Stopping Distances– GCSE Physics
Introduction
- The Total distance a vehicle covers from the moment a driver identifies a hazard until the vehicle comes to a complete stop, is known as Stopping Distances.
This concept is important:
- To Prevent Accidents
- To Be a More Aware Driver
- To Drive Safely in Different Conditions
- Understand how long it really takes to stop

What is Stopping Distances?
- Stopping Distance is how for a car moves between the driver noticing something in front of them and the car coming to a stop.
- It’s affected by two main features,
1. Thinking Distance:
- The Distance the vehicle travels while the driver reacts and decides to brake.
- It depends on reaction time (typically 0.5–2 seconds).
- Affected by driver alertness, distractions, fatigue, and intoxication.
2. Braking distance:
- The Distance the vehicle travels after the brakes are applied until it fully stops.
- It depends on speed, road conditions, vehicle weight, and brake efficiency.
- Affected by wet/icy roads, worn tires, or faulty brakes.
So,


Factors That Affect Stopping Distance
- Speed — Higher speeds mean longer stopping distances.

- Driver reaction time — Affected by tiredness, distractions, alcohol, or drugs.

- Road conditions — Wet, icy, or uneven roads increase braking distance.

- Vehicle condition — Things like brake quality and tire grip matter too.

How to Calculate Stopping Distance
- It involves two components: Thinking Distance and Braking Distance.
- The Total Stopping Distance is the sum of these two.

Where,
Thinking Distance:
- The distance traveled while the driver reacts before applying the brakes is called the Thinking Distance.

- Speed = Vehicle speed (Typically in m/s).
- Reaction time = Around 0.7 to 1.5 seconds, depending on the driver and conditions.
Braking Distance:
- The distance traveled while the vehicle decelerates to a stop after the brakes are applied is called the Braking distance.

- v = Speed in m/s.
- a = Deceleration in m/s² (depends on brakes, road surface, tires, weather, etc.)
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: If a car is traveling at 72 km/h. The driver has a reaction time of 1.5 seconds, and the car decelerates at 6 m/s² when the brakes are applied. Calculate the Total Stopping Distance.
Solution:
Step #1: Convert speed to m/s
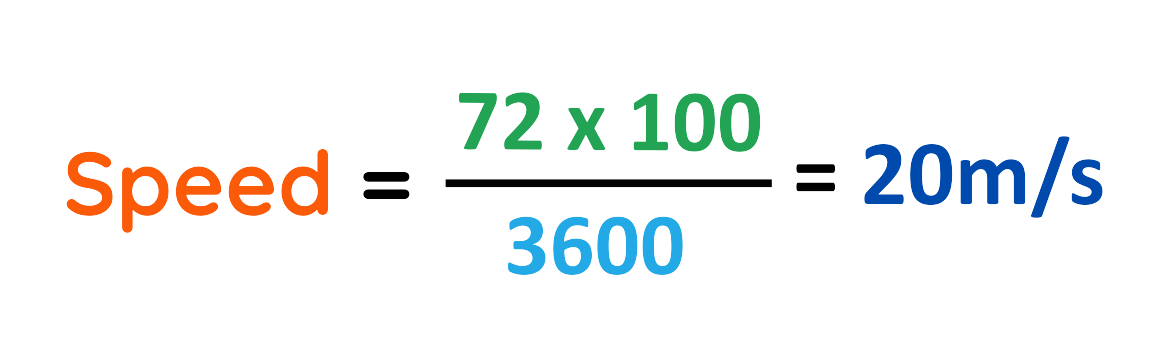
Step #2: Calculate Thinking Distance:

Step #3: Calculate Braking Distance:
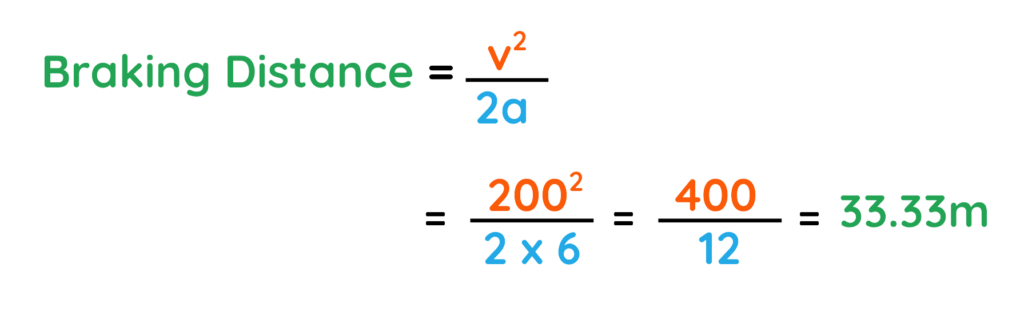
Step #4: Calculate Total Stopping Distance:

Total Stopping Distance is 63.33m.
Final Answer: 63.33m
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A motorcycle is moving at 54 km/h. The rider’s reaction time is 1.2 seconds. The motorcycle decelerates at 7 m/s² after braking. Find the Total Stopping Distance.
Solution:
Step #1: Convert speed to m/s

Step #2: Calculate Thinking Distance:

Step #3: Calculate Braking Distance:

Step #4: Calculate Total Stopping Distance:

Total Stopping Distance is 34.07m.
Final Answer: 34.07m
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A truck travels at 90 km/h. The driver reacts in 2 seconds. The truck decelerates at 5 m/s². Find the total stopping distance.
Solution:
Step #1: Convert speed to m/s

Step #2: Calculate Thinking Distance:

Step #3: Calculate Braking Distance:

Step #4: Calculate Total Stopping Distance:

Total Stopping Distance is 112.5m.
Final Answer: 112.5m
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Stopping distance is the total distance a vehicle travels from the moment the driver perceives a hazard until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. It includes thinking distance (reaction time) and braking distance.
Solution:
- Speed (most critical, braking distance ∝ speed²)
- Road conditions (wet, icy, or dry surfaces)
- Tire condition & brake efficiency
- Driver reaction time (affected by fatigue, distractions, alcohol)
Solution:
Higher speeds exponentially increase braking distance (e.g., doubling speed quadruples braking distance).
Example:
At 30 mph, stopping distance ≈ 23 meters (75 ft)
Solution:
Thinking distance = Distance covered during driver’s reaction time.
Braking distance = Distance needed to stop after brakes are applied.
Solution:


