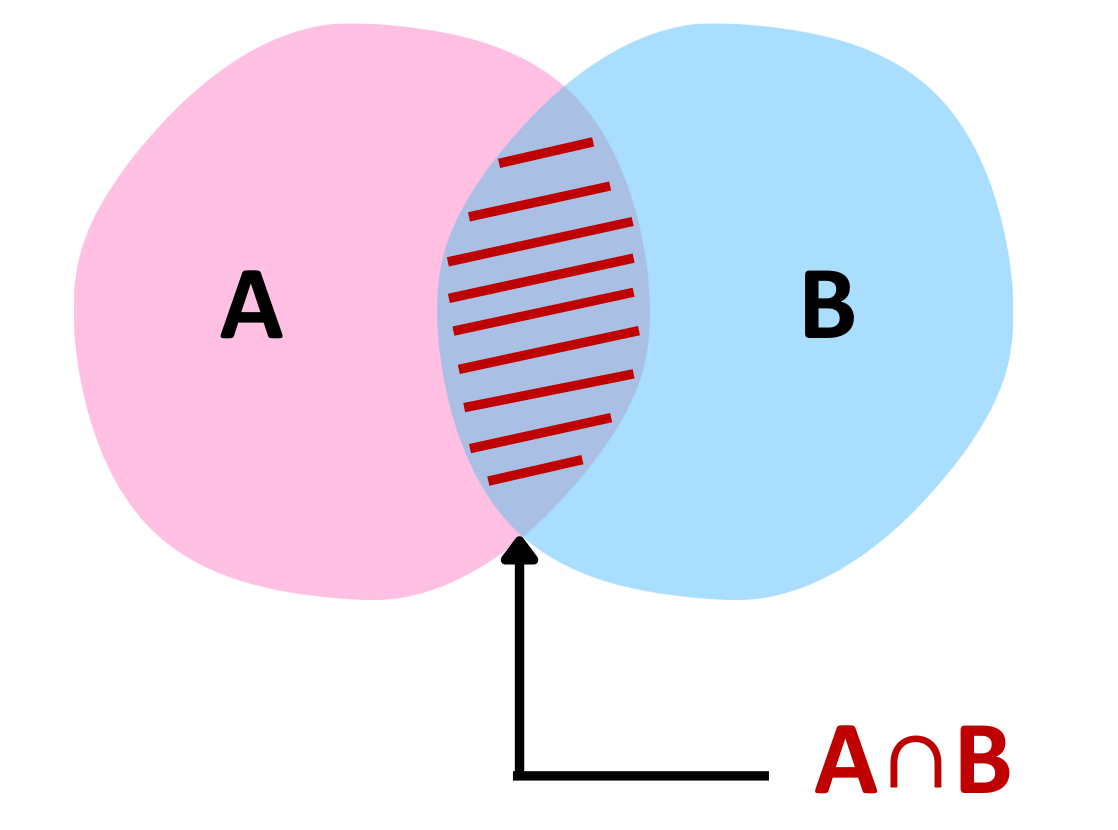
where,

Compliment of a Set:
- The Compliment of a set represents that all elements not in set A, but in the universal set.
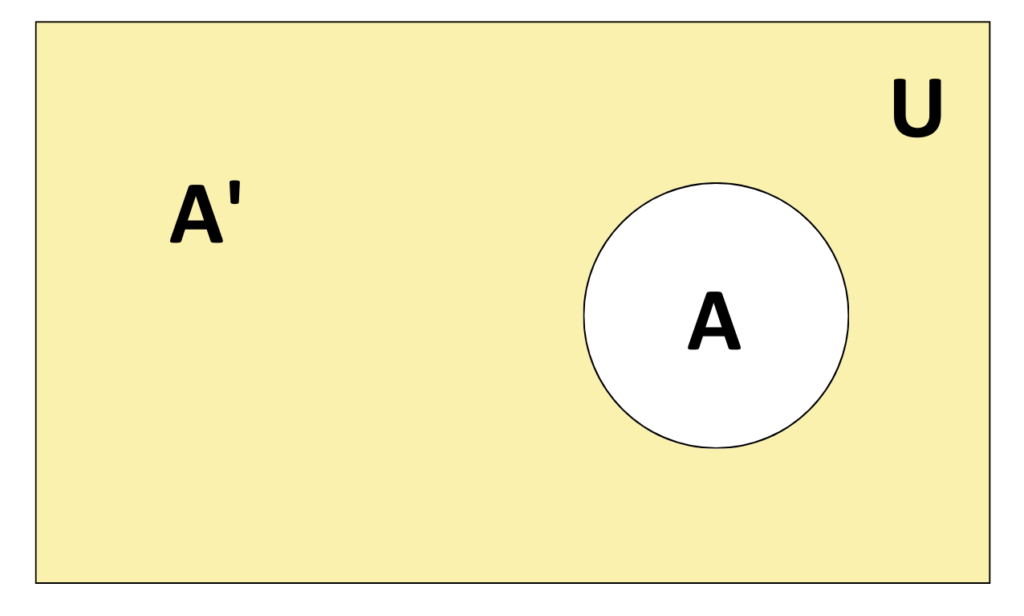
where,

Difference of Set:
- The Difference of set represents that elements in A but not in B or elements in B but not in A.
