Momentum– GCSE Physics
Introduction
- Momentum is a measure of an object’s resistance to stopping or changing its motion.
- It helps us to understand motion and explain collisions.
Examples:


What is Momentum?
- Momentum is a measure of how much Motion an object has.
- It represents the quantity of motion an object has and how difficult it is to stop or change its motion.
Key properties:
- A heavier or faster-moving object has more Momentum.
- Momentum depends on both the speed and the direction of motion.
- In a closed system,
- Total momentum before and after a collision remains constant.
Example:
If a Truck and a Car are moving at the same speed, the Truck has more momentum because it has more mass.

A small car hitting a truck won’t move the truck much, because the truck has way more Momentum.
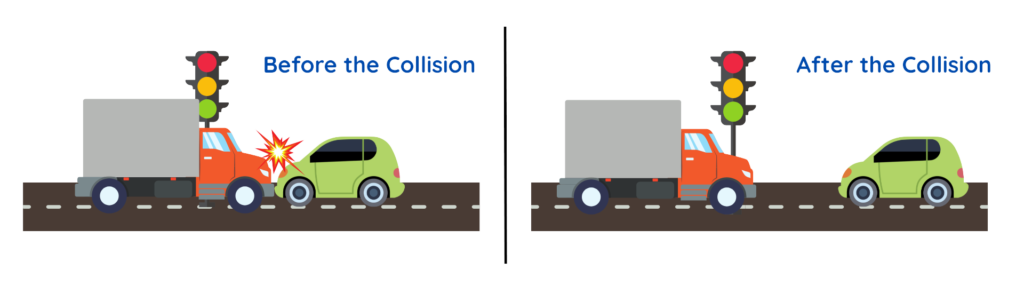
How to calculate Momentum?
- Momentum depends on Mass and Velocity.
- It is a Vector Quantity.
- Mathematically,

Where,
- p = Momentum
- m = Mass
- v = Velocity
SI Unit: Kilogram-meter per second (kg.m/s)
 Solved Example: Momentum GCSE Questions
Solved Example: Momentum GCSE Questions
Problem: A car has a mass of 1000 kg and is moving at a velocity of 20 m/s in North side. What’s the Momentum of car in the direction it’s moving?
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- m = 1000 kg
- v = 20 m/s
Step #2: Using the Formula:

Step #3: Putting the values:

The car’s momentum is 20,000 kg·m/s in the direction it’s moving.
Final Answer: 20,000 kg·m/s
Can Momentum be Positive or Negative?
- Yes, Momentum can be both positive and negative, which indicates the direction of an object’s motion.
Positive Acceleration:
Directional Reference:
- Object moves in the defined positive direction (e.g., right/east/up/north).
Meaning of Signs:
- +p: Object moves in the positive direction.
Example:
Problem: A 10 kg soccer ball is kicked eastward at 5 m/s.
Solution: Let East = positive (+) direction.

Negative Acceleration:
Directional Reference:
- Object moves in the opposite (negative) direction (e.g., left, west, down)
Meaning of Signs:
- –p: Object moves in the negative direction.
Example:
Problem: A 10 kg soccer ball is kicked westward at 5 m/s.
Solution: Let West = negative (-) direction.
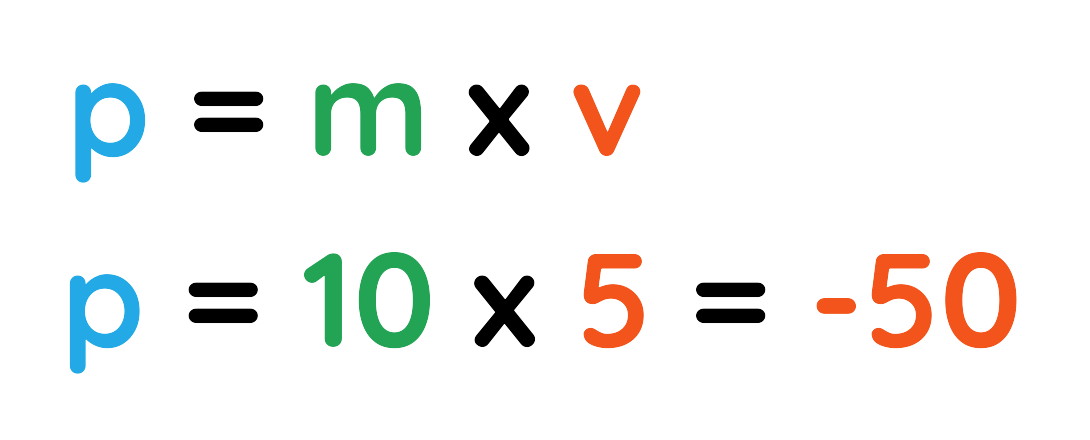
Relationship Between Force, Momentum & Acceleration
- Momentum and Acceleration are fundamental concepts in physics, connected through Newton’s Second Law of Motion.
- Momentum depends on velocity, any change in velocity (i.e. acceleration) causes a change in momentum.

