Electrolytic Process – GCSE Chemistry
Introduction
- The Electrolytic processes are basically a method in which we use electricity to decompose a ionic compound/solution into its constituent elements.
- The apparatus in which the process occurs is called Electrolytic cell, it involves electrodes, battery and an electrolyte(ionic compound).
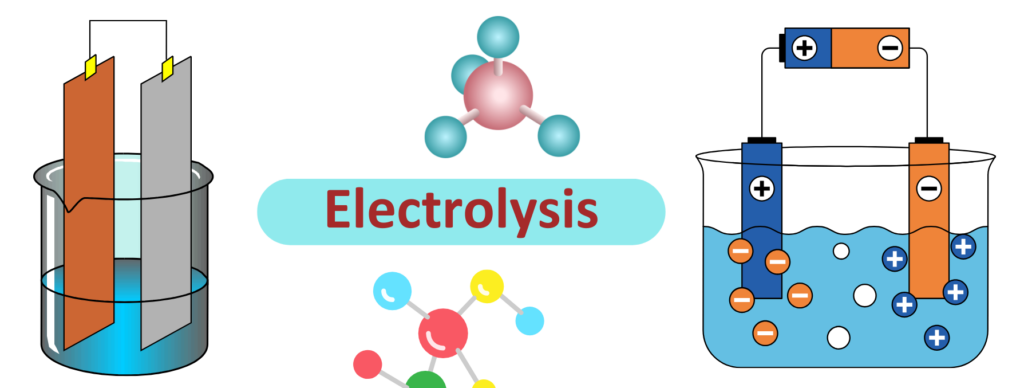
- The process of Electrolysis is used in processes like Electroplating, Water Electrolysis and Purifying Metal etc.
Electrolyte
- An Electrolyte is a substance that produces ions when dissolved in water (or in molten state).
- Electrolytes conduct electricity through movement of ions. Electrolytes are crucial in various applications.
Characteristics of Electrolyte
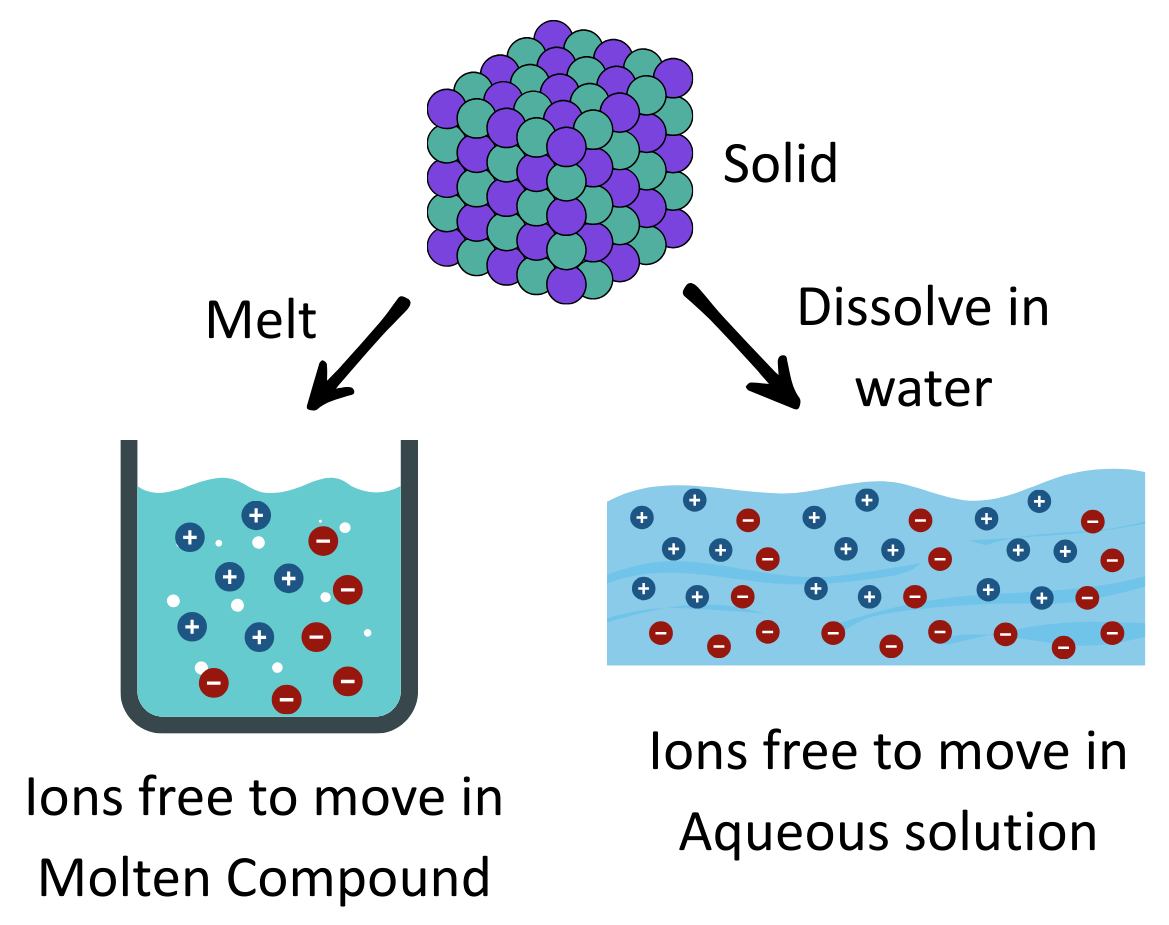
- Ionisation/Dissociation: When electrolytes are in soultiion or when they melt they ions become free to move.