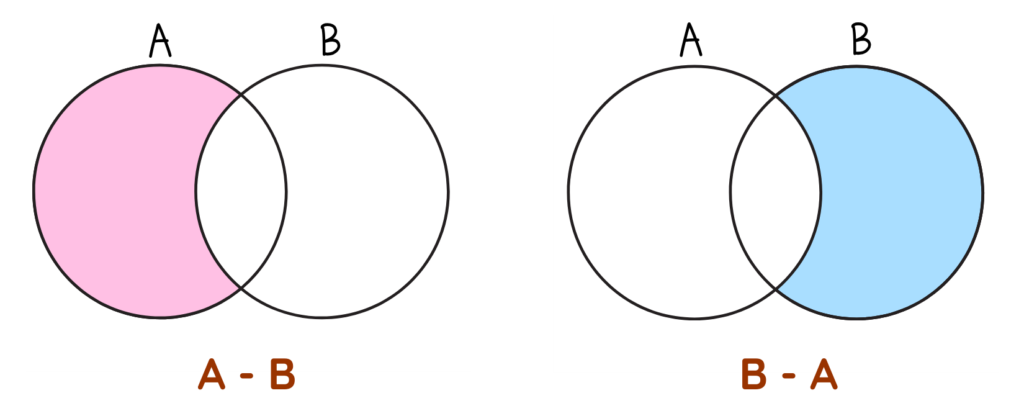
where,
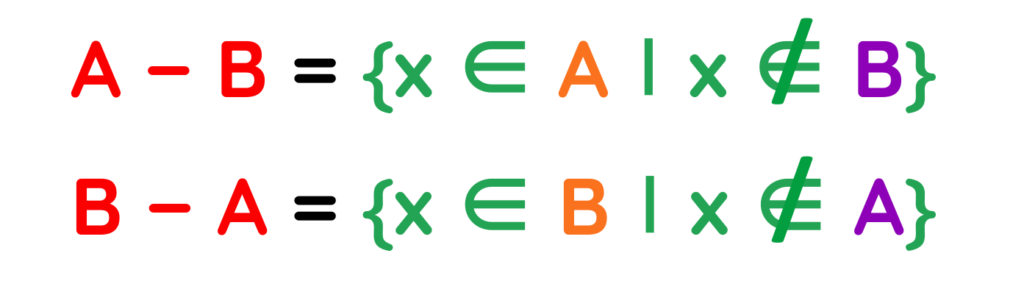
How to Calculate Probability Using Venn Diagram?
- Probability can be visualized and calculated using Venn diagrams with the help of common set operations:
Steps to Calculate Probability Using a Venn Diagram
- Step #1: Define the Sample Space
- Step #2: Define the Events
- Step #3: Draw the Venn Diagram
- Step #4: Calculate the Probabilities
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: Roll a fair 6-sided die. Define two events
- Event A: Roll an even number
- Event B: Roll a number > 3
Find the Probability of P(A) and P(A and B).
