Reversible reactions and equilibria - GCSE Chemistry
Introduction
- In many chemical reactions, the reactants change into products, and the products can also change back into the reactants again under certain conditions.
- These reactions are called reversible reactions.
- Reversible reactions are important because-
In Industries:
- These reversible reactions help industries to control conditions for maximum product yield.

In Real-life:
- These reversible reactions help us understand environmental cycles and are used in daily life (fizzy drinks) to maintain equilibrium in systems.

What is Reversible Reaction?
- In some chemical reactions, when the products of the reaction can react to produce the original reactants then it is called reversible reactions.
- These reactions are shown with a double arrow (⇌) in chemical equations, meaning they can go both ways:
Forward direction (→): Reactants turn into products.
Backward direction (←): Products turn back into reactants.
So,

For Example-
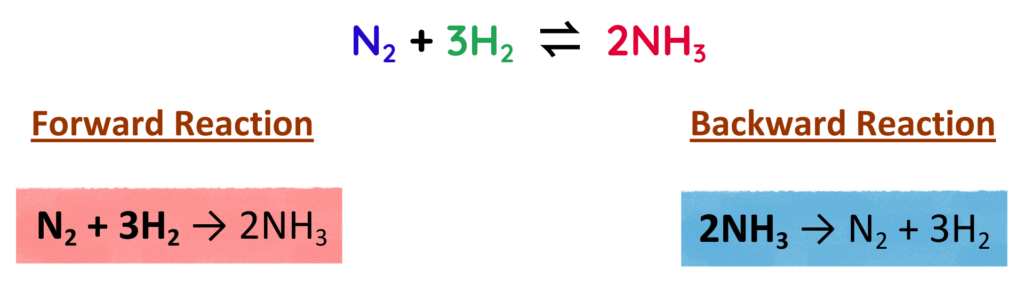
- We change the direction of a reversible reaction by changing the conditions.
- So, if the forward reaction happens when it is hot, cooling it down can make the backward reaction happen instead.
For Example: Ammonium chloride
- When we heat ammonium chloride, it breaks down into ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases:
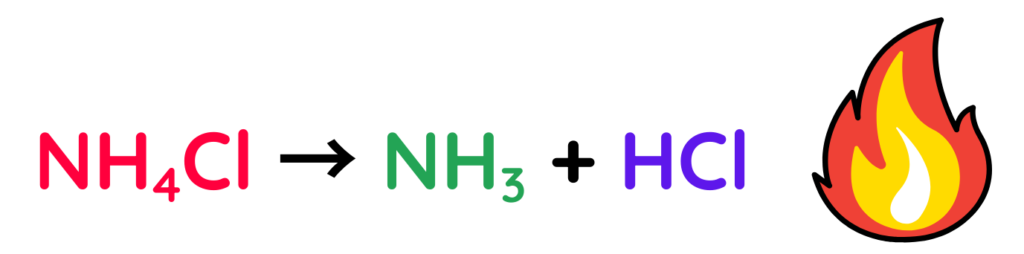
- If you cool the gases, they react back to form solid ammonium chloride:

What is Equilibrium?
- Equilibrium is the state in a reversible reaction when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction.
- This means that the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time.
- This is called dynamic equilibrium, where reactions are still occurring, but there is no overall change in the amounts of reactants and products.
Example:

Where:
- N2 = Nitrogen
- 3H2 = Hydrogen
- 2NH3 = Ammonia
- At equilibrium, ammonia is being formed and broken down at the same rate, so the amount of ammonia stays the same.
What is Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions in Equilibrium?
- In reversible reactions, when the system is at equilibrium, whether heat is taken in or given out during the forward and backward reactions will decide how the equilibrium shifts when you change the temperature.
- These reactions are-
Exothermic Reaction:
- A reaction which releases heat to the surroundings is called exothermic reaction.
- Example: Formation of ammonia in the Haber Process.

- In this reaction heat is released during the forward reaction.
Endothermic Reaction:
- A reaction which absorbs heat from the surroundings is called endothermic reaction.
- Example: Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate.

- In this reaction heat is absorbed for the forward reaction to happen.
What Are The Factors Which Affect The Position of Equilibrium In a Reversible Reaction?
- When a system in dynamic equilibrium is disturbed, it shifts to oppose the change and restore equilibrium.
- Three main factors affect the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction:
Effect of changing temperature:
- If we increase the temperature, equilibrium moves in the direction of the endothermic reaction.
- If we decrease the temperature, equilibrium moves in the direction of the exothermic reaction.
Effect of changing concentration:
- If we change the concentration of a reactant or product, the system is no longer at equilibrium. The concentrations will adjust until a new equilibrium is reached.
- If the concentration of reactants increases, then equilibrium shifts right and making more products.
- If the concentration of products decreases, then equilibrium shifts left, making more reactants.
Effect of changing pressure:
- Increase in pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with fewer gas molecules.
- Decrease in pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with more gas molecules.
Frequently Asked Questions
A reaction where products can turn back into reactants under certain conditions.
Using the ⇌ symbol, showing the reaction can go in both directions.
It is when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backward reaction, so concentrations stay constant.
No, the reaction continues in both directions, but there is no overall change in amounts.
- Increasing temperature moves equilibrium towards the endothermic direction.
- Decreasing temperature moves equilibrium towards the exothermic direction.
- Increasing pressure shifts equilibrium to the side with fewer gas molecules.
- Decreasing pressure shifts it to the side with more gas molecules.