- Conductivity: The free ions of electrolytes in solution or molten state carry electricity.
- Electrolysis: They allow electrochemical reaction (Example: Decomposition by electric current)
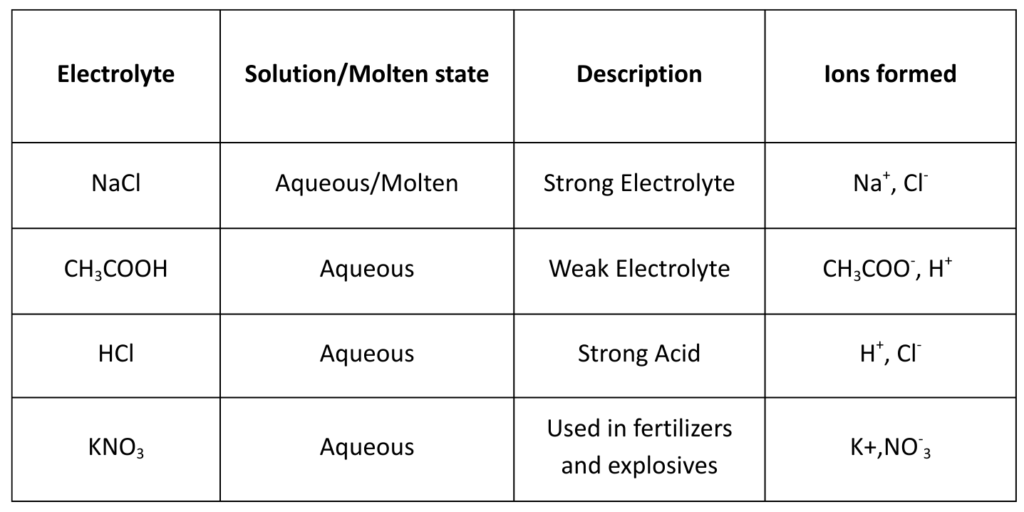
Types of Electrolytes
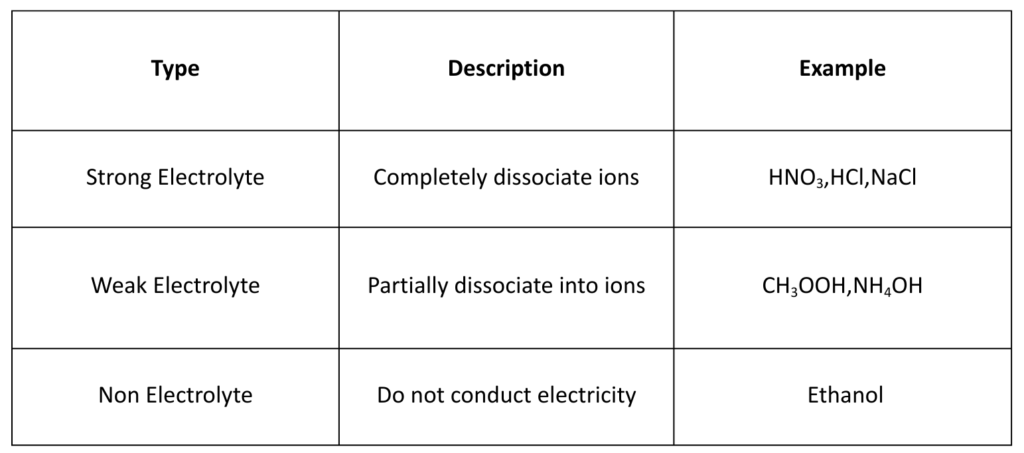
Example of Electrolytes with free ion movement
Basics of Electrolysis
- Electrolytes are main components of batteries as they contain electrodes that carry ions, Electrolytes are also used in Electroplating.