Solution:
Step #1: Define the Sample Space
All possible outcomes:
S = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
- Total outcomes = 6
Step #2: Define the Events
- Event A: {2, 4, 6}
- Event B: {4, 5, 6}
Step #3: Draw the Venn Diagram
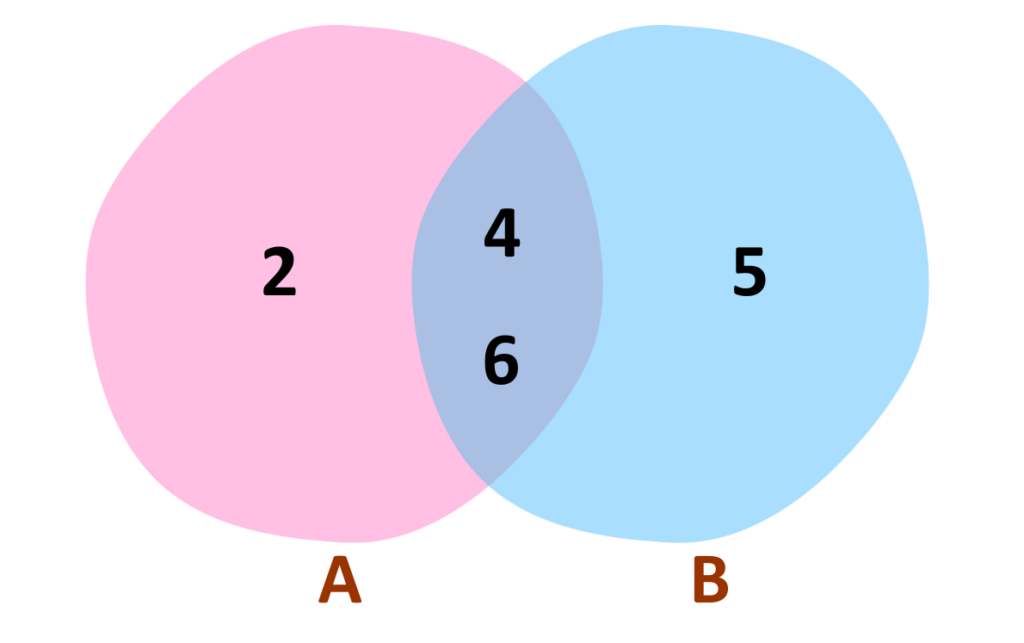
Step #4: Calculate the Probabilities
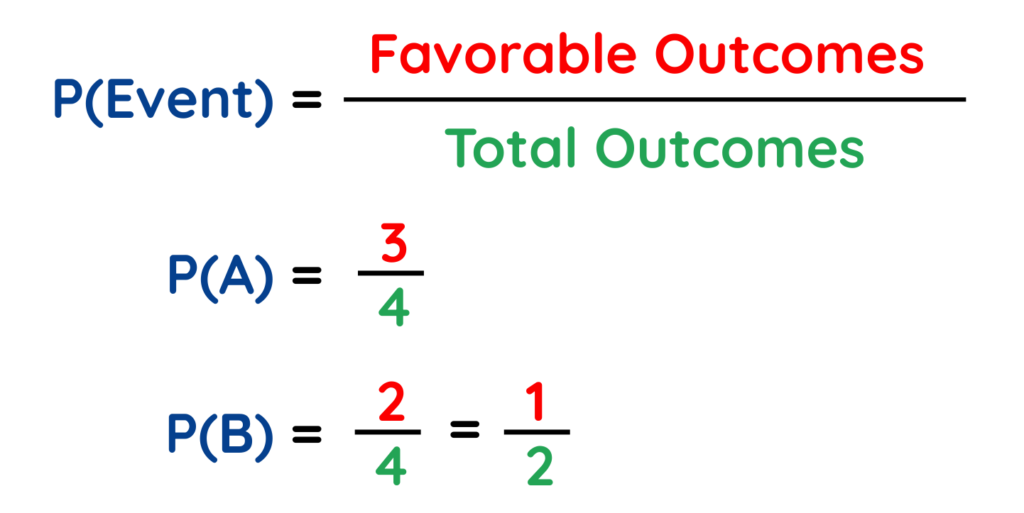
Probability of an event,
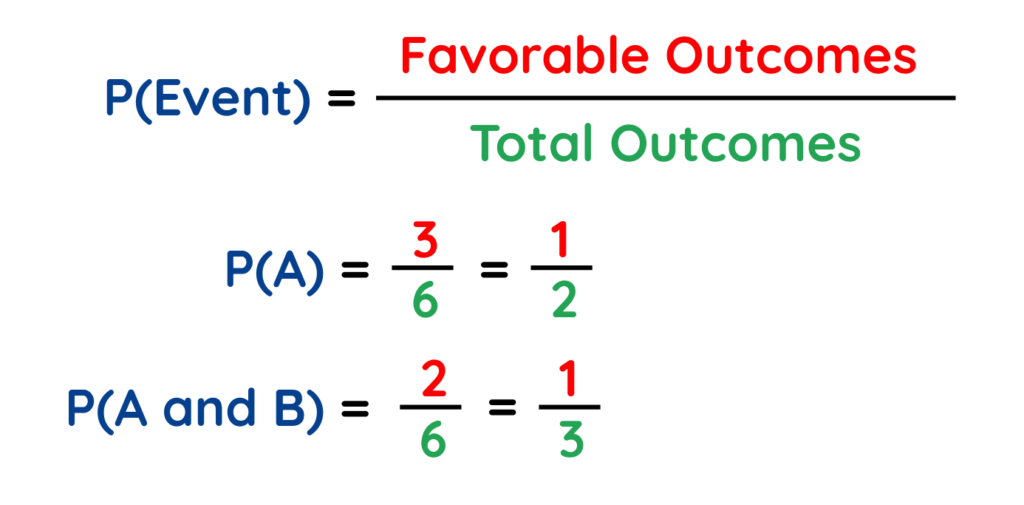
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
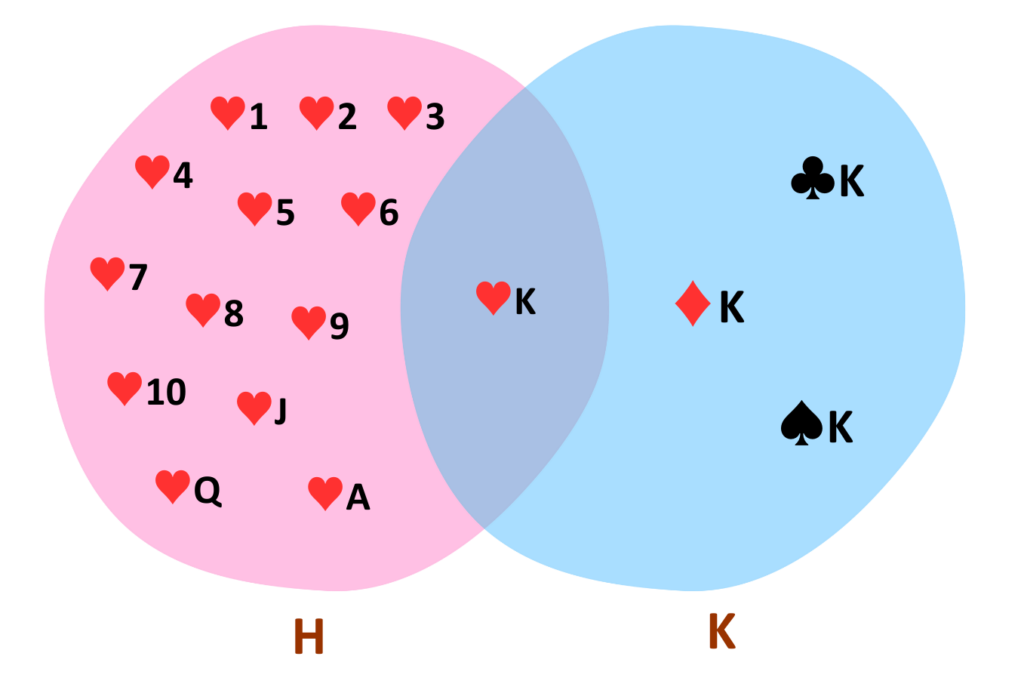
Problem: Draw 1 card from a standard 52-card deck. Define two events:
- Event H: Draw a Heart(♥)
- Event K: Draw a King (♠K, ♥K, ♦K, ♣K)
Find the Probability of P(H), P(K) and P(not H).