But Since,

And Momentum is:

Then change in momentum is:

Substituting this into equation 1,
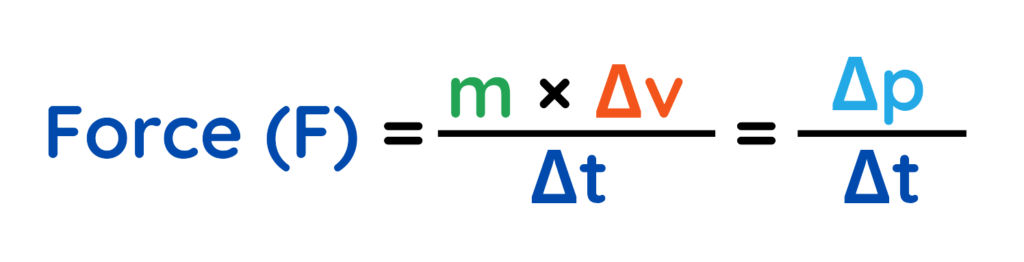
It says:
- The Force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of its Momentum.
- If an object’s momentum changes quickly, a large force is involved.
- If it changes slowly, the force is smaller.
- It can also be written as,

 Solved Example: Momentum GCSE Questions
Solved Example: Momentum GCSE Questions
Problem: A cricket ball of mass 0.2 kg is moving at a speed of 25 m/s. What is the momentum of the ball?
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- m = 0.2 kg
- v = 25 m/s
Step #2: Using the Formula:

Step #3: Putting the values:

The momentum of the cricket ball is 5 kg·m/s.
Final Answer: 5 kg·m/s.
 Solved Example: Momentum GCSE Questions
Solved Example: Momentum GCSE Questions
Problem: A car of mass 1200 kg moves backward with a velocity of 5 m/s. What is its momentum?
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- m = 1200 kg
- v = 5 m/s
Step #2: Using the Formula:

Step #3: Putting the values:
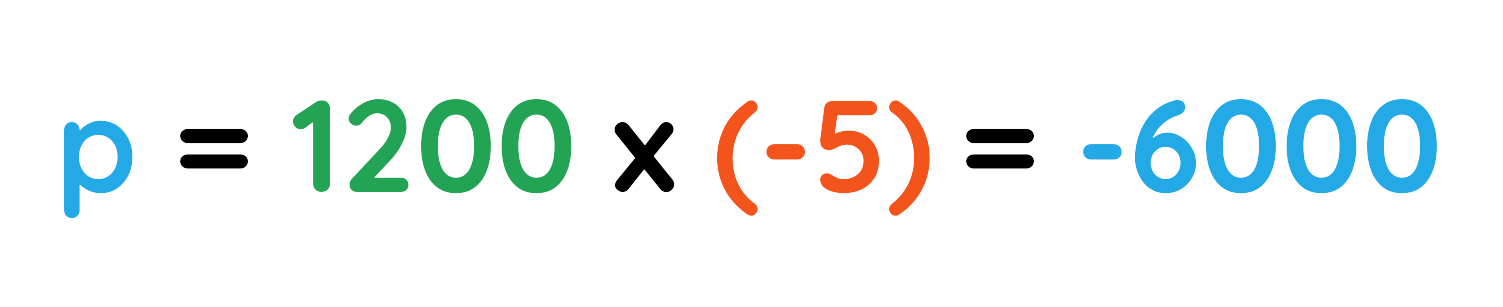
The momentum of the car is -6000 kg·m/s.
Final Answer: -6000 kg·m/s.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Momentum is a measure of the motion of an object and is the product of its mass and velocity. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
Solution:
The principle states that in a closed system (no external forces acting), the Total momentum before a collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision
Solution:
Formula for Momentum:
p = m x v
Where,
- p = Momentum
- m = Mass
- v = Velocity
Solution:
SI Unit for Momentum is kilogram-meter per second (kg·m/s)
Solution:
Yes, Momentum is a Vector Quantity which depends on both direction and magnitude.