Equipment
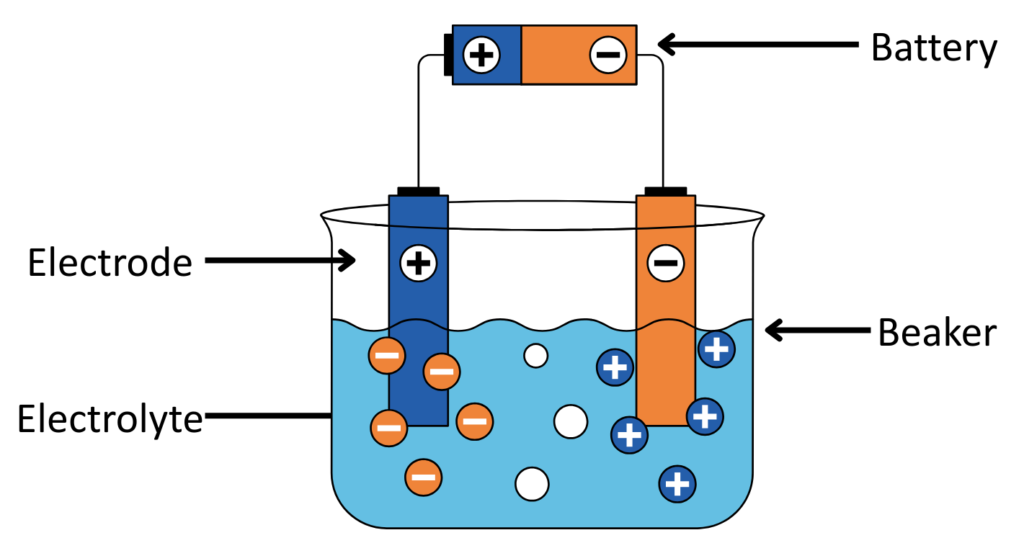
- The Equipment of Electrolytic cell consist of –
- Electrolyte: Ionic compound( a Solution or Molten compound)
- Electrode: A conductor that carries current into and out of substance
Types of Electrolysis
- 1. Molten Electrolysis
- 2. Aqueous Electrolysis
- 3. Water Electrolysis
- 4. Electrolytic Refining
- 5. Electroplating
Example of Electrolysis
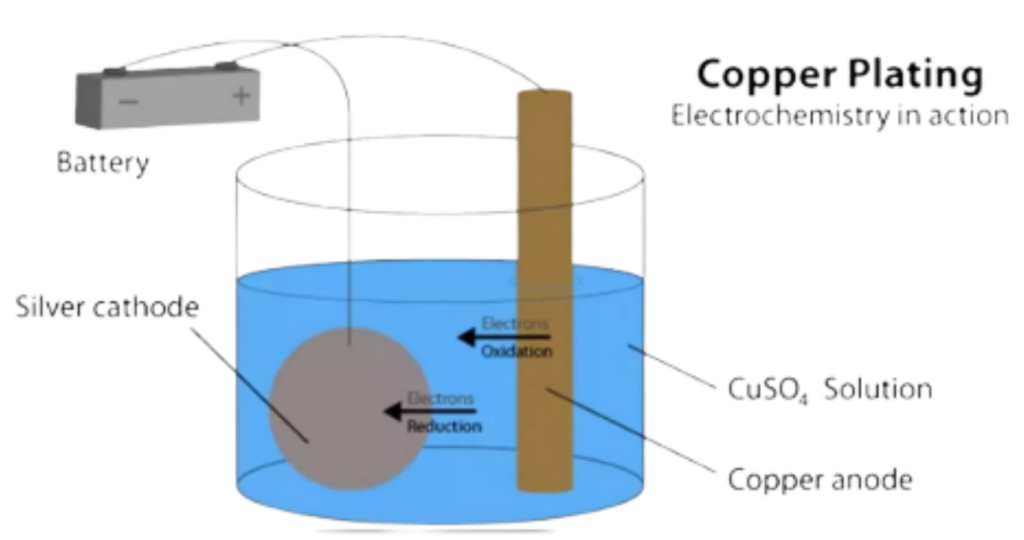
- Here is an example in which Electrolysis of Copper Sulphate (CuSO4) solution is explained in detail –
- A beaker is taken in which CuSO4(Electrolyte) and two electrodes connected with a battery are present.
- When electricity is passed trough battery then the current flow starts in electrodes.
- The solution then starts decomposing into ions of its constituent elements and the positive ions Cu2+ and H+ gets attracted towards the negative Cathode, in a similar way the negative ions OH–, SO42- gets attracted towards the positive Anode.