Solution:
Step #1: Define the Sample Space
All possible outcomes:
- Total cards = 52
- Hearts = 13
- Kings = 4
Step #2: Define the Events
- Event H = 13 cards
- Event K = 4 cards
- H ∩ K (King of Hearts) = 1 card (♥K)
Step #3: Draw the Venn Diagram
Step #4: Calculate the Probabilities
Probability of an event,
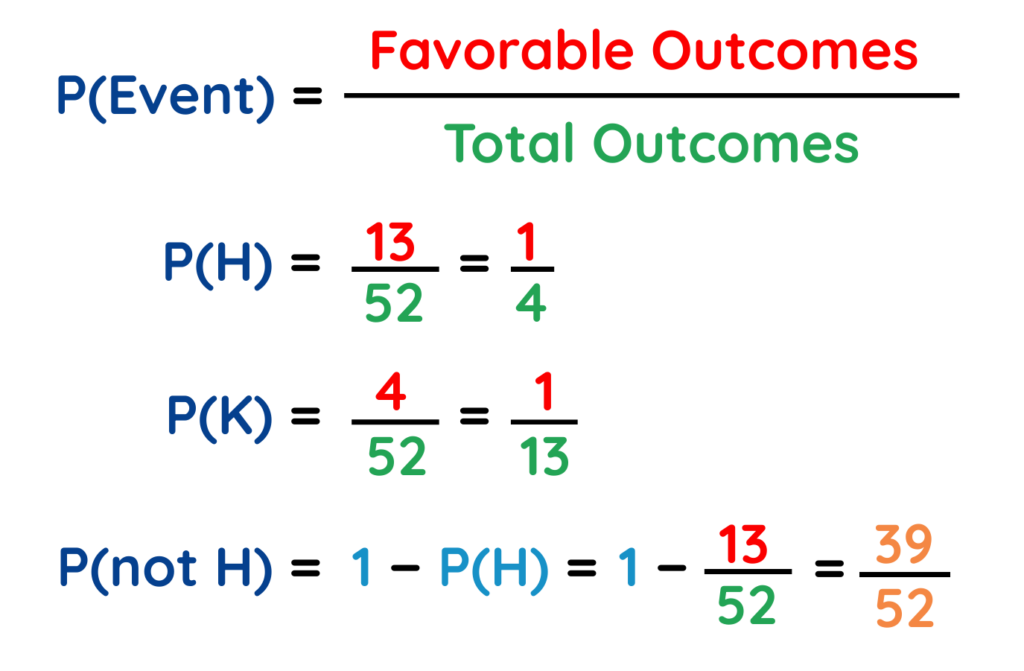
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
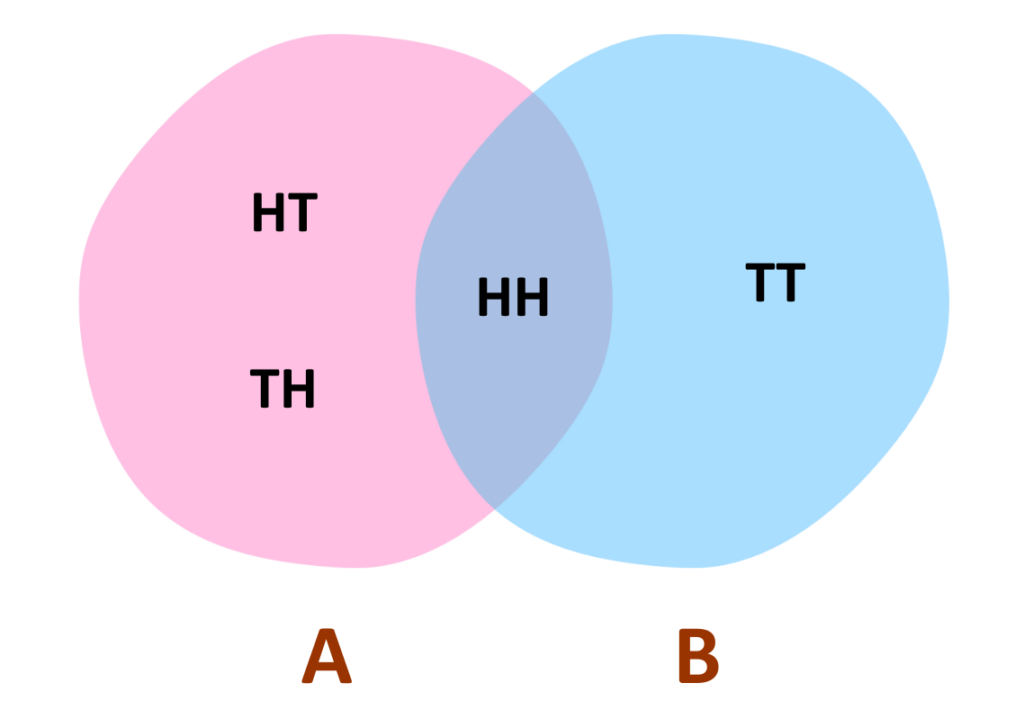
Problem: Toss two fair coins A and B. Define two events:
- Event A: At least one Head appears
- Event B: Both coins show the same face
Find the Probability of P(A) and P(B).

Solution:
Step #1: Define the Sample Space
All possible outcomes:
S = {HH,HT,TH,TT}
- Total outcomes = 4
Step #2: Define the Events
- Event A (At least one Head) = {HH, HT, TH}
- Event B (Same face) = {HH, TT}
- A ∩ B (Both A and B) = {HH}
Step #3: Draw the Venn Diagram
Step #4: Calculate the Probabilities
Probability of an event,