Energy Efficiency– GCSE Physics
Introduction
- The concepts of Energy and Power Efficiency are essential for understanding how systems use resources and how to optimize them for better performance and sustainability.
- Efficiency is a way of describing how good a machine is at transferring energy into useful forms.
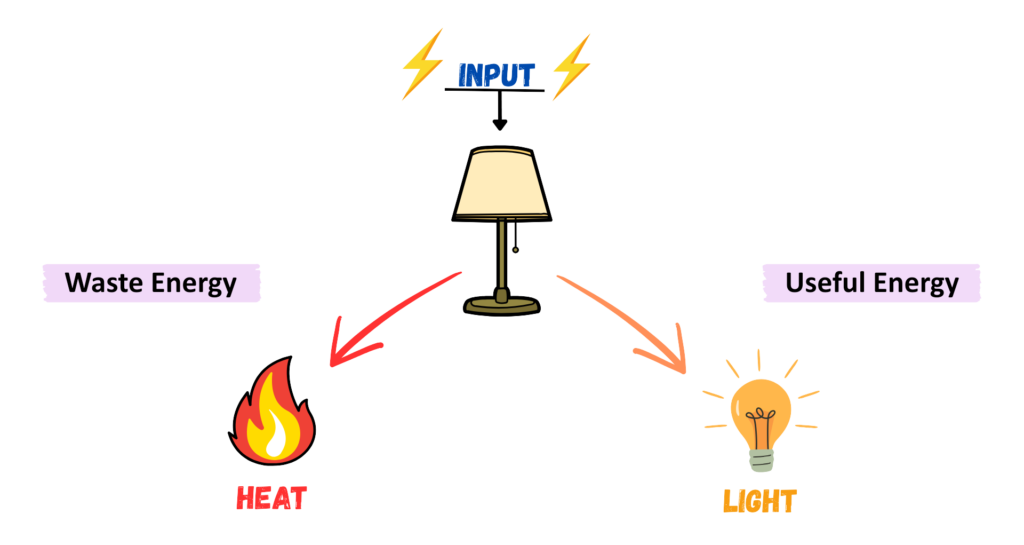
What is Energy Efficiency?
- Energy Efficiency measures how effectively a system, device, or process converts input energy into useful output energy to perform a desired task.
- It measures how efficiently Energy is converted into useful work while minimizing waste.
- Formula:
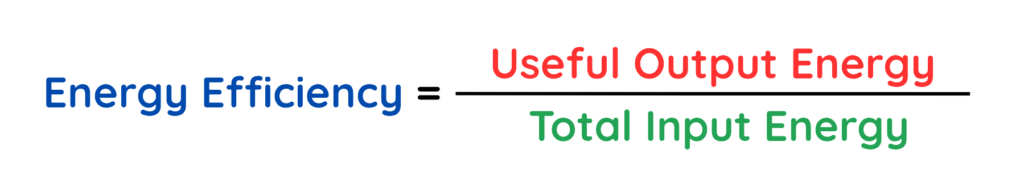
where,
Example:
LED Bulb and Incandescent Bulb:
- An LED bulb converts about 80-90% of the electrical energy into light, with very little wasted as heat.
- An Incandescent bulb, on the other hand, converts only about 10% of the electrical energy into light — the rest is lost as heat.
- The LED bulb is more energy-efficient.
What is Power Efficiency?
- Power efficiency is the ratio of useful output power to the total input power supplied to a system or device.
- It measures how efficiently Power is converted into useful work while minimizing waste.
- Formula:

Where,
- Output power is the power used to perform the desired task.
- Input power is the total power supplied to the system.
- The rest is usually lost as heat, noise, or vibration.
Example:
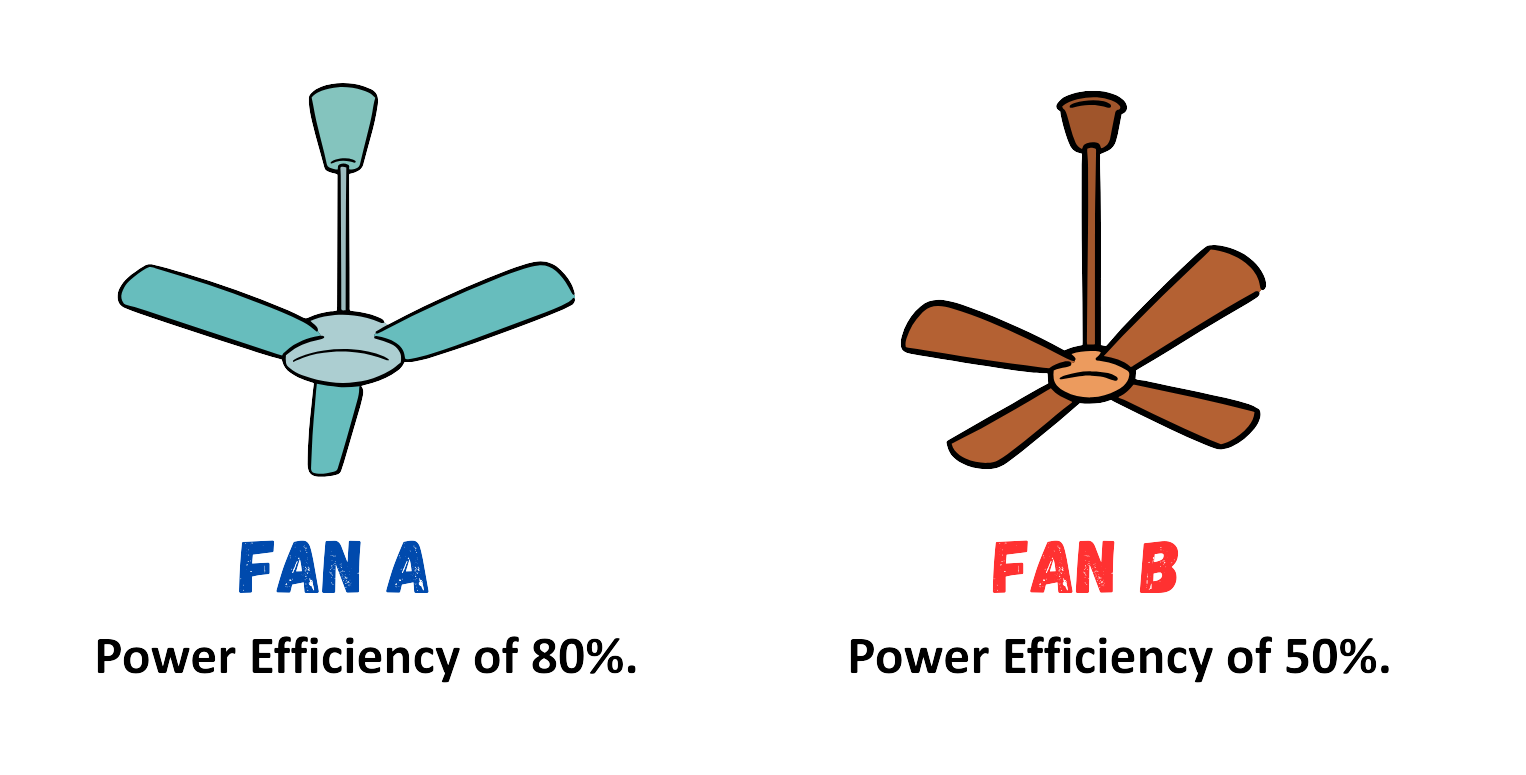
- Fan A is more power-efficient because it converts more of the input power into useful mechanical power, while wasting less power as heat, noise, or friction.
How to Calculate Efficiency?
- Efficiency tells us how well a device or system converts input energy or power into useful output.
- It’s usually expressed as a percentage.
Formula for Energy Efficiency:

Formula for Power Efficiency:

Steps to Calculate Efficiency:
- Step#1: Find the input value (energy or power supplied to the system).
- Step#2: Find the useful output value (energy or power used for the intended purpose).
- Step#3: Apply the formula.
- Step#4: Multiply by 100 to convert it into a percentage.
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A light bulb takes 100 joules of electrical energy and produces 60 joules of light energy. The rest is lost as heat. Calculate the energy efficiency of the light bulb.
Solution:
Step #1: Find the input value
- Total Input Energy = 100 J
Step #2: Find the useful output value:
- Useful Output Energy = 60 J
Step #3: Apply the formula:
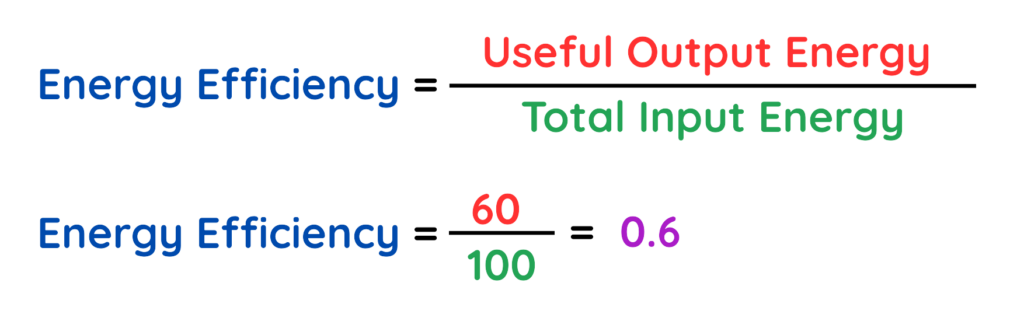
Step #4: Multiply by 100:

The light bulb has an energy efficiency of 60%.
Final Answer: 60%
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A water pump uses 500 watts of electrical power and delivers 400 watts of useful mechanical power to pump water. Calculate the power efficiency of the pump.
Solution:
Step #1: Find the input value
- Total Input Power = 500W
Step #2: Find the useful output value:
- Useful Output Power = 400W
Step #3: Apply the formula:
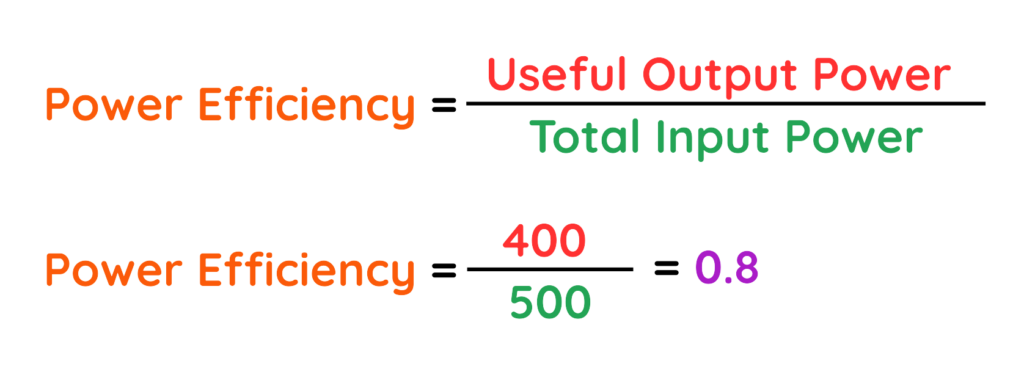
Step #4: Multiply by 100:

The water pump has a power efficiency of 80%.
Final Answer: 80%
Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
Efficiency measures how well something (a machine, device, or system) converts input (like energy) into useful output without wasting resources.
Solution:
We can reduce unwanted energy transfers by using lubrication to reduce friction, insulation to prevent heat loss, and streamlining to reduce air resistance.
Solution:
Energy efficiency means using less energy to do the same job. It helps save money and reduces waste.
Example:
- An LED bulb (energy-efficient) gives the same light as an old incandescent bulb but uses much less electricity.
Solution:
Power efficiency measures how well a device converts input power (electricity) into useful output (like light, motion, or computation) without wasting it as heat.
Example:
- A 90% efficient power supply wastes only 10% of electricity as heat, while a 60% efficient one wastes 40%.
Solution:
- Saves money (lower electricity bills).
- Reduces pollution (less energy waste = fewer power plants needed)

