Rotational Force – GCSE Physics
Introduction
- Rotational force is the force that causes an object to rotate around a point or axis (pivot point) instead of moving in a straight line.
- This force is also called:
Moment
Torque
- Rotational force plays a crucial role in daily life and machines because it helps us turn, rotate, or twist objects using force applied at a distance from the axis.
Daily-Life Example:

What is Moment?
- A Moment (in physics) refers to the rotational effect produced by a force acting at a distance from a pivot point (axis of rotation).
- It is essentially a turning force that causes an object to rotate.
- Moment is another name for rotational force.
Moment Formula:

Where:
- M = Moment in – Nm
- F = Force applied in – N
- d = Perpendicular distance from the pivot in – m
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A student applies a force of 20 N at the end of a spanner to loosen a nut. The distance from the nut to the point where the force is applied is 0.3 m. Calculate the moment (rotational force) about the nut.
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- F = 20N
- d = 0.3m
Step #2: Using the formula:
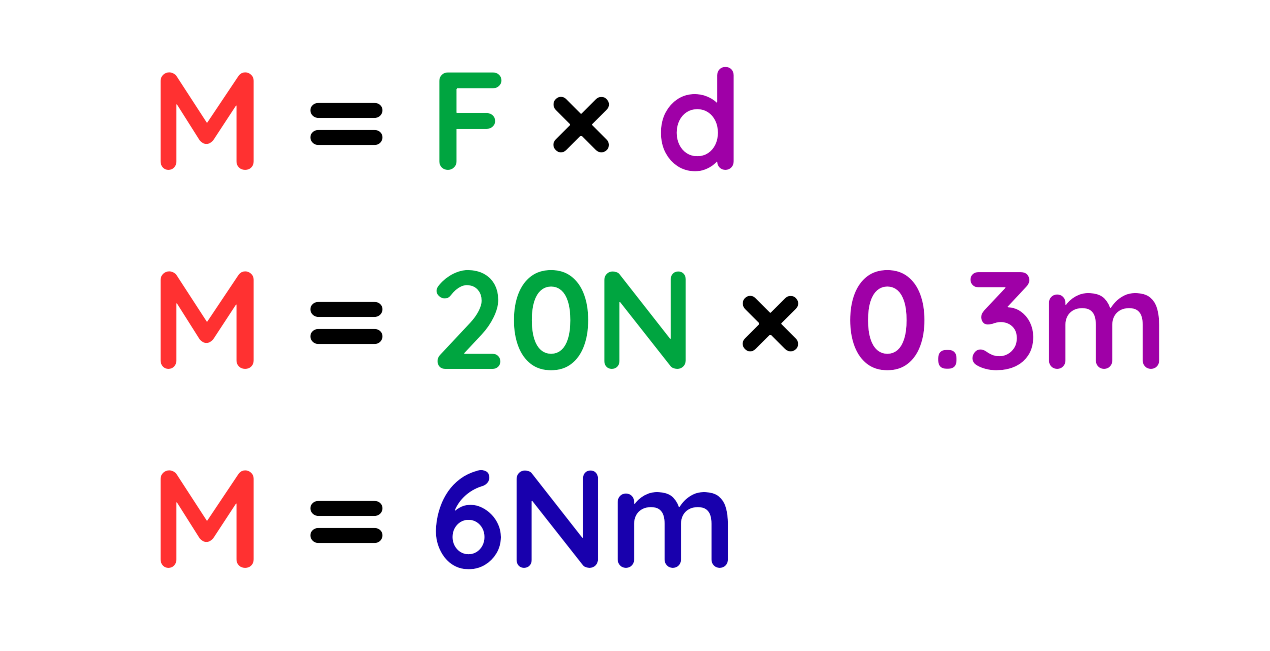
The moment about the nut is 6 Nm.
Final Answer: 6 Nm
How Is Moment Related To Torque?
- Moment tells us how strong the turning effect of a force is where torque is a special type of moment that not only makes something turn but also causes it to spin faster or slower (rotational acceleration) around an axis.
- Torque is another name for moment; both mean the turning effect of a force about a point.
- Torque is a specific term for the turning effect around the axis of rotation, especially used in mechanics, engines, and rotational systems.
- Example: When you push a door to open it, you are using moment and torque together: Moment explains how your push causes the door to rotate around its hinges and torque explains how strong that rotation will be.
Formula For Both:
When the force is perpendicular to the pivot point:

Where:
- F = Force applied in – N
- d = Perpendicular distance from the pivot in – m
When the force is at any angle or not perpendicular:
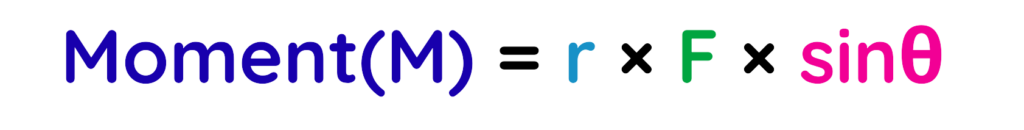
Where:
- F = Force
- r = Distance from axis to point where force is applied.
- θ = Angle between F and r.
How to Calculate Rotational Force?
- Calculation for rotation in terms of moment involves finding how much a force causes an object to turn around a point or pivot.
To Calculate Moment in Physics, We Follow These Simple Steps:
- Step#1: Identify the given values.
- Step#2: Apply the formula and plug in the values.
- Step#3: Calculate the moment.
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A force of 12 N is applied perpendicularly at a distance of 0.4 m from the hinge of a gate. Calculate the moment.
Solution:
Step#1: Identify the given values:
Given
- F = 12N
- d = 0.4m
Step#2: Apply the Formula and plug in the values:
The formula for moment is:

Now plug in the values:

Step#3: Calculate the Moment:

The moment is 4.8 Nm in the anticlockwise direction.
Final Answer: 4.8 Nm
 Solved Example:
Solved Example:
Problem: A flagpole painter applies a force of 150 N perpendicularly on a brush attached to a rope that is tied 250 cm from the base of the flagpole to rotate and clean it. Calculate the moment about the base of the flagpole.

(Rotational Force GCSE Questions)
Solution:
Step#1: Identify the given values:
Given
- F = 150N
- d = 250cm
Step#2: Apply the Formula and plug in the values:
Convert cm to m:

The formula for moment is:

Now plug in the values:

Step#3: Calculate the Moment:

The moment about the base of the flagpole is 375 Nm in the anticlockwise direction.
Final Answer: 375 Nm
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A shopkeeper pushes down on the handle of a heavy shop shutter with a force of 400 N perpendicular to it, producing a moment of 800 Nm about the hinge. Find the distance from the hinge where the force is applied.

Solution:
Step#1: Identify the given values:
Given
- F = 400N
- M = 800Nm
Step#2: Apply the Formula and plug in the values:
The formula for moment is:

Rearranged it:
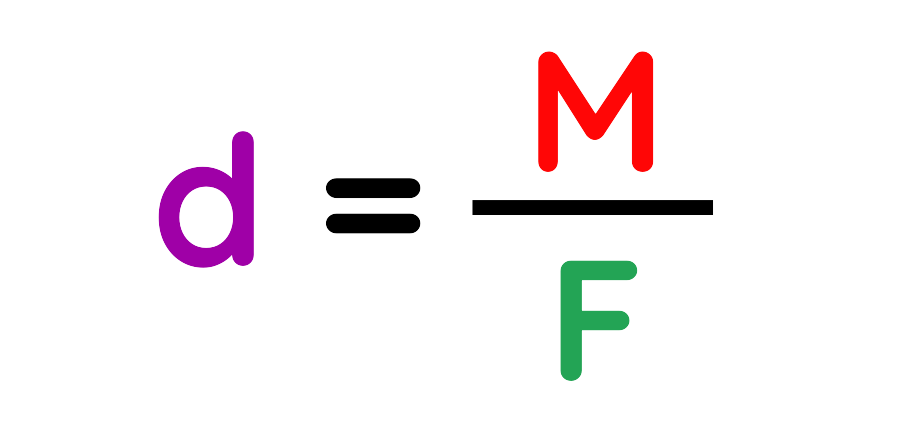
Now plug in the values:

Step#3: Calculate the Moment:
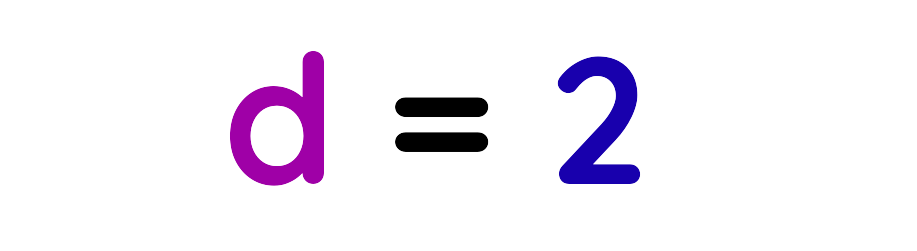
The perpendicular distance is 2 meters.
Final Answer: 2 Meters
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: Child B weighs 350 N and sits 1.6 m from the pivot on a balanced seesaw. Calculate the moment of child B about the pivot. Give your answer in newton-metres (Nm).

Solution:
Step#1: Identify the given values:
Given
- F = 350N
- d = 1.6m
Step#2: Apply the Formula and plug in the values:
The formula for moment is:

Now plug in the values:

Step#3: Calculate the Moment:

The moment is 560 Nm.
Final Answer: 560 Nm.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Rotational force (torque or moment) is the tendency of a force to cause an object to rotate around a point or axis.
Solution:
Yes, both measure rotational effect of a force.
Solution:
Formula for moment:
M = F × d
Solution:
Newton-meter (Nm).
Solution:
- If the force causes clockwise rotation – moment is negative.
- If it causes anticlockwise rotation – moment is positive.
Solution:
The moment increases, making it easier to rotate heavy objects.
Solution:
Opening a door, using a spanner, turning a steering wheel, or pushing a swing are daily examples of rotational forces.