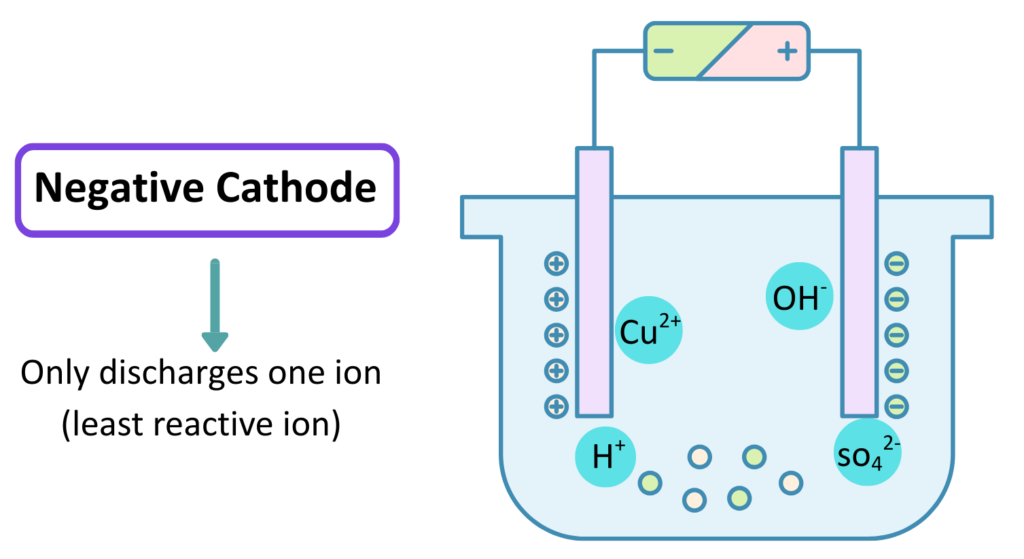
- Copper ions gets discharged to form Copper metal which deposits at the cathode. Chemical Reaction –

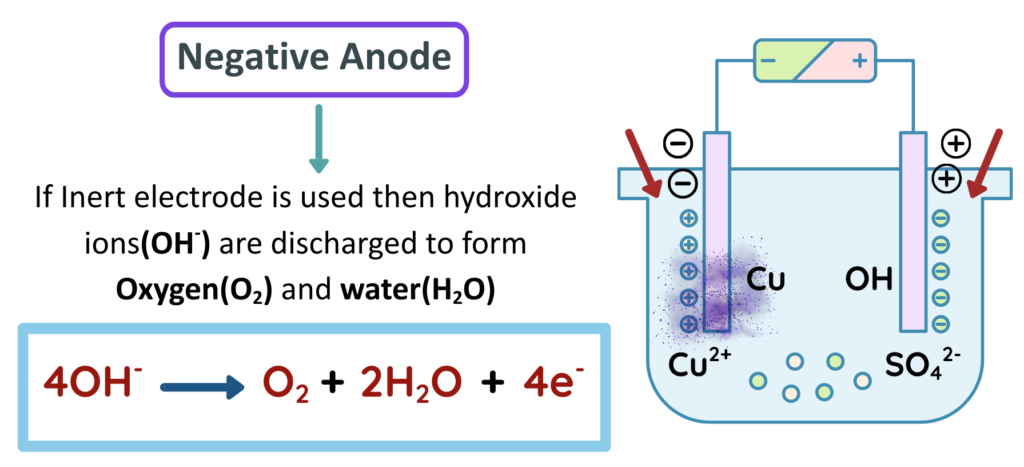
If the Anode is made of Copper it will dissolve in the solution as Cu2+ while these ions in the solution deposit at Cathode.
Conclusion
- The Electrolysis of CuSO4 involves transfer of Cu2+ ions from solution to cathode, where they are reduced and deposited as copper metal. If Inert electrodes are used then Oxygen is produced at Anode. Sulphate ions remain in solution. If copper electrodes are used, the anode dissolves and form the copper ions in solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Electrolysis is the process in which electrodes are used to decompose the electrolyte(solution) into ions of its constituent elements.
Electrodes are used in an Electrolytic cell as they can conduct electricity(allow electron flow). Thus, in brief electrodes play the role to discharge the ions present in solution by the process of oxidation and reduction.
Yes, Electrolytic process is widely used in purifying metals. Some of the examples include Copper electrolytic refining, Silver electrolytic refining etc. This method is widely used for such purpose because it provides high purity and can remove selective impurities based on ionic criteria.
Water Electrolysis, Molten Electrolysis( saparation of lead from Lead Bromide), Electroplating(Aqueous Solution: Copper plating).
Inert Electrode like Platinum and Graphite, reactive electrodes like Copper and Zinc.
Table of Content

