Acceleration – GCSE Physics
Introduction
- Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time.
- It is a vector quantity.
- It measures the motion of an object.
Real-life Scenario:


What is Acceleration?
- Acceleration is the rate of change of the Velocity of an object with respect to time.

Types of Acceleration:
- Uniform Acceleration – Velocity changes at a constant rate .
Examples:

- Non-Uniform Acceleration – Velocity changes at a varying rate.
Examples:

Acceleration Formula
Basic Acceleration Formula:
- This formula defines Acceleration as the rate of change of velocity over time.

Where:
- a = acceleration (m/s2)
- Δv = change in velocity (v − u)
- Δt = time taken (s)
 Solved Example
Solved Example
Problem: A truck speeds up from 5 m/s to 25 m/s in 10 seconds. Find the acceleration.
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- v = 25m/s
- u = 5m/s
- t = 10s
Step #2: Using the formula:

Step #3: Putting the values and solve:
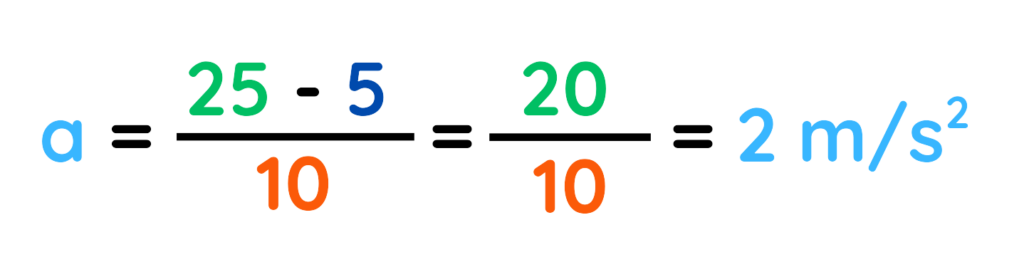
Acceleration is 2 m/s2
Final Answer: 2 m/s2
Acceleration Formula (Kinematic Equation)
Formula #1:
- When Acceleration is constant, and time is not directly involved then this equation is used.
- It helps calculate Final Velocity, Initial Velocity, Acceleration, or Displacement
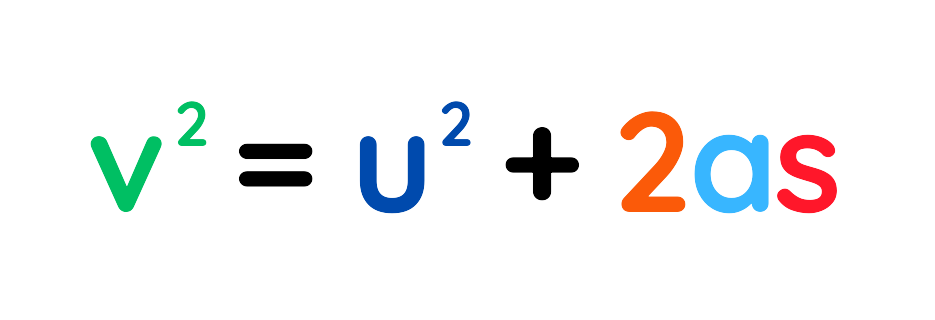
Where:
- v = final velocity (m/s)
- u = initial velocity (m/s)
- a = acceleration (m/s2)
- s = displacement (m)
Formula #2:
- This equation is used to calculate the Final Velocity of an object when Initial Velocity, Acceleration, and Time are known.

Where:
- v = final velocity (m/s)
- u = initial velocity (m/s)
- a = acceleration (m/s2)
- t = time (s)
 Solved Example: Acceleration GCSE Questions
Solved Example: Acceleration GCSE Questions
Problem: A bike starts from rest and accelerates at 3 m/s2 over a distance of 50 meters. Find its final velocity.
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- u = 0 m/s
- a = 3 m/s2
- s = 50m
Step #2: Using the formula:
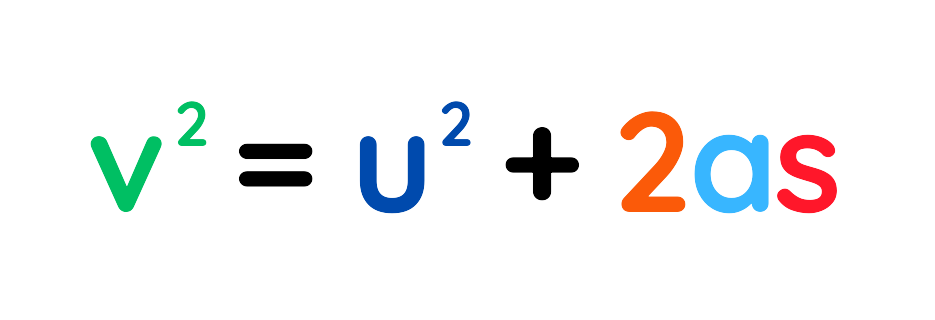
Step #3: Putting the values and solve:
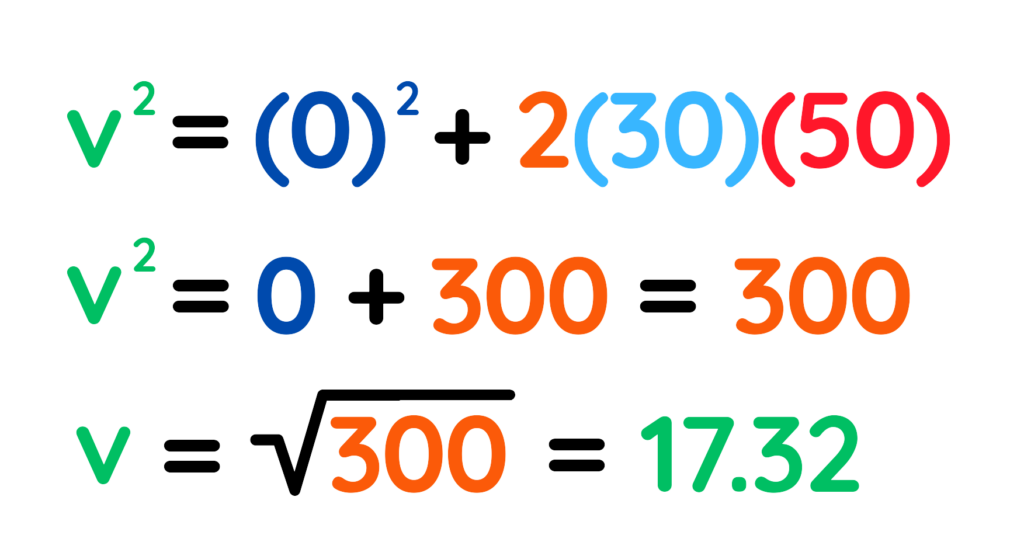
Final velocity is 17.32 m/s
Final Answer: 17.32 m/s
 Solved Example: Acceleration GCSE Questions
Solved Example: Acceleration GCSE Questions
Problem: A car starts from rest and accelerates at 4 m/s2 for 5 seconds. Find the final velocity of a car.
Solution:
Step #1: Given
- u = 0 m/s
- a = 4 m/s2
- t = 5s
Step #2: Using the formula:

Step #3: Putting the values and solve:

Final Velocity is 20 m/s
Final Answer: 20 m/s
Can Acceleration be Positive or Negative?
- Yes, acceleration can be both positive and negative, depending on an object whether it is speeding up or slowing down.
Positive Acceleration:
- When an object’s velocity increases over time, then the acceleration is in the same direction as its velocity, and it consider as Positive Acceleration.
Examples:
- Car speeding up
- Launching a Rocket into a Space
- A Plane Taking Off
- Ball Rolling Down a Hill
Negative Acceleration:
- When an object’s velocity decreases over time, then the acceleration is in the opposite direction to its velocity, and it consider as Negative Acceleration.
Examples:
- Car Braking to Stop
- Bicycle Stopping After Pedaling
- Throwing a Ball Upwards
- Parachute Opening During a Skydive
Learn More About Click this Link: Acceleration GCSE Physics
What is Acceleration due to Gravity?
- Without any forces acting on an object, when it falls freely under the influence of Earth’s Gravity then the Acceleration is said as Acceleration due to Gravity.
Value of g on Earth:

Frequently Asked Questions
Solution:
A negative acceleration is called deceleration. It means the object is slowing down.
Solution:
Acceleration is measured in metres per second squared (m/s2).
Solution:
Acceleration is a vector — it has both size and direction.
Solution:
It is 9.8 m/s2, often rounded to 10 m/s2 in GCSE calculations.
Solution:

Use this when you know Initial Velocity, Final Velocity, and Time.

